Description

Figure 2: No Copyright Infringement Intended
Context:
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has cautioned people against co-operative societies which are using the word "bank" in their titles and accepting deposits from non-members.
Details
- post the amendment in the Banking Regulation Act, 1949, which became effective from September 29, 2020, co-operative societies cannot use the words "bank", "banker" or "banking" as part of their names, except as permitted under the provisions or by the RBI.
- the insurance cover from Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) is also not available for deposits placed with these societies.
About Cooperative Bankings:
- A Co-operative bank is a financial entity which belongs to its members, who are at the same time the owners and the customers of their bank.
- Co-operative banks in India are registered under the States Cooperative Societies Act. The Co-operative banks are also regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and governed by the
- Banking Regulations Act 1949
- Banking Laws (Co-operative Societies) Act, 1955.
Features of Cooperative Banking:
- Customer Owned Entities
- The members democratically elect a board of directors and they have equal voting rights
- A significant part of the yearly profit is usually allocated to reserves and a part of it can also be distributed to the members
- They have played a significant role in the financial inclusion of unbanked rural masses.
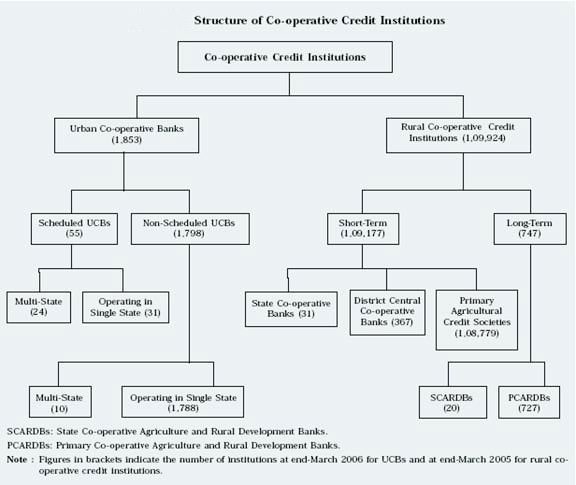
Structure of Cooperative Banks:
Advantages of Cooperative Banks:
- These banks have provided aid to the rural population by granting loans and credits with interest rates, lower in comparison to that asked by local money lenders
- They have their reach at every corner of the country and have managed to maintain a personal rapport with the customers
- Since the bank is owned and governed by the members themselves, they do not seek huge profits and believe in mutual help
- The interest rate on deposits is high and on loans is low
- They promote productive borrowing, in order to reduce the risk of loss
- Co-operative Banks have helped the farmers by providing them agricultural credits to buy basic products like fertilizer, seeds, etc.
The Banking Regulation Amendment Bill, 2020
The Banking Regulation Amendment Bill, 2020 was introduced in the wake of PMC Bank scam, and seeks to strengthen cooperative banks by increasing professionalism, enabling access to capital, improving governance and ensuring sound banking by giving more powers to RBI. The features of the bill include:
- Cooperative banks will be audited as per RBI norms, while administrative issues will be guided by Registrar of Cooperative Societies.
- RBI has the powers to supersede the board, in consultation with the state government if the cooperative bank is under stress.
- Appointment of the chief executives will be based on certain qualifications and under the supervision of RBI.
- The bill aims to infuse proper regulation and better management of Cooperative banks to protect the interests of depositors.
- The amendments will apply to all cooperative banks including urban cooperative banks and multi-state cooperative banks.
Issues with the Cooperative Banks in India:
- Politicians in local as well as in state use them to increase their vote bank and usually get their representatives elected over the board of director in order to gain undue advantages.
- The cooperatives in northeast states and in states like West Bengal, Bihar, Odisha are not as well developed as the ones in Maharashtra and Gujarat. There is a lot of friction due to competition between different states, this friction affects the working of cooperatives.
- A serious problem of the cooperative credit is the overdue loans of the cooperative banks which have been continuously increasing over the years.
- Large amounts of overdues restrict the recycling of the funds and adversely affect the lending and borrowing capacity of the cooperative.
- The cooperatives have resource constraints as their owned funds hardly make a sizeable portfolio of the working capital.
- Raising working capital has been a major hurdle in their effective functioning.