Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Start-ups these days are now focusing more on revenue-based funding.
What is Revenue-Based Finance?
- Revenue-based financing (RBF) refers to the strategy to raise capital for a firm. It is generally taken from investors who are compensated with a portion of the company’s ongoing gross revenues in return for their investment.
- In an investment using revenue-based financing, investors get a recurring cut of the company’s profits up until a preset sum is paid. This fixed sum is often a multiple of the principal investment and typically varies between three and five times the initial investment.
- It is a logical progression for early-stage venture investment and private equity financing.
- Revenue-Based Financing (RBF) is an innovative financing model gaining prominence within the startup ecosystem and among digital SMEs.
- Unlike traditional loans, RBF does not require collateral; instead, it offers capital in exchange for a percentage of a company's gross revenue.
- This alternative funding avenue has seen increased traction primarily due to the dry spell in venture capital investments and the limited accessibility of traditional credit facilities for many emerging businesses.
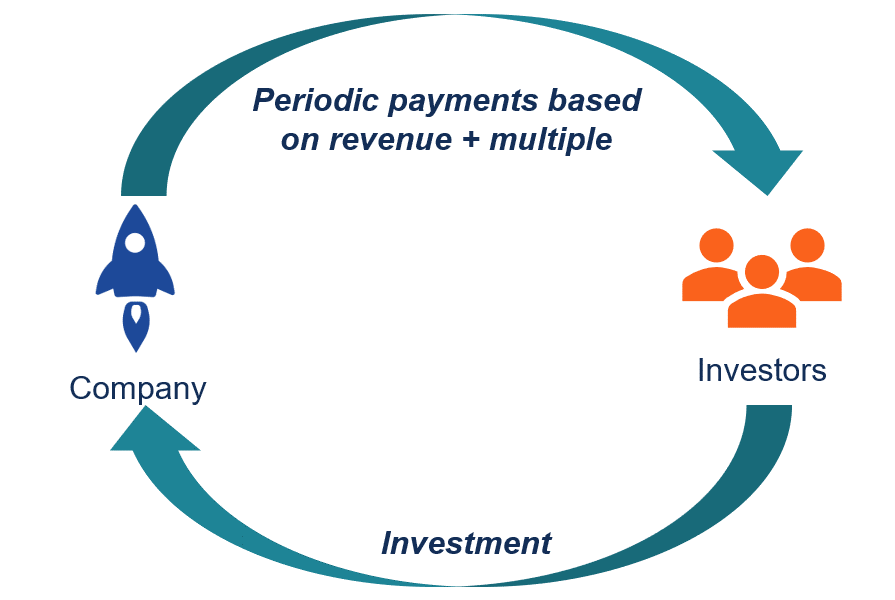
How Revenue-Based Financing Works?
- Revenue-based financing refers to securing borrowing (credit) by utilising projected profits. The investor or lender gets a certain percentage of the borrower’s income, commonly known as the revenue share. The lender then receives payment for the principal amount plus the revenue share.
- To understand how revenue-based financing works, let us take an example. Let’s say, firm A makes an average of Rs 30 lakh every month. As a result, they expect to make Rs. 3.6 crore a year. It offers this estimate to an RBF supplier and suggests that they pay for it with Rs 30 lakh.
- This lender lends the money following an evaluation for a 12% revenue share. As a result, firm A must pay back Rs. 336,000, or Rs. 300 000 + Rs. 360 000. (finance cost or revenue share).
- Revenue-based financing considers several parameters like revenues, cash flow, scalability, growth capital, etc., when it comes to auditing. They will lend the agreed amount to the borrower’s account if convinced.
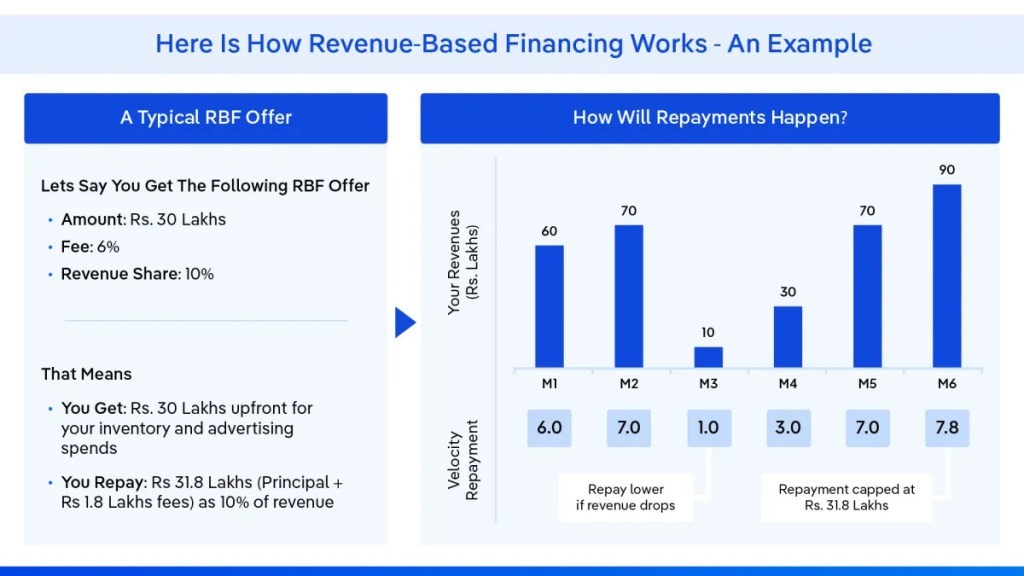
Key Characteristics of RBF
- Repayment Structure: Instead of fixed monthly payments, RBF arrangements involve a monthly repayment proportional to the company's revenue. This structure aligns with the company's cash flow, making it particularly attractive for businesses with fluctuating revenue streams.
- Fixed Fee Component: In addition to the revenue-based repayment, RBF agreements typically include a fixed fee, usually ranging between 8-10% of the principal amount. This fee compensates the investor for the risk associated with the financing.
When do Companies Seek Revenue-Based Financing Options?
Revenue-based financing is attractive to:
- Businesses that are currently releasing a new product.
- Growth stage of businesses seeking to add more salespeople.
- A business that has a sizeable market but not one that attracts venture capital firms.
- Owners don’t want to sell stock or pledge guarantees on loans.
- Organisations to launch a significant marketing initiative.
Applicability of RBF
- Target Audience: RBF is well-suited for digitally-enabled businesses with steady revenue streams but limited access to traditional financing options. Examples include e-commerce merchants, software-as-a-service (SaaS) firms, cloud kitchens, and financial services providers.
- Equity Preservation: Some companies opt for RBF to avoid diluting equity by seeking venture capital investment. For startups in early stages, retaining ownership can be crucial for maintaining control and future growth opportunities.

Pros and Cons of Revenue-Based Financing
Revenue-based financing has its own set of benefits and drawbacks.
Pros
- It is more affordable than alternatives: Compared to options that entail equity financing, revenue-based financing is less costly. Alternative sources of finance, like angel investors and venture capitalists, demand 10 to 20 times more in returns. Additionally, companies that offer revenue-based financing have an interest in her success.
- One can possess authority: With revenue-based financing, one can preserve her company’s equity financing and ownership and management.
- Flexible monthly payments: Slow months won’t impact her capacity to pay because monthly payments are dependent on revenue. Her cost is correlated with her revenue and, with careful preparation, should stay manageable.
- No personal guarantee is required on loan: All assets are at risk when one chooses financing choices like bank loans, which require one to guarantee a loan. That commitment is not necessary for revenue-based financing.
- One can raise funds rapidly: One will only have to make a few pitches to get the funding one need with revenue-based financing. Most lenders will decide and issue a credit to ensure good future revenue.
Cons
- One have to generate revenue: A startup can only use this type of funding with a steady source of income since a firm must generate revenue to qualify.
- Availability of less money: Revenue-based financing covers around three to four months of a business’s monthly recurring revenue. In comparison, other funding options offer heavy investing.
- Mandatory monthly payments: Businesses have to make monthly payments in this arrangement.
- Minimal regulation: One must conduct a thorough study before signing any agreements since there is no regulation of revenue-based financing. It makes it difficult to avoid taking out a predatory loan.
Advantages of Revenue-Based Financing
- Revenue-based financing has many advantages compared to venture capital firms’ loans. Here is the list of the advantages that one should know:
Non-dilutive
- As a company owner, one retain complete control over her enterprise. One is not required to give up any equity financing interests in exchange for the funding one obtain. It is crucial for firms that are expanding quickly and require finance for it.
No Personal Guarantee Needed
- Some revenue-based financing lenders might not require a personal guarantee or security during the application process, making it a less risky and quicker choice for borrowing funds.
Loan Repayments are Flexible
- Revenue-based financing has payback terms that depends on how well her company performs. When sales are brisk, one pays more; when they’re sluggish, one pay less. This also implies that one will always have adequate growth capital to get through her post-holiday sales downturn.
Fast-Growing Companies Settle Quicker
- Companies with rapid growth and expected high future revenue make quick repayments. As a result, they end up giving low revenue.
Cheaper than Equity
- Repayments are often far less expensive than interest, making it a much more cost-effective choice than getting her first investment from angel investors or venture capital organisations.
Fast Funding
- Compared to venture capital firms’ funds and bank loans, one gets revenue-based financing within a week. On the other hand, the other forms of bank loans take months for the funds to be released.
Works well with other Funding Sources
- Early-stage firms benefit from revenue-based financing by gaining momentum, making other investment sources more available and affordable.
Who can benefit from Revenue Based Finance?
Revenue-based financing is advantageous for many different company models, but some industries stand out to gain the most.
E-commerce Businesses
- Online retailers are particularly well-suited to revenue-based financing since it gives them the flexibility to invest in marketing or inventory to fulfil demand swiftly.
- Due to their internet sales, these companies make it simple for lenders to predict their success using information from their marketing and accounting accounts.
Companies with Seasonal Performance
- Online retailers are particularly well-suited to revenue-based financing since it gives them the flexibility to invest in marketing or inventory to fulfil demand swiftly.
- Due to their internet sales, these companies make it simple for lenders to predict their success using information from their marketing and accounting accounts.
SaaS and Subscription Businesses
- Businesses with predictable and steady monthly incomes are more likely to benefit from revenue-based financing. This is because revenue-based repayments are based on MRR.
- SaaS and subscription firms get payments every month. They know exactly how much income to anticipate each month. They can make their monthly payments better with reduced administrative costs and this consistency.
Comparison with Other Financing Options
- Venture Debt: While venture debt has been a common choice for startups, RBF is gaining traction, especially for short-term capital needs. RBF offers more flexibility in repayment terms and is accessible to a broader range of businesses.
Drivers of RBF Adoption
- Market Demand: The dry spell in venture capital funding and the limited availability of traditional credit have created a significant market gap, driving businesses towards alternative financing options like RBF.
- Awareness and Accessibility: Increasing awareness among entrepreneurs and investors about RBF's benefits has contributed to its growing popularity. Platforms specializing in RBF, such as GetVantage, Velocity, and Klub, have emerged to meet this demand.

Challenges and Considerations
- Cost Considerations: RBF may come at a higher cost compared to traditional loans, with the fixed fee and revenue-based repayment structure potentially impacting the company's profitability.
- Cash Flow Management: The monthly repayment structure based on revenue percentages can pose challenges to cash flow management, particularly for businesses with variable revenue streams.
Investor Perspective
- Risk-Return Balance: Investors in RBF assess the risk associated with each investment and expect returns commensurate with that risk. While RBF presents higher risks, investors seek returns that justify the risk undertaken.
Conclusion
- Revenue-Based Financing offers a flexible and accessible financing option for startups and digital SMEs, addressing the working capital needs of businesses while preserving equity and offering more flexibility than traditional loans.
- Despite certain challenges, the growing interest in RBF reflects its potential to fill the financing gap in the market and support the growth of emerging businesses.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. How many of the following statements regarding Revenue-Based Financing (RBF) is/are correct?
1.Investors get a recurring cut of the company’s profits up until a preset sum is paid.
2.In RBF, a company owner is required to give up equity financing interests in exchange for the funding one obtain.
3.RBF does not require collateral.
Choose the correct code.
A)One only
B)Two only
C)All
D)None
Answer. B) Two only
Statement 2 is incorrect.
|