Topic Important for: General Studies- 2 I Issues relating to development and management of Education.
Context:
The central government has proposed the draft National Education Policy projecting an expansion of the Right to Education Act to cover the three years of preschool before Class 1.
Background:
- The Committee was constituted by the Ministry of Human Resource Development in June 2017.
- The Committee for Draft National Education Policy Chaired by Dr. K. Kasturirangan submitted its report on May, 2019.
- The report proposes an education policy which seeks to address the challenges of: access, equity, quality affordability, accountability faced by the current education system.
- The draft Policy provides for:
ü Reforms at all levels of education from school to higher education
ü Increase the focus on early childhood care
ü Reform the current exam system
ü Strengthen teacher training
ü Restructure the education regulatory framework.
About:
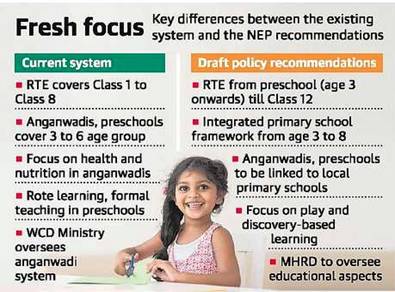
- The draft policy seeks the early childhood education to be monitor and regulated by the Ministry of Human Resource Development (HRD) as part of the school system.
- The policy will also change in the Anganwadi system of education which has been overseen by the Ministry of Women and Child Development (WCD).
- The draft Policy incorporates a new integrated curricular framework for 3 to 8-year olds.
- It provide for flexible system based on play, activity and discovery
- The policy will also begin exposure to three languages from age 3 onwards.
|
Article 21A Right to Education: – “The State shall provide free and compulsory education to all children of the age of six to fourteen years in such manner as the State may, by law, determine.”
- The Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education (RTE) Act, 2009, which represents the consequential legislation envisaged under Article 21-A, means that every child has a right to full time elementary education of satisfactory and equitable quality in a formal school which satisfies certain essential norms and standards.
- Article 21-A and the RTE Act came into effect on 1 April 2010
|
Current vs Proposed education policy:
Challenges in Implementation of policy:
- Recruitment and training teacher,
- Infrastructure bottle necks
- Learning materials and amenities to students,
- Nutritional aspects of children (including the proposal to provide breakfast to young children)
- Accurate data on what percentage of children are neither in pre-schools nor the anganwadi system.
Source Link:https://www.thehindu.com/education/draft-national-education-policy-proposes-formal-education-from-age-of-three/article27706234.ece
All states can now constitute foreigners tribunals
Topic Important for: General Studies- 3 I Governance, Constitution.
Context:
The Ministry of Home Affairs has provided specific guidelines to detect detain and deport foreign nationals staying illegally across the country.
About:
- The central government has amended the Foreigners (Tribunals) Order, 1964.
- It empowered district magistrates in all States and Union Territories to set up tribunals to decide whether a person staying illegally in India is a foreigner or not.
Note: Earlier, the powers to constitute tribunals were vested only with the Centre.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs has sanctioned around 1,000 Tribunals to be set up in Assam in the wake of publication of the final National Register of Citizens.
- The amendment in Foreigners (Tribunal) Order, 2019 also empowers individuals to approach the Tribunals.
- The amended also allows District Magistrates to refer individuals who haven’t filed claims against their exclusion from NRC to the Tribunals to decide if they are foreigners or not.
|
National Register of Citizens (NRC)
- The National Register of Citizens (NRC) is a document manufactured by the Government which contains the conduct of the Census of 1951 in respect of each village, showing the houses or holdings in a serial order and indicating against each house or holding the number and names of persons staying therein.
- The NRC was published once in 1951.
|
Some important Facts:
Section 6A of the Citizenship Act, 1955
- According to Section 6A of the Citizenship Act, 1955 those who came from Bangladesh between 1966 and 1971 will have to register themselves with the Foreigners Regional Registration Officer
- They will be included in the NRC, but will not have voting rights for 10 years from the date of registration.
Source Link: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/all-states-can-now-constitute-foreigners-tribunals/article27706366.ece
ISRO gears up for Chandrayaan-2 mission
Topic Important for: General Studies- 3 I Achievements of Indians in science & technology
Context:
The Indian Space Research Organisation has marked mid-July for the take-off Chandrayaan-2 mission.
About:
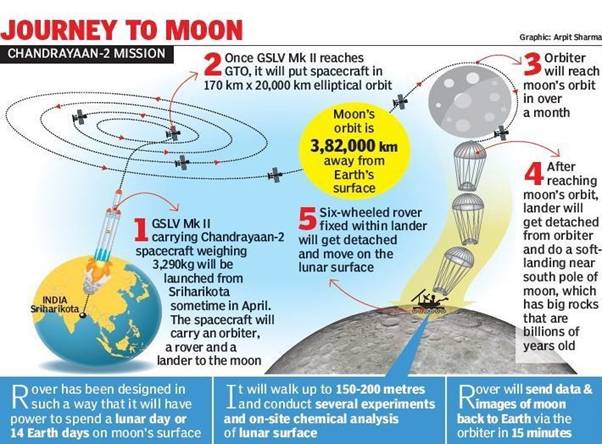
- Chandrayaan-2, India’s second lunar mission has three modules namely Orbiter Lander (Vikram) & Rover (Pragyan)
- The mission will be launched using rocket GSLV MK-III from Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota.
- Chandrayaan-2 Weighing about 3,500 kg
- The lander is named Vikram (meaning valour, after the father of the Indian space programme, Vikram Sarabhai).
- It will release a small robotic rover, named Pragyan (wisdom), to move around, feel and understand the lunar surface.
- Vikram must gently descend on a harsh rugged lunar surface, without getting damaged. It must also avoid landing in a shadowy patch. It needs sunlight for generating its power.
|
The GSLV-Mk III
- GSKV-Mk III is capable of launching four-tonne satellites in the Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO).
- The rocket is also capable of placing up to eight tonnes in a Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
- It is India’s first fully functional rocket to be tested with a cryogenic engine that uses liquid propellants — liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen.
|
Source Link: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/isro-gears-up-for-chandrayaan-2-mission/article27705909.ece
E-cigarette ban comes after sustained effort
Topic Important for: General Studies- 2 I Issues relating to development and management of Health
Context:
The Rajasthan government has announced the decision to ban production, distribution, advertisement and sale of e-cigarettes.
Background:
- The previous government had appointed a committee of experts to study the effects of e-cigarette and suggests recommendations.
- The committee was headed by medical expert Nalin Joshi.
- The committee found that the nicotine-laced and heat-not-burn devices were “extremely harmful” recommended a ban on e-cigarettes.
- The committee recommended an immediate ban on E-cigarette







