Description
Context:
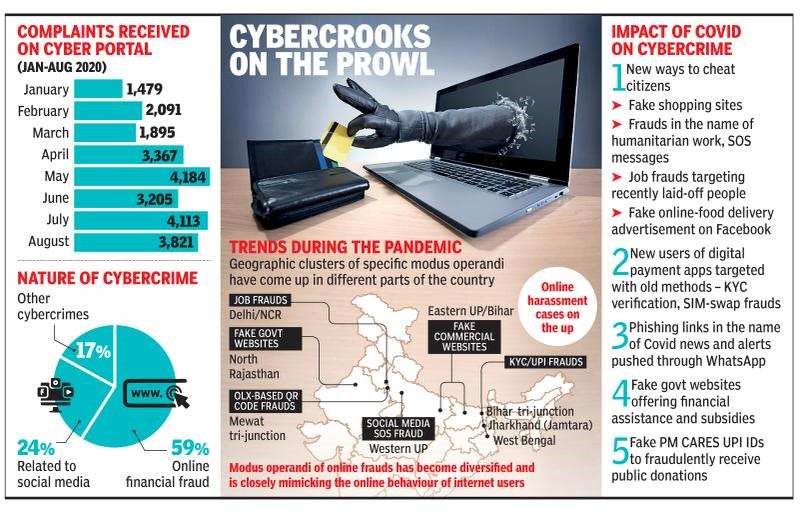
- The Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) observed over 07 lakh cyber security incidents in the first six months of 2021.
- Almost 12,000 incidents were related to government organizations.
- According to the logs analysed and made available to CERT-In, the IP addresses of the computers from where the attacks appear to have originated belong to various countries, including Algeria, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, Hong Kong, Indonesia, Netherlands, North Korea, Pakistan, Russia, Serbia, Singapore, South Korea, Sri Lanka, Taiwan, Thailand, Tunisia, Turkey, the U.S., and Vietnam.
Cyber security situation in India:

Why India needs a robust cybersecurity strategy?
- Demonetisation and Covid-19 have pushed indians to adopt digitisation. Work from home is now accepted as a new normal.
- India’s digital growth will not be sustainable if we do not have a strong shield in the form of data protection laws and privacy policies.
- To address the issue of protecting critical information infrastructure in cyberspace, build integrated capabilities to prevent and respond to cyber threat.
- India has one of the highest number of internet users in the world and is also among the top-10 countries facing cyberattacks.
- To address the current gaps in governance and to provide a strong framework to handle issues related to cybersecurity.
- There is no centralised command to have oversight and coordinate efforts to handle larger cybersecurity issues.
- To protect domestic interest: The discovery of potential North Korean malware at both the Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant and the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) last year, and recent revelations of a Chinese firm tracking Indians’ personal data highlight just how vulnerable Indian cyberspace can be.
Suggestions:
Unified cybersecurity framework:
- Dedicated authority: Currently National Cyber Security Coordinator (NCSC) and Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) are handling cybersecurity issues in India. There is an urgent need of having a comprehensive and unified government institution for creating a cyber defence network
- Unified inter-regulator: Currently, RBI, SEBI, IRDAI, TRAI, PFRDA, etc, have different cybersecurity framework for their regulated entities. However, none of the frameworks talk about inter-regulator coordination or integrated approach to handle cybercrime.
- A holistic cybersecurity strategy with a possible amendment in the IT Act, as some of its provisions have become redundant and can’t address issues arising from the evolving threats.
- Cyber Defence Agency: Government needs to consider creating a Cyber Defence Agency, which is to be entrusted with the responsibility to implement the cyber defence strategy solely for national security.
- Constitution of cyber commando force as a part of the defence program to neutralise any cross-border cyber terrorism or cyber-attack.
- Create specialised cyber police cadres in all State police departments.
- Sectorial CERT and state-level CERT would be more effective for rapid response on any cyber-attack. The state-level CERT team will need to ensure speedier incident response and coordination with national agencies.
- Building a business ecosystem to leverage artificial intelligence and robotics to improve cyber defence.
- Pass the proposed Data Protection Bill to protect critical information like personal data, business information, and financial information.
Conclusion:
- It is high time that we consider amendment of the existing IT Act, 2000, which is not fully synced with today’s cyber threat.
- In addition to the IT Act, it’s already delayed but high time to introduce data privacy laws.
https://www.thehindu.com/business/cert-in-observed-more-than-607-lakh-cyber-security-incidents-till-june-2021-government/article35726974.ece?homepage=true