Description
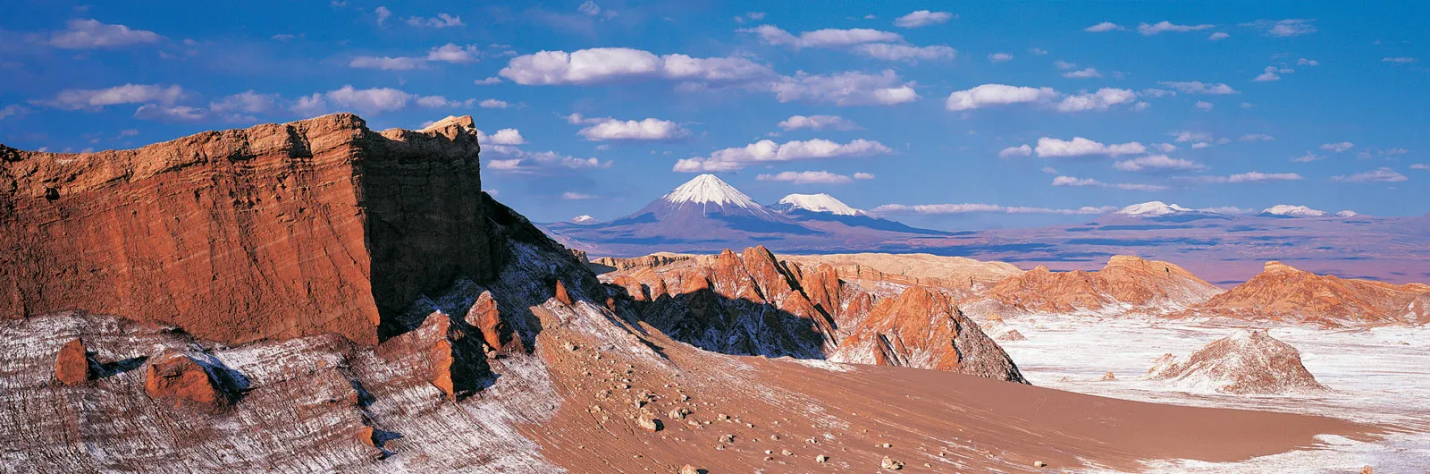

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://www.britannica.com/place/Atacama-Desert
Context: The discovery of a rich microbial biosphere buried deep beneath the Atacama Desert's surface sheds light on the resilience of life in extreme environments and has implications for the search for life on Mars.
Key points from the research findings:
Depth of Microbial Biosphere
- Previous studies had identified microbial life in the Atacama Desert down to depths of about 2.6 feet. However, the new research discovered a microbial community residing much deeper, between 6.6 feet and at least 13 feet below the surface.
- This deeper biosphere is dominated by Actinobacteria, a diverse group of bacteria known for inhabiting extreme environments like boiling hot springs and salty seas.
|
Methodology and DNA Analysis
The researchers developed a method to differentiate between intracellular DNA (from living cells) and extracellular DNA (from dead cells) to assess microbial diversity accurately. This approach provides insights into the distribution and adaptation of microbial life at different depths and environmental conditions within the Atacama Desert.
|
Isolation and Resilience
- The microbial community found in the deeper layers of the Atacama Desert is described as "completely isolated from the surface." This isolation highlights the resilience and adaptability of these microorganisms to survive under extreme conditions.
- Actinobacteria and Firmicutes, identified in the deeper layers, demonstrate adaptations to high salt concentrations and anaerobic conditions, respectively.
Survival Mechanisms
- The researchers propose that these microbes survive at depth by extracting water from gypsum, a mineral present in the Atacama Desert's soils. The reaction between gypsum and water can release water under certain conditions, providing a potential source of hydration for the microbes.
Implications for Mars Exploration
- The Atacama Desert serves as an analogue for studying Martian conditions due to its extreme aridity and mineral composition.
- Similarities between the Atacama Desert and Mars, including the presence of gypsum deposits, suggest that subsurface microbial life could exist on Mars. Understanding microbial survival strategies in the Atacama may inform the search for life beneath Mars' surface.
About Atacama Desert
- The Atacama Desert is located on the Pacific coast of South America, stretching over 1,600 km along the west of the Andes Mountains.
- It is the driest non-polar desert in the world, receiving very little precipitation. Some areas have not seen significant rainfall for centuries.
- The extreme aridity is the result of geographical factors like the rain shadow effect caused by the Andes and Chilean Coast Range, as well as ocean currents and climatic conditions.
- Some areas of the Atacama Desert have been compared to Mars due to their environmental similarities, making them ideal for Mars mission simulations.
- Despite its harsh conditions, the Atacama Desert supports a variety of flora and fauna adapted to arid environments. Unique plant species like llareta, cacti, and saltgrass thrive, along with animals such as Andean flamingos, guanacos, and Darwin's leaf-eared mouse.
- The Atacama Desert has been inhabited by indigenous cultures like the Chinchorro and Atacameño tribes for millennia. Historical periods include the Inca and Spanish empires, marked by mining activities and the development of coastal cities.
- Rich in mineral resources like copper, gold, and sodium nitrate, the Atacama Desert has been a significant mining area since the 19th century.
- The desert's unique environmental conditions make it an ideal location for astronomical observations, hosting world-class observatories like La Silla and Paranal.
Conclusion
- The discovery of a deep microbial biosphere in the Atacama Desert expands our understanding of microbial life's resilience and adaptation to extreme environments. This knowledge not only enhances our appreciation of Earth's biodiversity but also informs astrobiological research, particularly in the context of exploring potential habitats for life beyond our planet.
Source:
LiveScience
Wikipedia
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Consider the following statements in the context of the Atacama Desert:
1. It is one of the driest places on Earth.
2. It is located in Africa.
3. It is the largest desert in the world.
4. It experiences extreme temperature fluctuations between day and night.
How many of the above statements are correct?
A) Only one
B) Only two
C) Only three
D) All four
Answer: B
|











