Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Context: The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) announced that it will grant financial assistance to states to assist poor prisoners.
Details
Significance
- The announcement by the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) is in line with one of the Union Budget 2023-24 announcements, 'Help for Poor Prisoners.' The initiative intends "financial support to poor individuals who are in jails and are unable to afford the penalty or the bail fee."
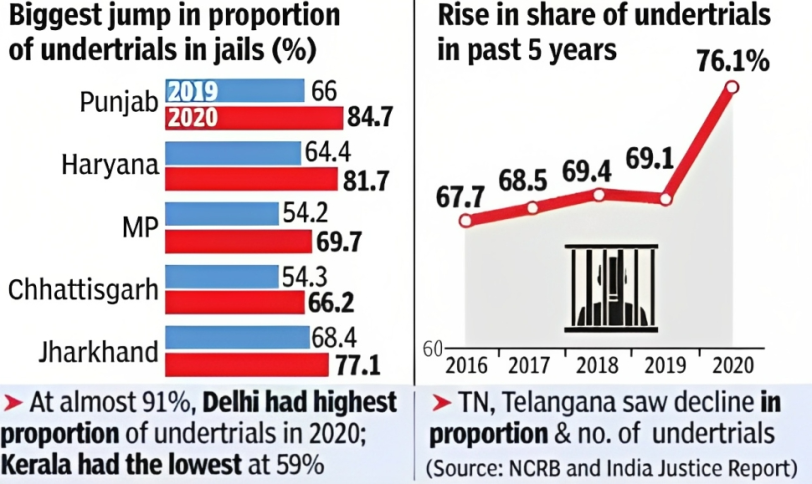
- According to the Prisons Statistics of India Report, 2021, around 5.54 lakh prisoners were imprisoned, while the entire capacity of Indian jails was approximately 4.25 lakh, representing a 130% occupancy rate.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs plan will allow underprivileged prisoners, the majority of whom are members of socially disadvantaged or marginalised groups with lower levels of education and money, to be released.
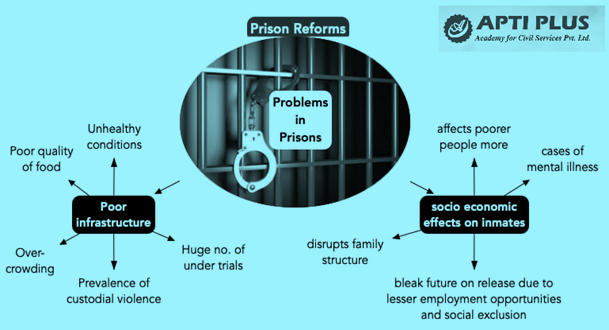
- The step will reduce the pressure on Indian Jails and improve the efficiency of prison, and prisoners reform programmes.
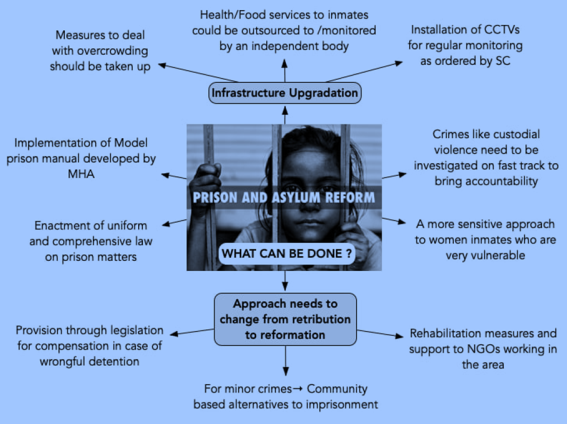
Recommendations
- The Ministry stated that to further strengthen the process following steps will be taken;
- Technology-driven solutions would be implemented to guarantee that benefits reach the poor prisoners, as well as enhance the E-prisons platform, the District Legal Services Authority.
- Stakeholders' capacity development.
- Awareness campaign to ensure that needy poor prisoners have access to high-quality legal assistance.
Keywords
Bail
- A bond is a set of pre-trial limitations put on an accused to guarantee that the legal process is not hampered. Bail is the conditional release of a suspect in exchange for the commitment to appear in court when called upon.
- Bail usually refers to a bail bond or a payment of money or property to the court in exchange for release from pre-trial custody. If the suspect fails to appear in court, the bail is forfeited, and the accused may be prosecuted for failure to appear. Bail is returned after the trial if the offender appears to make all mandatory appearances.
- A suspect is granted bail when detention is not justified but there is a need to offer an incentive for the suspect to appear in court.
- Bail amounts may vary based on the nature and severity of the offence the accused is accused of, as well as the methods for calculating bail amounts.
District Legal Services Authorities
- The Authorities are headed by the District Judge, who serves as the authority's Chairperson.
- They are established by the State Government in coordination with the Chief Justice of the High Court for each district within the State.
- They provide different legal assistance and awareness programmes, assist in easing the load on courts by regulating Lok Adalats to give free legal services to the weaker sectors of society and help in reducing the strain on courts.
Must Read Articles:
Undertrial Prisoners: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/undertrails-prisoners
Prison Reforms: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/prison-reforms
Bail provisions in India: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/bail-provisions-in-india
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Consider the following Statement;
1. Regular Bail is granted to the person who has been arrested or is in police custody.
2. Interim Bail is a long-term bail.
3. A person can apply for anticipatory bail when he/she finds out that he could be arrested for a non-bailable offence.
Which of the following Statement is/are correct?
(A) 1 and 2 only
(B) 2 and 3 only
(C) 1 and 3 only
(D) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: C
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: Regular Bail is granted to the person who has been arrested or is in police custody.
Statement 2 is incorrect: Interim Bail is a short-term bail granted for a short period. It is granted before the hearing for the grant of anticipatory bail.
Statement 3 is correct: A person can apply for anticipatory bail when he/she finds out that he or could be arrested for a non-bailable offence. At the time of granting anticipatory bail the Court imposes certain terms and conditions which if violated, the Court may cancel the anticipatory bail.
|

https://epaper.thehindu.com/ccidist-ws/th/th_delhi/issues/31682/OPS/GTUB38SGA.1.png?cropFromPage=true














