Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- IRDAI has rejected the proposal of Go Digit Infoworks Services to convert the company’s holdings into compulsory convertible preferred shares (CCPS).
Basics
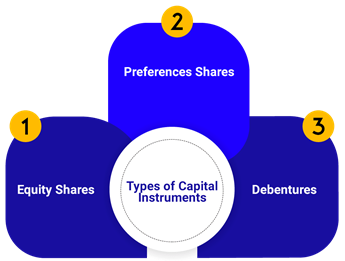
Preference Shares
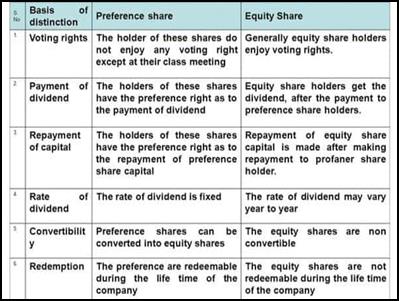
- From the name itself, preference shares are understood as shares that have preference over other shares. In an investment environment, the company issuing preference shares must pay a dividend to them before offering a single penny to equity Similar is the situation in the event of bankruptcy; the residual money is used first to pay to the preference shareholders.
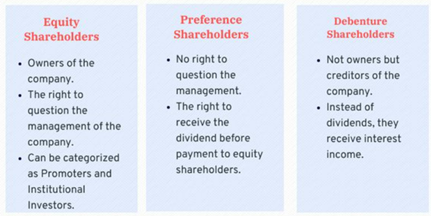
Types of Preference Shares
- Various types of preference shares are seen in the market. The classification is on the basis of their different structure, maturity terms, the extent of participation, nature of dividend payment, etc.

CCPS
- Compulsory Convertible Preference Shares (CCPS) are one of the sources for raising funds for the corporate sector.
- It is an advanced version of equity shares. CCPS is a type of preferred share/stock that gives holders the option to convert their preference shares into a fixed number of equity shares of the issuing company after a specified date.
- Thus, if an early investor has CCPS, he can have more rights than other investors who come in later at a higher valuation.
- Compulsorily Convertible Preference Shares are a key element of start-up financing.
Simplifying it further…
To get a clear picture, let’s understand how CCPS works with the following example. Company A raised funds by issue of CCPS at 3.5%, convertible into equity after 7 years. The CCPS holder will get a fixed dividend of 3.5% of the nominal price of the security subject to sufficiency of profit. In case the Company does not have sufficient profit to payout dividend on both Equity Shares and Preference Shares, the Preference Shareholders get priority in dividend payout. Similarly, if at the time of bankruptcy, if the Company’s assets are insufficient to repay the share capital brought via Equity and Preference Shares, the priority will be given to Preference Shareholders. The amount remaining, if any, after repayment to the Preference Shareholder will then be distributed to the Equity Shareholders. The CCPS holders will receive these benefits until conversion into Equity Shares. In the above example, at the end of 7 years, the CCPS will be converted into equity shares at a predetermined ratio. This ratio is referred to as the conversion ratio.
This conversion ratio is determined with the guidance of the valuer. The conversion ratio depends on the value of equity at the time of issue. If the conversion ratio is 1:3, the CCPS holder will receive 3 equity shares against one CCPS each. By agreeing to the terms of CCPS, the investor agrees with the underlying risks of fluctuations in share price.

Benefits
CCPS Helps in Avoiding Valuation Gap
- CCPS are particularly offered to fill the gap between the valuation expectations of the founder and the investors that are generally linked to the performance of the Company. CCPS offers investors the opportunity to participate in the growth of companies while mitigating the risk of lower valuation of companies that underachieve the targets.
For Promoters
- Anti-Dilution: The promoters of the company are benefitted by the Compulsorily Convertible Preference Shares (CCPS) by maintaining the equity stake intake whenever the company issues equity shares to a new investor. The promoters can convert the CCPS taken at the time of lower valuation of shares at a time when new investor brings the money at a higher valuation and hence, the promoters can increase its stake without bringing money at a higher cost.
- These shares get converted to ordinary equity shares after 10-15 years but that is more than sufficient time for most start-ups to give their investors an exit.
- CCPS also helps founders keep control of a company even if their stake is lower than that of investors.

Private Equity Investors
- CCPS also benefits private equity (PE) investors. At the time of conversion, the investors can link the company’s performance. These fundamentally mean that the shares will get converted only when the Company achieves the target growth. In case the target set is not made, then the PE firm reserves the right to increase its stake.
- It helps investors maintain their stake and have a say even if their stake gets diluted later.
Start-ups
- The CCPS also provides help to the founder of start-up companies in controlling their stake at the funding stage of new investors without the infusion of new funds. As CCPS are also anti-dilution securities, the founders can manage their equity without adding any further funds. Since the CCPS are also anti-dilution securities so the founders can manage their equity stake to lead the company by holding a substantial stake in the company.
Regulation for compulsorily convertible preference shares
- The law dealing with preference shares is the Companies Act 2013. Under the previous companies law (Companies Act 1956), section 85 of the act regulates both equity shares and preference shares. Equity shares are ordinary shares issued by the company. Preference shares are shares issued by the company which has preferential treatment in respect of shareholders.
- Apart from the Companies Act, the SEBI guidelines provide a specific requirement for the operation of shares.
https://indianexpress.com/article/business/companies/go-digit-irdai-no-to-fairfax-proposal-for-ccps-conversion-8259565/
















