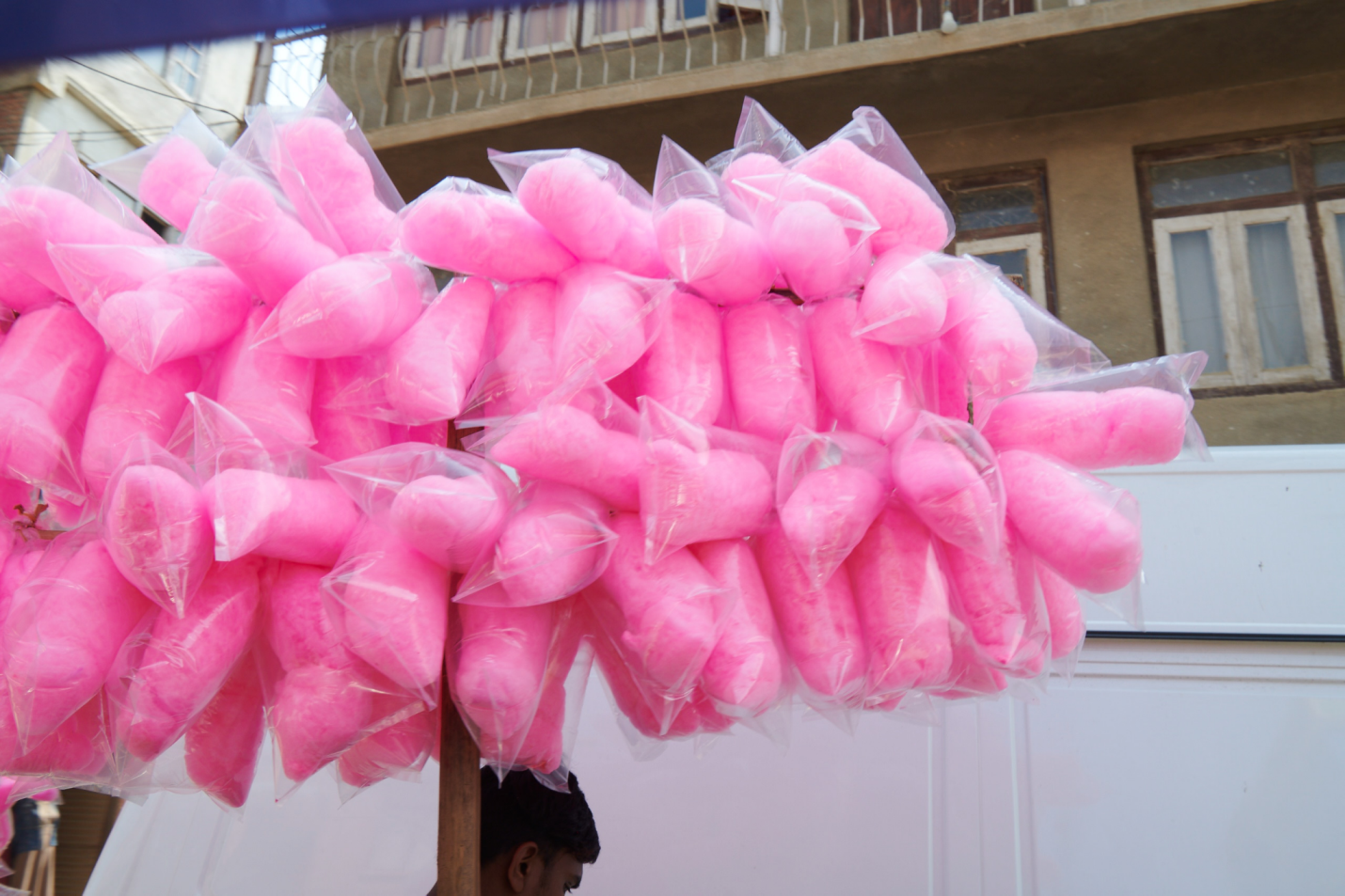






Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://english.makalukhabar.com/2024/01/170024/
Context: The Tamil Nadu government banned the sale and production of cotton candy in the state due to the presence of the harmful chemical Rhodamine-B, as confirmed by samples tested by the food safety department, aligning with food safety standards and regulations to protect public health.
About Rhodamine-B
|
Aspect/Property |
Description |
|
Chemical Structure |
Complex structure with a rhodamine core, nitrogen-containing heterocyclic ring system, and various substituents. Structure varies based on formulation and synthesis methods. |
|
Appearance |
Dark red to pink powder or crystals. Color may vary with formulation and concentration. |
|
Solubility |
This compound is water-soluble, meaning it can dissolve in water. Interestingly, when Rhodamine B comes into contact with water, it exhibits a striking change in colour, turning vividly fluorescent pink, which is a characteristic feature. |
|
Toxicity and Regulation |
The use of Rhodamine B in food-related applications is strictly prohibited by regulations such as the Food Safety Standards Act, 2006, due to its toxic nature. Regular consumption can lead to severe health issues, including brain damage. |
|
Fluorescence Properties |
Rhodamine B exhibits strong fluorescence properties, emitting intense orange-red fluorescence when exposed to green light. This characteristic makes it valuable in fluorescence-based applications such as microscopy and flow cytometry. |
|
Brightness and Stability |
It possesses high brightness, enabling easy detection even in dilute solutions. Moreover, Rhodamine B demonstrates good stability, being resistant to photobleaching (loss of fluorescence upon prolonged exposure to light) and chemical degradation. |
|
Toxicity and Biodegradability |
While it is considered low-toxic for most applications, Rhodamine B can cause significant harm if ingested or exposed to the body. However, it is biodegradable and can decompose naturally in the environment over time. |
|
Applications |
Water Tracing: Used to study water flow in rivers, lakes, and oceans. Fluorescent Microscopy: Labels cells and biological molecules for visualization. Laser Dyes: Employed in scientific and medical lasers. Textile Dyeing: Imparts a pink colour to fabrics. Paper Printing: Utilized in creating colored paper and printing inks. Cosmetics: Found in eyeshadows and lipsticks. Biomedical Research: Used as a tracer in drug delivery studies. Environmental Monitoring: Detects leaks and pollutants in water systems. |
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Rhodamine B is used in a variety of applications for: 1. Labeling single molecules for microscopy 2. Dyeing textiles 3. Tracing leaks in pipelines 4. Identifying counterfeit currency Select the correct code: A) Only one B) Only two C) Only three D) All four Answer: c Explanation: While Rhodamine B has applications in all the listed areas, its use in identifying counterfeit currency (4) is not typical. Other fluorescent dyes, such as those in security inks, are specifically designed for this purpose. Labelling single molecules for microscopy: Rhodamine B is indeed commonly used as a fluorescent dye to label single molecules for microscopy due to its bright and stable fluorescence properties. Dyeing textiles: Rhodamine B has been used for dyeing textiles, although its use is declining due to safety concerns and regulations in some countries. Tracing leaks in pipelines: Rhodamine B is a popular tracer dye used to detect leaks in pipelines due to its high visibility and water solubility. Identifying counterfeit currency: While some security features in banknotes use fluorescence, Rhodamine B itself is not typically used for this purpose. Counterfeit detection often relies on specialized inks, watermarks, and security threads not involving Rhodamine B. |







© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved