Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context:
- Recent discussions in India have highlighted the decline in household savings, primarily driven by a significant reduction in net financial savings.
- This decline is evident in the household net financial savings to GDP ratio, which has reached a four-decade low.
ALL ABOUT HOUSEHOLD SAVINGS: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/households-debt-and-savings-report
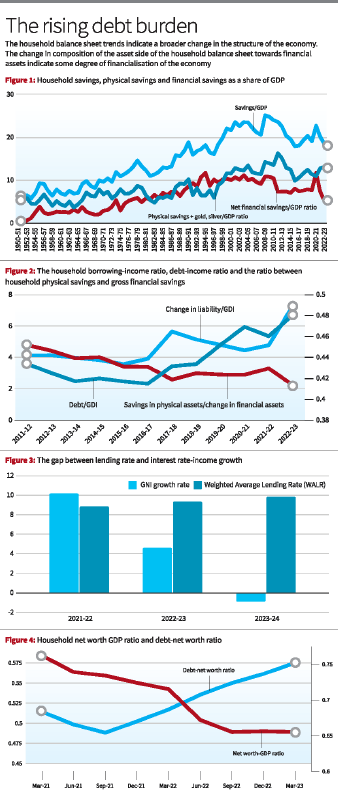
Trends in Household Savings
- Figure 1 illustrates the trends in household savings, physical savings, gold, and net financial savings.
- Despite a slight recovery in physical savings, there has been a sharp reduction in household net financial savings in the fiscal year 2022-23.
Interpreting Lower Financial Savings
- Net financial savings, calculated as the difference between gross financial savings and borrowing, reflect the extent to which household financial assets change over a period.
- Gross financial savings include bank deposits, currency, and financial investments.
Factors Affecting Household Net Financial Savings
- Financing Additional Consumption Expenditure: Households may finance higher consumption expenditure by increasing borrowing or depleting gross financial savings, stimulating aggregate demand and output.
- Financing Higher Tangible Investment: Similarly, households may finance higher tangible (physical) investment through increased borrowing or depletion of gross financial savings, stimulating aggregate demand and output through the investment channel.
- Increased Interest Payment Burden: A rise in interest payments, due to factors such as higher interest rates, can lead households to meet the increased burden through borrowing or by depleting gross financial savings, resulting in a reduction in net financial savings.
Implication of Higher Debt Burden
- The rise in household debt burden raises concerns about debt repayment and financial fragility.
- Household debt sustainability depends on the difference between the interest rate and the income growth rate.
- If households fail to meet their debt repayment commitments, it can reduce the income of the financial sector and deteriorate their balance sheets.

Impact on Consumption Demand
- Higher household debt can reduce consumption expenditure in several ways.
- Firstly, if higher household leverage is perceived as an indicator of higher default risk, banks may reduce credit disbursement, affecting consumption.
- Secondly, higher debt can increase the interest burden, further reducing consumption expenditure.
Macroeconomic Implications
- The trends suggest that households are becoming increasingly vulnerable.
- The policy of higher interest rates to counter inflation can leave households with a rising level of debt, potentially pushing them into a debt trap.
- This, in turn, can have adverse effects on household consumption and aggregate demand.
Data and Statistics
- Household Net Financial Savings to GDP Ratio: Attained a four-decade low.
- Gross Financial Savings to GDP Ratio (2022-23): Declined by 3 percentage points (7.3% to 5.3%).
- Household Physical Investment to GDP Ratio (2022-23): Increased by only 0.3 percentage points (12.6% to 12.9%).
- Household Borrowing to Income Ratio (2022-23): Registered a sharp spike.
Conclusion
- The changing composition of household balance sheets towards financial assets indicates a broader shift towards financialization of the economy.
- This shift from a production-based economy to a monetary or financial exchange-based economy can make the economy both jobless and fragile, impacting economic growth and stability.
ALL ABOUT HOUSEHOLD SAVINGS: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/households-debt-and-savings-report
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Direct taxes play a crucial role in India's fiscal policy and economic development. Discuss the role of direct taxes in promoting economic equity and stability in a country.
|