Description
Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: www.specialeducationnotes.in
Context: The Odisha government declares leprosy a reportable disease in the state, necessitating all healthcare providers to report diagnosed cases promptly, thereby aiming to enhance early diagnosis and ensure complete treatment for this curable disease.
Details
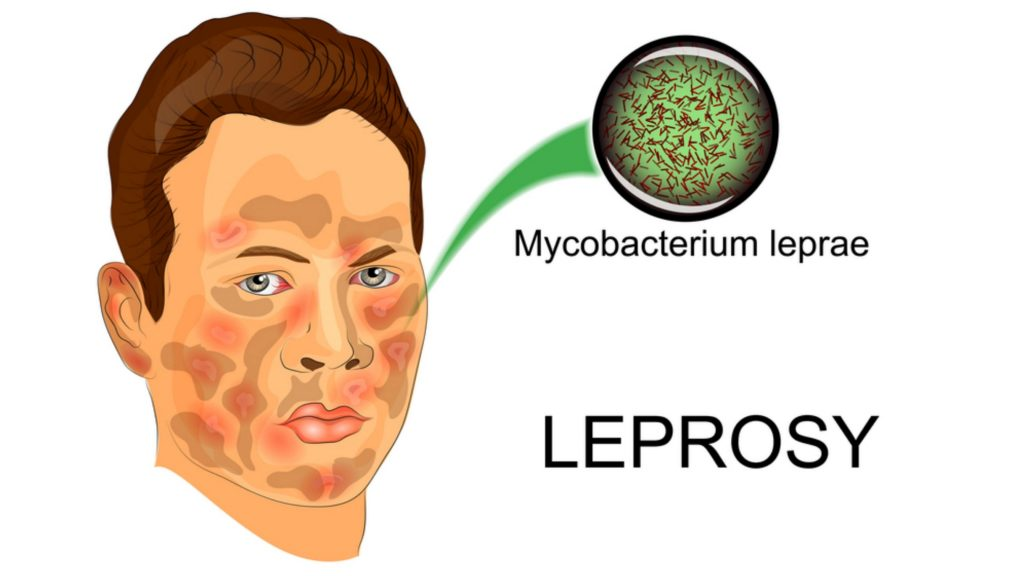
- Leprosy is a chronic infectious disease caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium leprae. It mainly affects the skin, nerves, eyes, and mucous membranes of the body.
- Leprosy has been known since ancient times and has been associated with stigma and discrimination throughout history.
Origin of leprosy
- The exact origin of leprosy is still unclear, but there are several hypotheses based on genetic, archaeological, and historical evidence.
- One hypothesis is that leprosy originated in Africa and spread to other continents through human migration and trade.
- Another hypothesis is that leprosy originated in Asia and was introduced to Africa and Europe by the expansion of the Indian Ocean trade network.
- A third hypothesis is that leprosy originated in multiple regions independently and evolved into different strains over time.

Transmission of leprosy
- Leprosy is transmitted from person to person through respiratory droplets or contact with infected skin lesions.
- The risk of transmission is higher in crowded and unsanitary conditions, where people have prolonged and close contact with each other. However, not everyone who is exposed to the bacterium develops the disease.
- Some people have a natural immunity or resistance to leprosy, while others have a genetic susceptibility or predisposition to it.
- The incubation period of leprosy can range from a few months to several years, meaning that the symptoms may not appear until long after the exposure.
Symptoms of leprosy
- The symptoms of leprosy vary depending on the type and severity of the disease. There are two main types of leprosy: paucibacillary (PB) and multibacillary (MB).
- PB leprosy is characterized by one or a few patches of skin that are lighter or darker than normal, numb, or have reduced sensation.
- MB leprosy is characterized by many patches of skin that are discoloured, thickened, or ulcerated, and may also affect the nerves, eyes, nose, mouth, and other organs.
- The nerve damage caused by leprosy can lead to loss of sensation, muscle weakness, paralysis, deformities, blindness, and chronic pain.
Cure of leprosy
- Leprosy can be cured with a combination of antibiotics that kill the bacteria and stop the progression of the disease. The treatment regimen depends on the type and extent of the disease but usually lasts from 6 to 12 months.
- The treatment can prevent further damage and complications from leprosy, but it cannot reverse the existing impairments or disabilities. Therefore, it is important to diagnose and treat leprosy as early as possible to avoid permanent consequences.

Conclusion
- Leprosy is a curable disease that still affects millions of people around the world. It has a long and complex history that has shaped its perception and response by different cultures and societies. Leprosy can cause serious physical and psychological harm to those who suffer from it, as well as their families and communities. However, with proper diagnosis, treatment, care, and support, people affected by leprosy can overcome the challenges and live a dignified and productive life.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Which bacterium causes leprosy?
A) Mycobacterium tuberculosis
B) Mycobacterium leprae
C) Streptococcus pyogenes
D) Staphylococcus aureus
Answer: B
Explanation:
Leprosy is caused by Mycobacterium leprae, a bacterium that primarily affects the skin and peripheral nerves.
|