Description
Copyright infringement not intended
In News
- World Health Organization (WHO) study highlighted that Non-communicable diseases such as heart disease and stroke, cancer, diabetes and respiratory illnesses are responsible for 74 % of all deaths across the globe.
- Non-communicable diseases, along with mental illnesses, kill more than 41 million people every year across all age groups.
Details
- NCDs are largely preventable and treatable; yet, the diseases kill more than 7 out of 10 people globally from risk factors like tobacco, alcohol, unhealthy diet, physical inactivity and air pollution.
- WHO suggested that the adoption of the right policies can prevent 39 million deaths by 2030.
- Low- and middle-income (LMICs) countries suffer the most: 86% of the 17 million people under the age of 70 who die of non-communicable diseases every year belong to LMICs.
- Prevention, treatment and Healthcare are out of reach for millions of people in LMICs.
- The study highlighted that with sufficient investment, 90% of these countries can meet the UN-mandated sustainable development goal to reduce premature deaths from non-communicable diseases by a third by 2030.
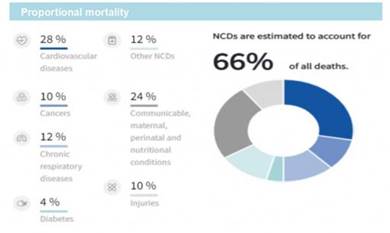
- In India, 66% of all deaths are the result of non-communicable diseases, with cardiovascular diseases accounting for the highest 28% of these deaths.
- According to the study; Tobacco use, unhealthy diet, harmful use of alcohol, physical inactivity and air pollution are the main risk factors.
- WHO suggested that “Eliminating these factors could prevent or delay significant ill health and many premature deaths from non-communicable diseases.”
- The study concluded that policies to reduce non-communicable diseases would also provide economic benefits for countries.
- Nearly 7 million lives could be saved for just $0.84 per person per year. This investment would provide a return of more than $230 billion as economic and societal benefits.

World Health Organisation (WHO)
- WHO is a specialized agency of the United Nations. It is working for improving international public health.
- The WHO's working principle includes:
- Working worldwide to promote health.
- Keeping the world safe.
- Serve the vulnerable.
- It provides technical assistance to countries, sets international health standards, and collects data on global health issues.
- It also releases the World Health Report, which provides assessments of worldwide health topics.
- WHO also serves as a forum for discussions of health issues.
- WHO has played a leading role in the eradication of smallpox, the near-eradication of polio, and the development of the Covid-19 vaccine.
- Its current priorities include communicable diseases, particularly HIV/AIDS, Ebola, COVID-19, malaria and tuberculosis, etc.
- WHO Headquartered is in Geneva, Switzerland.
- It has 6 regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide.
Way Forward
- World Health Organization (WHO) announced that a group comprising heads of governments has been formed to fast-track the goal to reduce premature death from non-communicable diseases (NCD) by a third. The focus areas of the group will be:
- Implementing the most cost-effective measures to prevent and control NCDs.
- Ensuring that the people living with NCDs have access to the medicines and care they need during humanitarian emergencies.
- Integrating NCDs within primary health care and universal health coverage.
- Develop Comprehensive NCD surveillance and monitoring system.
- Engaging the people living with NCDs and mental health conditions in policy-making and programming.
https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/health/one-death-from-non-communicable-diseases-every-2-seconds-who-recommends-policies-85045
https://t.me/+hJqMV1O0se03Njk9