





Disclaimer: Copyright infringement is not intended.
Context:
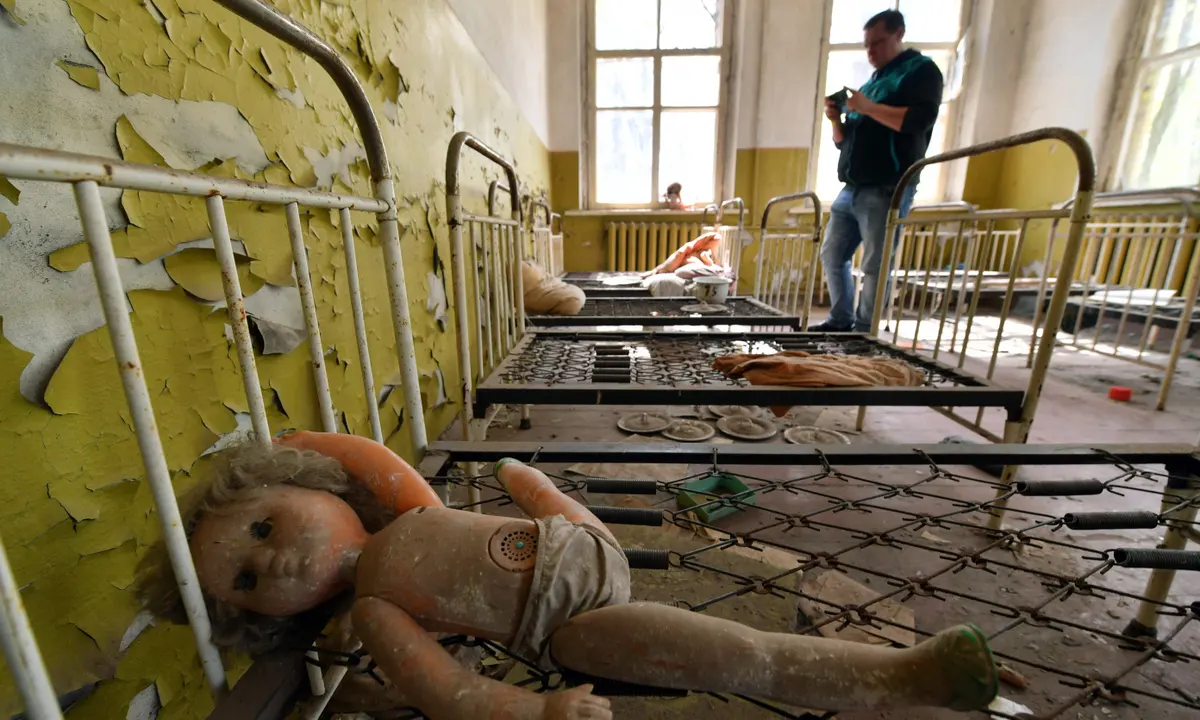
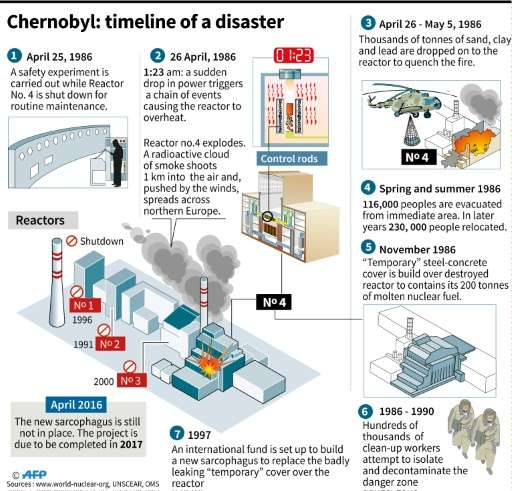
The Chernobyl disaster
What caused the Chornobyl accident?
Experts' view on causes:
Fatalities from disaster:
Who is to be blamed for the disaster?
|
RBMK ●The RBMK (Russian: reaktor bolshoy moshchnosti kanalnyy, "high-power channel-type reactor") is a class of graphite-moderated nuclear power reactors designed and built by the Soviet Union. It is one of two reactor types to be developed in the Soviet Union in the 1970s. ●The name refers to its (unusual)design where, instead of a large steel pressure vessel surrounding the entire core, the core is surrounded by a cylindrical annular steel tank inside a concrete vault, and each fuel assembly is enclosed in an individual 8 cm (inner) diameter pipe (called a "technological channel"). The channels also contain the coolant and are surrounded by graphite. ●The RBMK is an early Generation II reactor and the oldest commercial reactor design still in wide operation, although reactor units of the first generation type have all been decommissioned.
|
Source:
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q) Match the following:
A (a) - (iv), (b) - (iii), (c) - (i), (d) - (ii) B (a) - (iii), (b) - (iv), (c) - (ii), (d) - (i) C (a) - (ii), (b) -(i), (c) - (iv), (d) - (iii) D (a) - (ii), (b) - (iv), (c) - (i), (d) - (iii) Answer: B Explanation: (a) Chernobyl disaster - (iii) Radioactive substances smog: The Chernobyl disaster, which occurred on April 26, 1986, in Ukraine, involved a catastrophic nuclear accident. The explosion released a significant amount of radioactive material into the atmosphere, causing widespread contamination. The term "radioactive substances smog" refers to the radioactive particles and gases that were dispersed into the air as a result of the explosion. (b) Bhopal tragedy - (iv) Methyl Isocyanate: The Bhopal tragedy, which occurred on December 2-3, 1984, in Bhopal, India, is one of the world's worst industrial disasters. It involved the release of toxic methyl isocyanate (MIC) gas from a pesticide plant owned by Union Carbide India Limited (UCIL). The gas leak resulted in thousands of deaths and long-term health effects for many survivors. (c) Ozone hole - (ii) Chlorofluoro substances: The term "ozone hole" refers to the depletion of the ozone layer, particularly over Antarctica. This depletion is primarily caused by the release of chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) compounds into the atmosphere. CFCs were commonly used in refrigerants, aerosol propellants, and solvents before their harmful effects on the ozone layer were recognized. (d) Vizag gas leak - (i) Styrene: The Vizag gas leak, also known as the LG Polymers gas leak, occurred on May 7, 2020, in Visakhapatnam, India. It involved the release of styrene gas from a polymer plant owned by LG Polymers. Styrene is a toxic chemical used in the production of polystyrene plastics and synthetic rubber. The gas leak led to several fatalities and caused injuries to many people in the surrounding areas. |






© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved