Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: byron2000.en
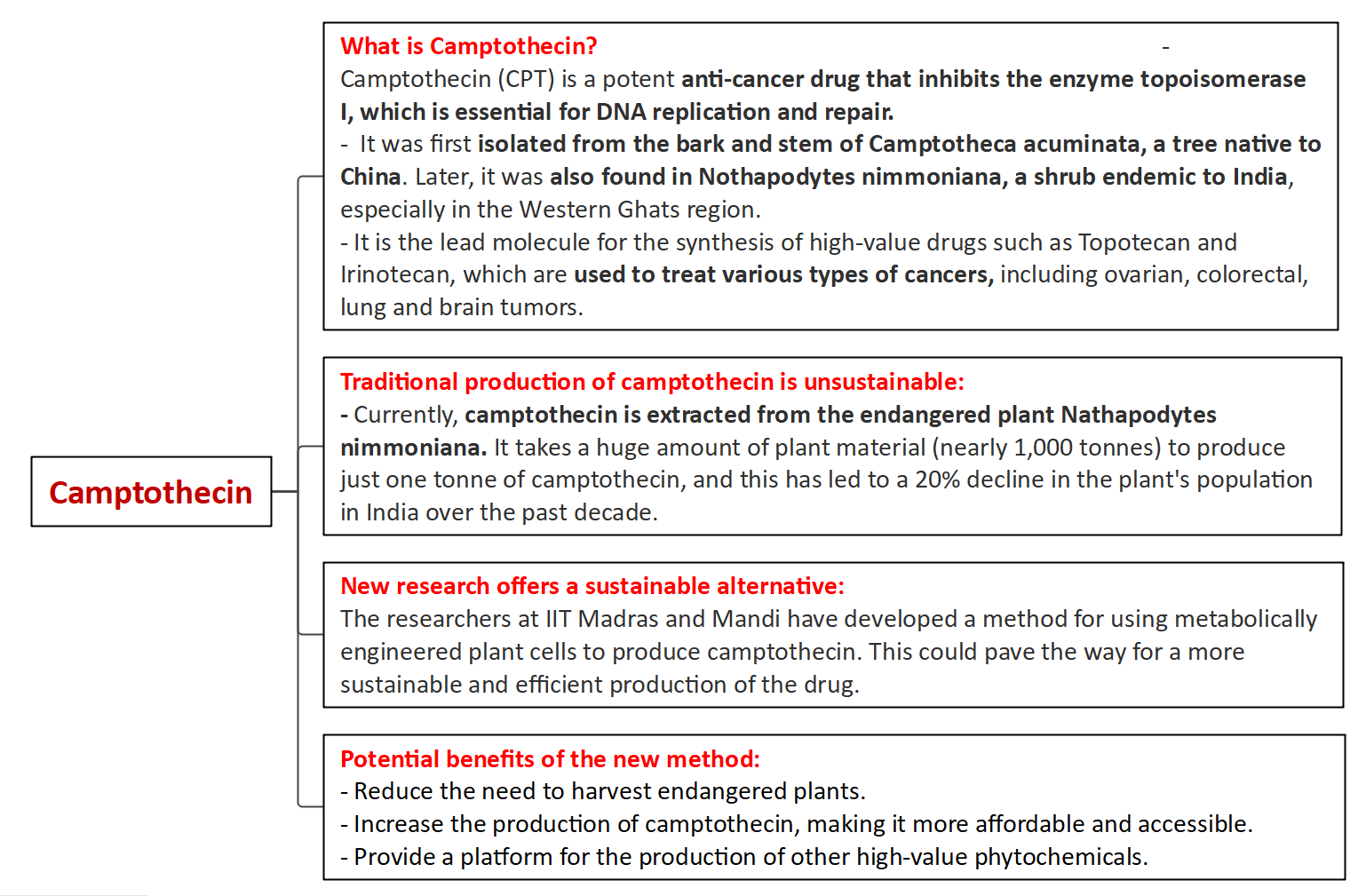
Context: The researchers at the Indian Institutes of Technology Madras and Mandi successfully enhanced the production of the anti-cancer drug camptothecin (CPT) by metabolically engineering plant cells.
Background
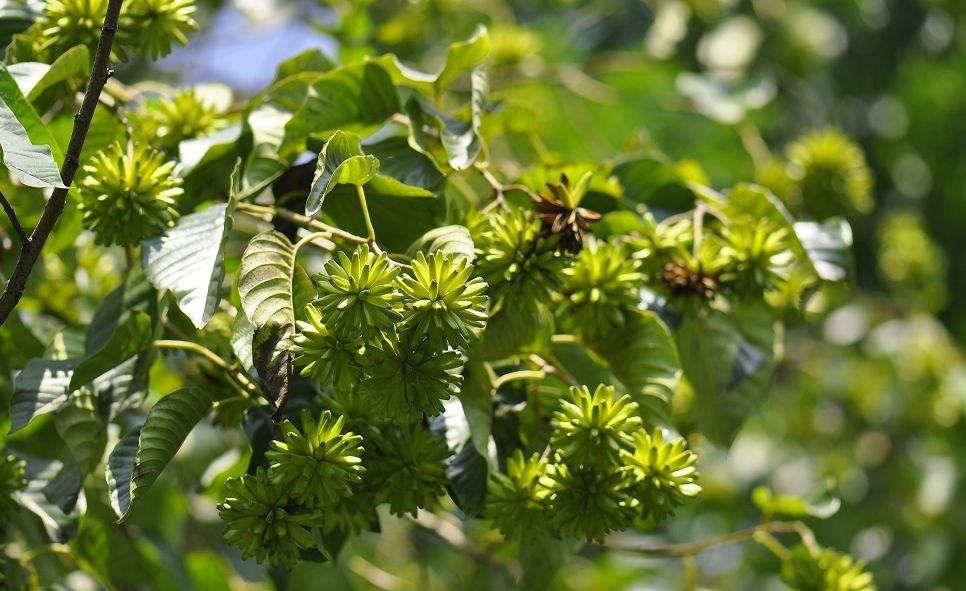
- Camptothecin (CPT) is an anti-cancer drug derived from Nathapodytes nimmoniana, a native and endangered plant.
- The extraction process is inefficient, requiring nearly 1,000 tonnes of plant material to produce 1 tonne of CPT.
- The plant is endangered, and its population has seen a 20% decline in the past decade.
Research Efforts
- In 2021, researchers from IIT Madras published a paper identifying a microbe as a sustainable and high-yielding alternative source for CPT.
- The Plant Cell Technology Lab at IIT Madras developed a genome-scale metabolic model for N. nimmoniana plant cells using computational tools.
- The study aims to enable effective and efficient commercial production of CPT and other important alkaloids while reducing the need to harvest endangered plants.
- The Science and Engineering Board (SERB) and the Department of Science and Technology funded the research.
- The research findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal Frontiers of Plant Science.

Metabolic Engineering
- The researchers focused on metabolically engineering plant cells to increase the production of CPT.
- They developed a model-based rational metabolic engineering platform for plant cells.
Cultivation and Engineering Process
- Plant cell cultures were grown in the lab, and cells were extracted and maintained in the lab.
- The engineered plant cells were optimized to enhance the production of camptothecin.
- The researchers are at technology readiness levels 3-4 and plan to optimize at the bioreactor level.
Commercial Viability
- The researchers aim to make the process commercially viable within three to five years.
- Integration of metabolic engineering with bioprocess engineering principles is emphasized for enhanced and sustainable drug production.
- The platform developed for model-based rational metabolic engineering could potentially be used to enhance the production of other high-value phytochemicals.
- The research offers a more sustainable method of producing camptothecin, reducing the reliance on endangered plants and contributing to conservation efforts.
Conclusion
- This research has the potential to revolutionize the production of camptothecin, an essential anti-cancer drug, by providing a more sustainable and efficient alternative to the current extraction methods from endangered plants.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Why has "camptothecin" been a topic of recent news coverage?
A) Due to its discovery in a new species of fungi.
B) As a result of its increased availability in common herbs.
C) Owing to its significance in the treatment of cancer.
D) For its newfound application in renewable energy sources.
Answer: C
Explanation:
Camptothecin has been in the news due to its importance in cancer treatment, particularly as a potential source of anti-cancer drugs.
|