




Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
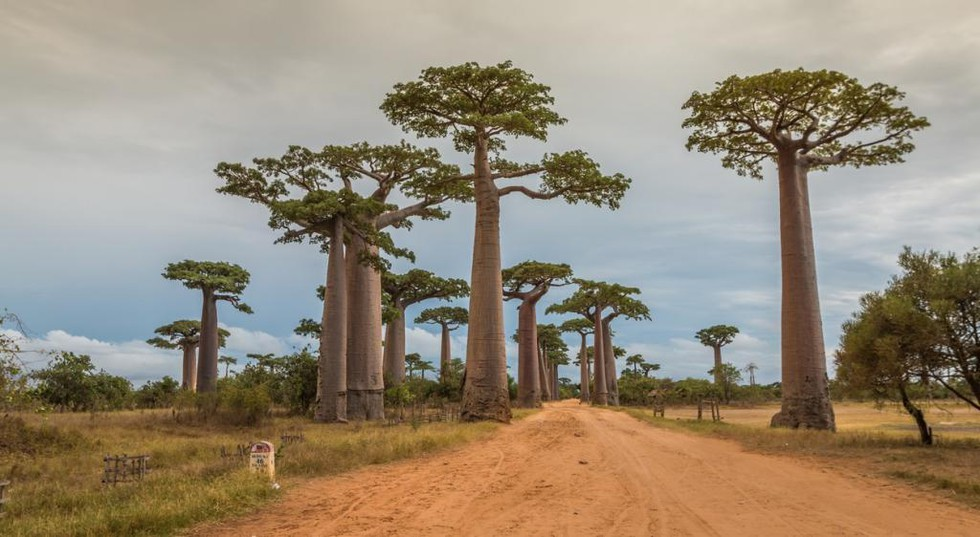
Baobabs
Significance:
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/invasive-species-natural-ecosystems-threaten-9262836/
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Which of the following statements about baobab trees is correct? a) Baobab trees are primarily found in Asia, with India being the main habitat for these trees. b) Baobab trees are not significant in African cultures and are mainly valued for their nutritional fruit. c) Baobab trees are not adapted to survive in harsh environments and are vulnerable to droughts. d) Baobab trees play a crucial role in carbon sequestration, helping mitigate climate change by storing carbon dioxide. Correct answer: d) |





© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved