Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/rift-valley/
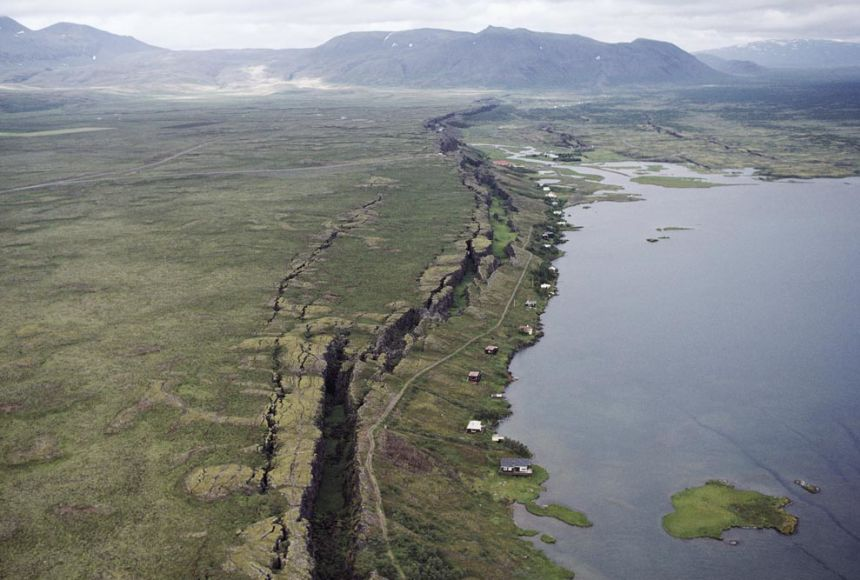
Context: A dam near Kenya's Rift Valley burst, resulting in 42 deaths due to heavy rains and floods, adding to East Africa's toll from natural disasters.
About Great Rift Valley
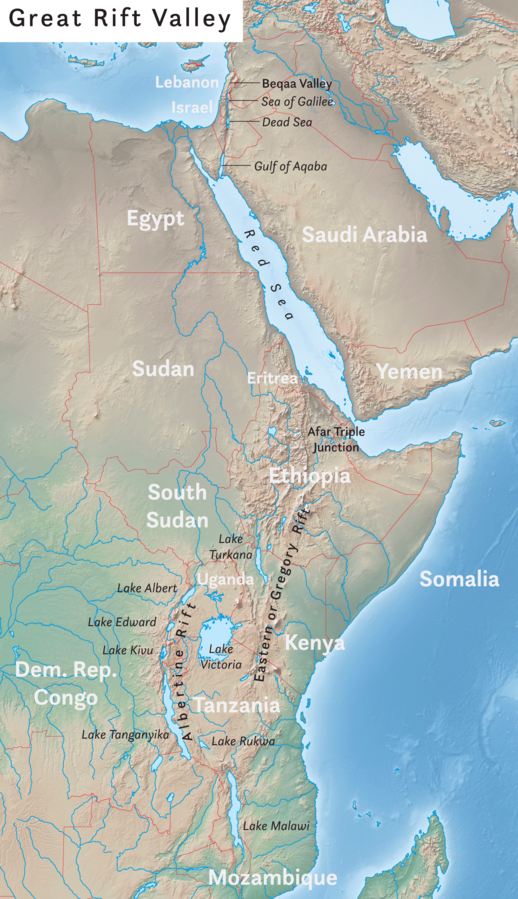
- The Great Rift Valley, also known as the East African Rift, extends approximately 7,000 kilometres from Lebanon in Asia to Mozambique in Southeast Africa.
Geographical Features
- The Great Rift Valley extends northward through the eastern part of Africa, reaching into Western Asia and passing through countries like Uganda, Kenya, Tanzania, and Mozambique.
- Within the valley, there are deep, elongated lakes known as ribbon lakes, such as Lake Malawi and Lake Tanganyika. These lakes contribute to the unique ecosystem of the region and are home to diverse wildlife.
- The valley is formed along the East African Rift, which is a divergent plate boundary. This rift is in the process of splitting the African Plate into two new and separate plates known as the Nubian Plate and the Somali Plate.
Historical Evolution
- Initially, the Great Rift Valley was thought to be a single feature extending from Lebanon to Mozambique, but it is now recognized as a complex system of interconnected rifts and faults.
- These rifts and faults were formed around 35 million years ago and have since evolved into distinct but connected features.
Regional Variations
- In Asia, the Rift includes the Dead Sea Transform, the Jordan Rift Valley, the Red Sea Rift, and the East African Rift. The Jordan River and the Dead Sea are part of this system.
- The East African Rift Valley follows the Red Sea before turning inland into the Ethiopian highlands. It runs along two separate branches: the Western Rift Valley (or Albertine Rift) and the Eastern Rift Valley. These branches are joined at their southern end in Southern Tanzania.
- The Western Rift Valley is bordered by high mountains, including the Virunga Mountains and Ruwenzori Range. It contains the Rift Valley lakes, which are among the deepest lakes globally.
Environmental Significance
- The Rift Valley lakes, including Lake Tanganyika and Lake Victoria, were formed as a result of the rift. They contribute to the region's biodiversity and are vital for local ecosystems.
- The valley's unique geography and climate have led to the formation of mineral-rich lakes, such as Lake Magadi and Lake Nakuru.
Source:
NEWS18
Wikipedia
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Consider the following statements in the context of the Rift Valley:
1. The Great Rift Valley is a continuous geological feature stretching from Lebanon to Mozambique.
2. Rift Valleys are characterized by the presence of grabens, which are down-dropped blocks of land bordered by parallel faults.
3. Rift Valleys are primarily formed due to tectonic faulting.
4. Rift Valleys can develop on both land and ocean floors.
How many of the above statements are correct?
A) Only one
B) Only two
C) Only three
D) All four
Answer: D
|












