Description
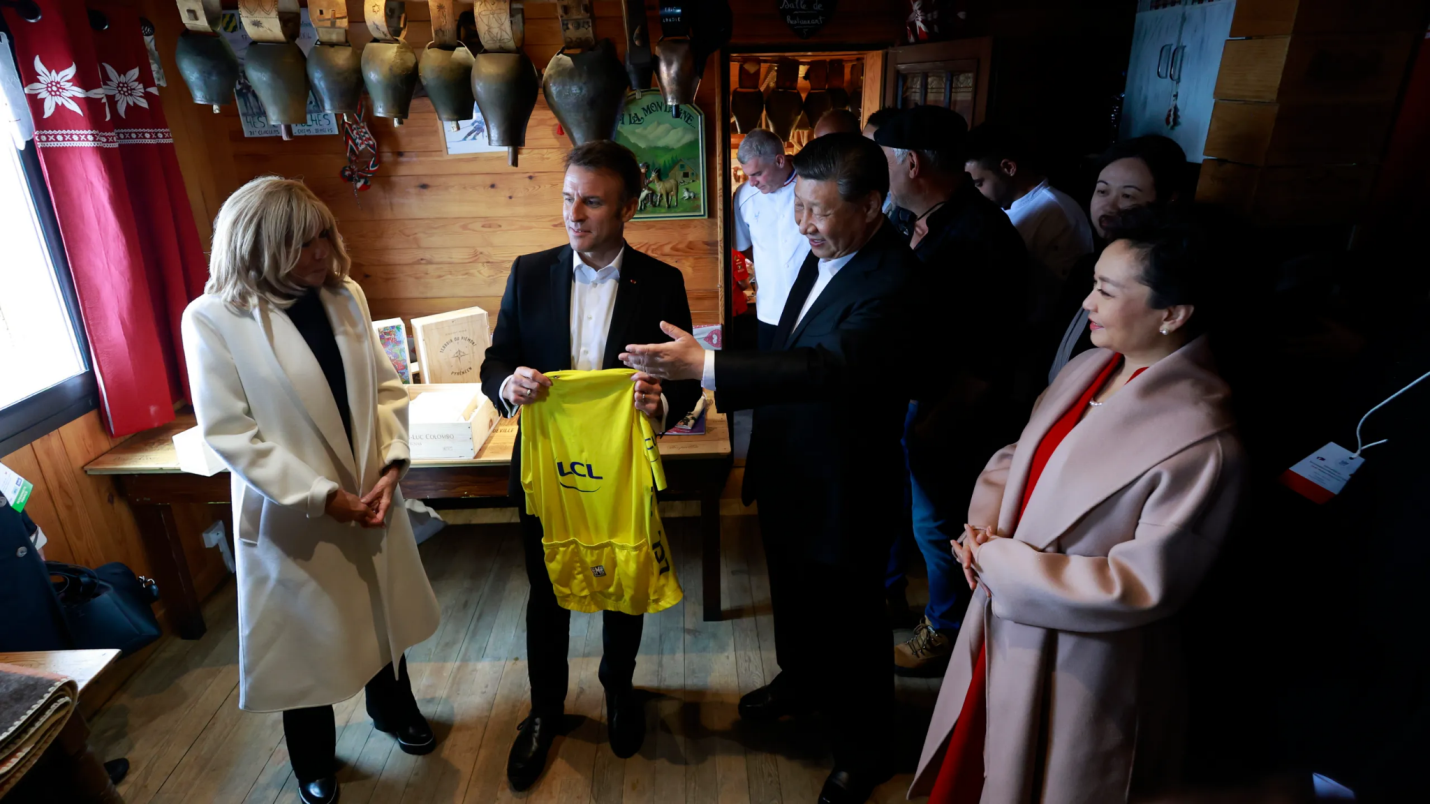

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://www.cbs42.com/news/international/ap-chinas-xi-visits-pyrenees-mountains-in-a-personal-gesture-by-frances-macron/
Context: The private meeting between Chinese President Xi Jinping and French President Emmanuel Macron at the Tourmalet Pass in the Pyrenees Mountains.
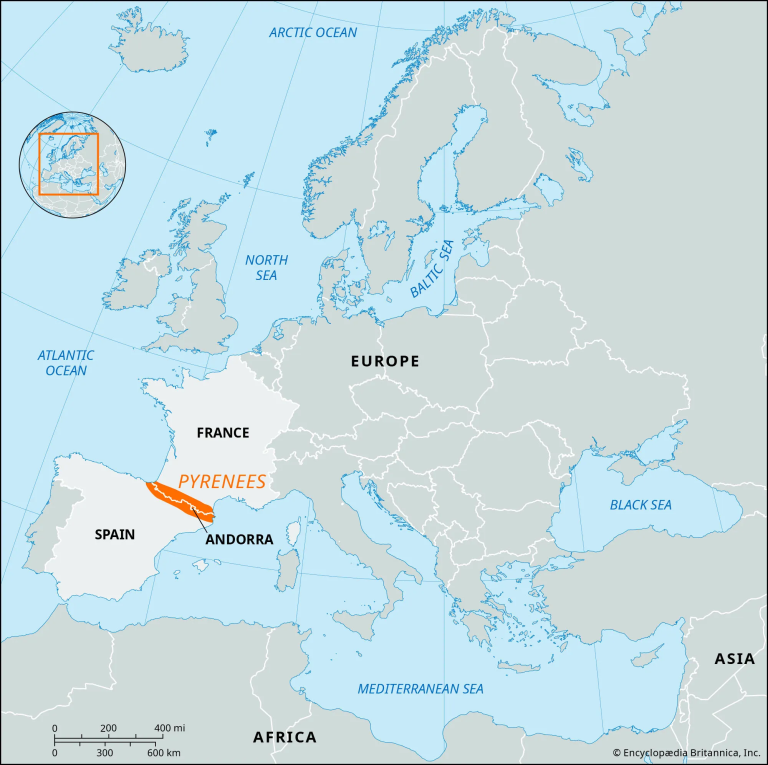
About Pyrenees Mountains
- The Pyrenees mountain range in the southwestern Europe, forming a natural boundary between France and Spain.
Geological History
- The Pyrenees are the result of complex geological processes spanning hundreds of millions of years.
- The initial formation of the Pyrenees dates back to the Variscan orogeny, which occurred between the late Devonian Period and the early Permian Period (370 to 290 million years ago).
- During this orogeny, intense tectonic forces folded and uplifted the Earth's crust, resulting in the formation of a vast mountain belt known as the Variscan or Hercynian orogeny.
- The remnants of this orogeny include not only the Pyrenees but also other mountainous regions like the Massif Central in France and the Meseta Central in Spain.
- The Pyrenees underwent subsequent tectonic activity during the Mesozoic Era, approximately 225 million years ago, when the collision between the Iberian and European tectonic plates initiated. This collision led to the uplifting and deformation of the Pyrenean block, resulting in the formation of the modern Pyrenees mountain range.
Physical Features
- The central region of the Pyrenees features ancient sedimentary rocks, slates, schists, limestones transformed into marble, and granites.
- The Pyrenees stretch for about 270 miles from the Mediterranean Sea to the Bay of Biscay.
- The width of the range varies significantly, being narrowest at the eastern end (about 6 miles wide) and widest at the central region (about 80 miles wide). The highest peak, Aneto, rises to 11,169 feet in the Maladeta massif.
Climate, Flora and Fauna
- The northern slopes receive oceanic influences, with cooler temperatures and higher precipitation levels. In contrast, the southern slopes have a more Mediterranean climate, characterized by hotter, drier summers and milder winters.
- Climate zones change with altitude, leading to distinct vegetation patterns. Lower elevations feature broad-leaved deciduous forests, while higher altitudes are dominated by coniferous forests and alpine meadows.
- The Pyrenees are home to a variety of wildlife adapted to mountainous habitats. Large herbivores such as chamois, ibex, and red deer inhabit the region, along with predators like brown bears, lynx, and wolves.
Source:
Oneindia
Britannica
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. French President Macron recently hosted a private meeting with Chinese President Xi Jinping in the Pyrenees Mountain region, emphasizing personal diplomacy amidst global challenges and bilateral discussions. Which countries border the Pyrenees mountain range?
A) France and Germany
B) France and Italy
C) France and Spain
D) France and Switzerland
Answer: C
|












