Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: elearnmarkets.com
Context: The projected GDP growth rate for 2023-24 stands at 6.5%. Simultaneously, the benchmark stock market index, Sensex, is currently at a level of 65,000. However, the potential impact of high inflation on returns from stock market movements is a concern.
Details
- Retail inflation spiked to 7.44% in July, creating uncertainty for investors. The Reserve Bank of India projects inflation to stay above 5% until the first quarter of 2024-25, with the potential for it to reach 6.2% in the current quarter. This exceeds the RBI's comfort level of 4%.
- Food price pressures, including surges in vegetable prices, cereals, pulses, spices, and milk, are expected to continue for a few months. Government interventions and fresh crop arrivals are expected to provide relief afterwards.
- High inflation can impact stock prices and gold, as well as increase interest rates and bond yields. This affects the cost of equity and debt, leading to changes in equity valuations. Despite rising inflation and high-interest rates, India's stock market has performed well due to a strong earnings outlook and macro conditions.
- India's market performance remains positive despite inflation and high rates. Earnings resilience is essential for sustained positive momentum. Long-term investors are advised to stay invested in strong holdings while exercising caution in applying for IPOs and considering equity mutual funds for long-term investments.
High Inflation and Interest Rates
- High inflation refers to a sustained and significant increase in the general price level of goods and services within an economy. It erodes the purchasing power of money over time, as consumers need more money to buy the same quantity of goods.
- Interest rates represent the cost of borrowing money or the return on investment. Central banks, like the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), use interest rates as a tool to influence economic conditions.

Relation and Impact
- Direct Relationship: High inflation and interest rates indeed often have a direct and positive correlation. Central banks frequently raise interest rates to counteract high inflation by reducing consumer spending and investment, which, in turn, can help control inflationary pressures.
- Impact on Borrowing: High inflation can increase the cost of living and doing business. To offset the eroding purchasing power of money caused by inflation, lenders typically demand higher nominal interest rates. This ensures that they maintain a real return on loans after accounting for the declining value of money. As a result, borrowing becomes more expensive for both consumers and businesses when inflation is high.
- Impact on Investment: Higher interest rates can discourage borrowing for investment purposes. When businesses face high borrowing costs, they may be less inclined to take out loans for expansion, research, and development, or other investments. Likewise, consumers might reduce borrowing for big-ticket purchases, such as homes and vehicles. This reduction in borrowing can potentially slow down economic growth since investment is a key driver of economic activity.
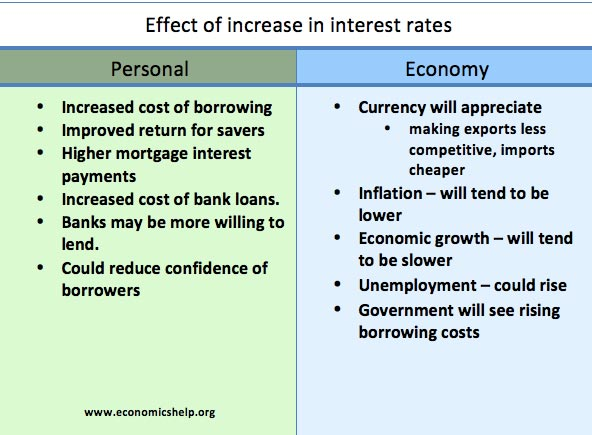
Key consequences and challenges associated with high inflation
- Rising Prices: High inflation leads to a widespread increase in the prices of goods and services. This affects not only individual consumers but also businesses that rely on various inputs for their operations. When costs of production rise, businesses might pass these increased costs onto consumers, leading to a spiral of increasing prices.
- Reduced Purchasing Power: As prices rise, the purchasing power of money diminishes. Consumers find that their money can buy fewer goods and services than before. This can lead to a lower standard of living, especially for those on fixed incomes or with limited resources, as they struggle to afford the same quantity of goods they used to.
- Uncertainty: High inflation introduces uncertainty into the economy. Businesses and investors find it challenging to make financial plans and decisions when price levels become unpredictable. This uncertainty can hinder long-term investment and planning, as well as erode consumer confidence.
- Distorted Allocations: Inflation can lead to misallocation of resources in the economy. When prices rise rapidly and unexpectedly, the price signals that guide businesses and individuals in their decision-making can become distorted. This can lead to inefficient allocation of resources, as businesses might invest in sectors that seem profitable due to the distorted prices but might not be sustainable in the long run.
Impact of High Inflation and Interest Rates
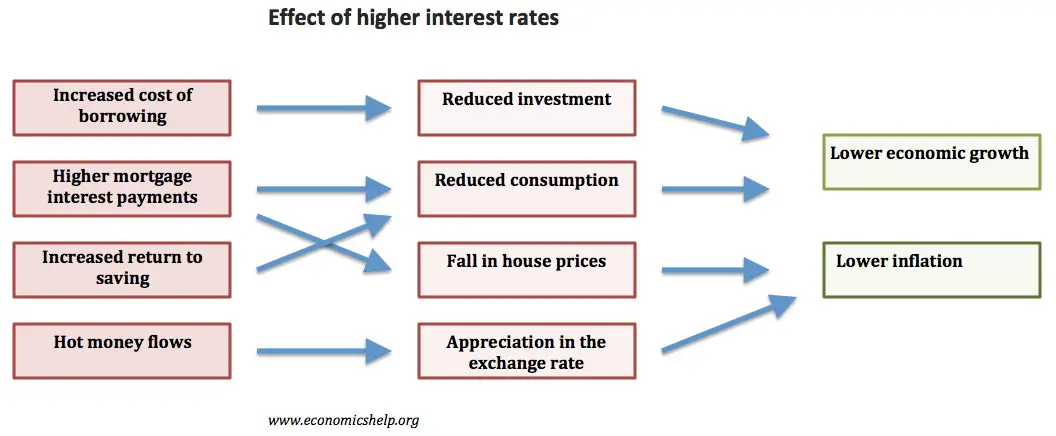
- Interest Rates: When facing high inflation, central banks often respond by raising interest rates. This is a measure to manage an overheating economy and to control the rapid rise in prices. Higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing, which in turn discourages spending and investments. This mechanism helps to rein in inflation by reducing overall demand.
- Investment Decisions: High-interest rates can significantly affect investment decisions. The process of discounting future cash flows at higher rates leads to lower present valuations for assets like stocks and bonds. The uncertainty caused by high-interest rates can also lead to more cautious business investment and expansion plans.
- Consumption: The impact of high inflation on consumer spending can be significant. As prices rise, consumers' purchasing power diminishes, leading them to prioritize essential purchases and cut back on discretionary spending. This shift in consumer behaviour can have a cascading effect on overall economic activity, potentially leading to slower economic growth.
- Savings: Fixed-income savers, particularly those relying on conservative investment options like savings accounts or bonds, can face challenges during times of high inflation. The returns on these investments might not keep up with the rising cost of living, causing a reduction in real purchasing power for these savers.
Steps Taken by India
- Monetary Policy: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) employs various monetary policy tools to manage inflation. One of the key tools is the repo rate, which is the rate at which banks borrow funds from the RBI. When inflation is high, the RBI might decide to raise the repo rate. This has the effect of making borrowing more expensive for banks, which can then lead to higher interest rates for consumers and businesses. The aim is to reduce excess liquidity in the economy, restrain borrowing, and consequently temper demand, thus helping to control inflation.
- Supply-Side Measures: To address inflation, especially when it's driven by supply constraints, the government can implement supply-side measures. These steps might include initiatives to increase the production and availability of essential goods, such as agricultural products. The government might also take measures to prevent hoarding and ensure efficient distribution of goods to prevent artificial scarcity and price spikes.
Challenges
- Policy Dilemma: Striking the right balance between controlling inflation and promoting economic growth is indeed a complex challenge. Aggressive interest rate hikes can slow down economic activity and potentially hinder job creation and investment. Conversely, keeping interest rates too low for too long could lead to continued inflationary pressures. This highlights the delicate task policymakers face in navigating these conflicting objectives.
- Structural Factors: Inflation can often be influenced by structural issues within an economy. Factors like supply-side constraints, inefficient distribution networks, and imbalances between supply and demand can contribute to inflationary pressures. Addressing these structural challenges requires comprehensive policy interventions and reforms.
- Impact on Vulnerable Groups: High inflation can have a disproportionate impact on low-income and vulnerable populations. Rising prices for essential goods and services can erode the purchasing power of individuals with limited resources. This can exacerbate income inequality and lead to a decline in the standard of living for those who are already economically marginalized.
Way Forward
- Effective Monetary Policy: Continuously monitoring inflation and adjusting interest rates are essential for central banks. A proactive approach to monetary policy helps maintain price stability while ensuring that economic growth is not unduly compromised.
- Supply Chain Reforms: Addressing supply-side constraints and improving distribution networks can contribute to stabilizing prices. By enhancing the production and availability of essential goods and reducing inefficiencies, economies can better withstand supply shocks that might lead to inflation.
- Financial Literacy: Educating the public about the implications of inflation on savings and investments is crucial. This empowers individuals to make informed financial decisions that protect their purchasing power and adapt to changing economic conditions.
- Inclusive Policies: Formulating policies that consider the impact of inflation on vulnerable groups is important for social equity. Ensuring that inflation-control measures take into account the potential adverse effects on low-income populations helps mitigate income inequality.
Balancing the management of high inflation and interest rates requires a comprehensive approach involving sound monetary policy, structural reforms, and inclusive policies to safeguard the interests of all segments of the population while maintaining economic stability.
Must Read Articles:
Inflation: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/inflation-19#:~:text=Inflation%20measures%20the%20average%20price,items%20is%20called%20%27deflation%27.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. How do high inflation and increased interest rates precisely influence an Indian economy? What immediate impacts can be observed? What measures have been implemented to address these effects? What challenges arise in the face of such economic conditions, and what strategies are being considered to steer the economy towards a more stable future?
|

https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-economics/high-inflation-and-interest-rates-impact-on-investors-markets-8909935/













