Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- The Rajasthan Government allocated 13000 crores for Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project.
Details
- The Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project aims to harvest surplus water available during the rainy season in rivers in southern Rajasthan such as Chambal and its tributaries including Kunnu, Parvati, Kalisindh and use this water in south-eastern districts of the state where there is a scarcity of water for drinking and irrigation. The project was announced in 2017.
Note
- Rajasthan, the largest state of India with a geographical area of 342.52 lakh hectares which amount to 10.4 per cent of the entire country, holds only 1.16 per cent of India’s surface water and 1.72 per cent of groundwater.
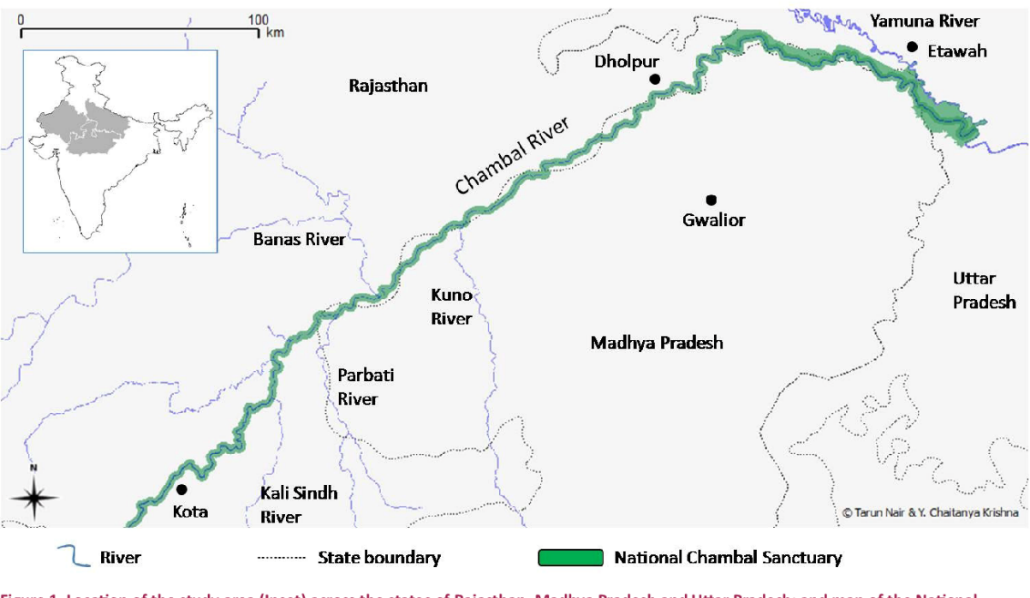
- Among the state’s water bodies, only the Chambal river basin has surplus water but this water cannot be tapped directly because the area around the Kota barrage is designated as a crocodile sanctuary.
- Through the help of diversion structures, intra-basin water transfers, linking channels and construction of pumping main feeder channels, the ERCP aims to create a network of water channels which will cover 23.67 per cent area of Rajasthan along with 41.13 per cent population of the state.
.jpeg)
Benefits Estimated in The Project
- ERCP is estimated to create an additional command area of 2 lakh hectares and an area of 4.31 lakh hectare will get irrigation facilities because of this project.
- The ERCP also intends to improve the groundwater table in rural areas of the state, positively influencing the socio-economic conditions of people from these areas.
- It also adds special emphasis on the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC), hoping that sustainable water sources will enhance and help industries grow in these areas resulting in investment and revenue.
- It will ensure the availability of water for drinking and irrigation purposes.
- It will improve the groundwater table of the state.
- It will promote socio-economic development in the state.
- It will ensure women's empowerment and also improve the standard of living of the people.
- It will help in encouraging investment in the state and also increase the revenue potential of the state.

About Chambal River
- The Chambal River is located in northern India and flows through three Indian states: Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh. The Chambal also forms part of the Rajasthan-Madhya Pradesh boundary.
- The perennial Chambal originates at Janapav, south of Mhow town, near Manpur, Indore, on the south slope of the Vindhya Range in Madhya Pradesh.
- About 885 km (550 miles) long, after rising in the old Vindhya Range and flows in northeastern direction. There, it becomes the second biggest tributary of the Yamuna River,which is the largest tributary of the Ganges.
- The Chambal and its tributaries drain the Malwa region of northwestern Madhya Pradesh, while its tributary, the Banas, which rises in the Aravalli Range, drains southeastern Rajasthan. It ends a confluence of five rivers, including the Chambal, Kwari, Yamuna, Sind, Pahuj, at Pachnada near Bhareh in Uttar Pradesh state, at the border of Bhind and Etawah districts.
- The main tributaries of Chambal include the Banas and Mej rivers on the left and the Parbati, Kali Sindh and Shipra rivers on the right.