SPOTLIGHT|RECORD FUND TRANSFERS UNDER DBT SCHEME
Context
- A record amount of nearly Rs 12.5 lakh crore was transferred to several beneficiaries through 1,300 crore transactions in the last two financial years under the Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT).
- It is nearly 44% of the cumulative DBT transfers since 2014.
Details
- While nearly Rs 6.17 lakh crore was transferred to people in the last financial year that ended March 31, 2023, over Rs 6.3 lakh crore was transferred to people in the financial year 2021-22.
- This was a quantum jump from earlier financial years when Rs 3.82 lakh crore was sent to people under DBT in 2019-20 before the Covid-19 pandemic.
Why the DBT jump?
- The Centre has brought increasing number of schemes under the DBT to cut down on leakages and the money falling into wrong hands.
- In 2022-23, the Centre transferred Public Distribution System (PDS) ration worth Rs 1.63 lakh crore to poor people in the country and the figure stood at Rs 2.17 lakh crore for 2021-22.
- This was in a big way due to the free ration scheme run by the Centre — PM Ann Yojana — during the Covid-19 pandemic.
- In the last financial year, the biggest payout under DBT was for fertilizer subsidy, which rose from 1.23 lakh crore in 2021-22 to 2.06 lakh crore in 2022-23.
- At present, 312 Central government schemes fall under DBT’s ambit.
DBT
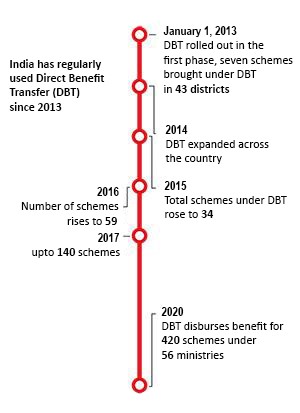
- Direct Benefit Transfer or DBT has travelled a long path since its early initiation by the Government of India on 1st January 2013 to change the mechanism of transferring cash subsidies and benefits.
- The program was aimed at the transfer of subsidies and cash benefits directly to the people through their Aadhaar-seeded bank accounts.
- Vision: Crediting subsidies directly into the bank accounts would substantially reduce leakages, and associated delays, owing to the flow of funds in a multi-hierarchy of administrative offices till it reaches the end beneficiary.
- The primary aim of this Direct Benefit Transfer program is to bring transparency and terminate pilferage from distribution of funds sponsored by Central Government of India.
- In DBT, benefit or subsidy will be directly transferred to the citizens living below poverty line.
- Central Plan Scheme Monitoring System (CPSMS), of the Office of Controller General of Accounts, was chosen to act as the common platform for routing of the Direct Benefit Transfer.
- CPSMS was used for the preparation of the beneficiary list, digitally signing the same and processing of payments in the bank accounts of the beneficiary using the Aadhaar Payment Bridge of NPCI.
Components of DBT
- Primary components in the implementation of DBT schemes include
-Beneficiary Account Validation System,
-a robust payment and reconciliation platform integrated with RBI,
-NPCI,
-Public & Private Sector Banks,
-Regional Rural Banks and Cooperative Banks (core banking solutions of banks, settlement systems of RBI, Aadhaar Payment Bridge of NPCI) etc.
Types of Schemes Covered in Direct Benefit Transfer
There are different schemes under the DBT Scheme. These include:
Cash Transfer
- The cash transfer scheme is rather simplistic. It involves the transfer of the subsidies directly to the beneficiaries from the government. The following methods can be used for the transfer of cash:
- Direct transfer into the beneficiary account.
- Use of the State treasury to transfer cash to the beneficiary.
- Government-appointed agencies make transfers.
- The State or Central Government makes cash transfers.
In-Kind Benefit Transfer
- In-kind benefit transfer is a transfer that provides benefits to the candidates directly or through some appointed third-party agency. The Government takes care of all the expenses incurred while procuring the benefit or subsidy.
- For example, the Government will buy a certain product and offer it to the public.
Other Transfers
- Apart from the cash and kind transfers, the DBT Scheme also allows transferring funds or subsidies to different non -governmental functionaries that enable the implementation of different government policies until the end.
- It includes all community workers, teachers in aided schools, NGO workers, etc. Such members are not beneficiaries but are still provided with training, wages, food, etc.
Direct Benefit Transfer Portal
- The government of India has recently launched an online portal that contains all the details of the Direct Benefit Transfer Scheme along with the necessary instructions for the candidates.
- The available funds and subsidies are also clearly marked and shown in detail on the portal for easy access to all citizens. Every single state and central welfare scheme can easily be accessed on the portal by administrators at any point.
- All necessary updates and changes are also constantly modified on the portal, keeping it up to date.
Benefits of the DBT scheme
The following are the key benefits of the DBT scheme:
- The DBT scheme prevents fraud. The Government sends the funds straight to the beneficiaries’ account, which removes the possibility of fraud through a middleman.
- The beneficiaries can be recognized with the use of their Aadhaar number. Because Aadhaar is a universal ID, the Government can easily verify the beneficiaries using their Aadhaar details.
- DBT promotes accountability in subsidy distribution. As a result, it aids in the elimination of inconsistency and delays in payments.
- DBT aids in the distribution of subsidies to deserving applicants living below the poverty level. It helps the Government reach out to the intended beneficiaries with ease.
- The scheme eliminates pilferage in the distribution of money and reduces the misuse of public funds.
- DBT is a powerful transaction and settlement technology that works with multiple organizations.
- DBT has proven to be an effective technique for connecting with people to distribute relief funds.
Pre-requisites for DBT
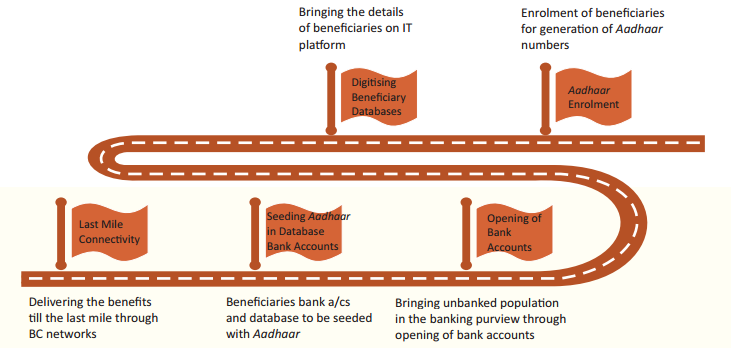
- Identification of beneficiaries and digitisation of beneficiary database
- Opening of bank accounts
- Aadhaar enrolment
- Seeding of Aadhaar in beneficiary database and bank accounts
- Last mile connectivity/service delivery
Key Enablers for DBT
The key success factors or enablers for an efficacious Implementation of DBT are:
JAM Trinity
- DBT by leveraging the JAM (Jan Dhan, Aadhaar and Mobiles) trinity and the technological prowess offers to drastically improve the benefit delivery system in the country.
- The JAM Trinity will enable this novel system to transfer benefits in a leakage-proof, well targeted, cashless and timely manner.
Business Correspondents (BC) Infrastructure
- BC is presently authorised to offer services such as cash transactions where the bank does not have a branch.
- As per census 2011, there are 23,333 villages with population above 5,000 and 1,19,761 villages above 2,000 populations. However, there are only 11,224 villages in the country with population above 5,000 which have a bank branch.
- Business Correspondents/ Bank Mitras will have a vital role in operationalising the programme and ensuring the last mile connectivity. The strong presence of BCs will ensure that payments are disbursed to the beneficiaries on time, at their doorstep and of full value.
Payments Bank
- A payments bank is like any other bank, but operating on a smaller scale, without involving any credit risk.
- It can carry out most banking operations and enable transfers and remittances through a mobile phone but cannot advance loans or issue credit cards.
- With payments banks, RBI seeks to increase the penetration level of financial services in the remote areas of the country.
Mobile money
- Mobile money is a fast-moving way of payment in the country and could be helpful in providing solution to last-mile issues for better accessibility of DBT.
- There is a need to develop a comprehensive eco-system for carrying out cashless transactions over mobile platforms using Aadhaar as identifiers. This will revolutionize the drive for financial inclusion.
Direct Benefit Transmission is Seeded in Major Central Schemes:
Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (Mahatma Gandhi NREGA):
- LPG Direct Benefit Transfer
- PM Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN)
- Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana
- Pradhan Mantri Gramin Awas Yojana (PMAY-G)
How successful has the Central Government been in bringing more subsidies under DBT?
- The first phase of DBT was initiated in 43 districts on January 1, 2013 and 78 districts were later added across 27 schemes pertaining to scholarships, women, child and labour welfare. It was further expanded across the country on December 12, 2014.
- In the current fiscal year, 312 schemes, including key subsidies being run by 54 Central Government Ministries and Departments, are part of DBT.
- The Public Distribution Scheme (PDS) saw the maximum gains with deletion of 3.99 crore duplicate and fake/ non-existent ration cards (between 2013 and 2020) and which resulted in an estimated saving of over Rs 1 lakh crore.
- MGNREGS saw 10 per cent savings on wages on account of deletion of duplicate, fake/ non-existent, ineligible beneficiaries. That apart, 4.11 crore duplicate, fake/ non-existent, inactive LPG connections have been eliminated.
Have State Governments also embraced DBT for distributing subsidies?
- All the 28 States and 9 Union Territories have adopted DBT for distributing various welfare initiatives, including subsidies.
- The Centre also releases rankings on DBT where Haryana is number one. This northern State has 151 schemes, including some Centrally Sponsored Schemes (for which both Centre and States contribute in a ratio), under DBT.
- In Tamil Nadu, 108 schemes are covered under DBT.
Wrapping it up
- Direct Transfer Benefit (DBT) has helped to reduce subsidy leakages and associated delays. These occurred due to fund distribution through various channels and multi-steps.
- The malpractices in diversion and duplication of funds owed to its flow in a multi hierarchy of administrative offices until it reached the end beneficiary.
- The GOI re-engineered the existing system for the faster and right flow of funds in welfare schemes.
https://newsonair.gov.in/Spotlight.aspx#

KAZIRANGA NATIONAL PARK
Context
- President Draupadi Murmu inaugurated the Gaj Utsav -2023 at the Kaziranga national park.
Kaziranga National Park: Key Facts
About
Rhino Population
Tiger Reserve
- Kaziranga National Park was declared a Tiger Reserve in 2006. It has the highest density of tigers in the world.
Other animals
Important Bird Area
Biodiversity Hotspot
- Located on the edge of the Eastern Himalaya biodiversity hotspot, the park combines high species diversity and visibility.
- Kaziranga is one of the largest tracts of protected land in the sub-Himalayan belt, and due to the presence of highly diverse and visible species, has been described as a "biodiversity hotspot".
Rivers
- The park area is circumscribed by the Brahmaputra River, which forms the northern and eastern boundaries, and the Mora Diphlu, which forms the southern boundary. Other notable rivers within the park are the Diphluand Mora Dhansiri.
Soil
- Kaziranga has flat expanses of fertile, alluvial soil, formed by erosion and silt deposition by the River Brahmaputra.
Ecoregions
Big Five
- The Indian rhinoceros, royal Bengal tiger, Asian elephant, wild water buffalo and swamp deer are collectively known as 'Big Five' of Kaziranga.
Migratory Birds and other
Vultures
Snake
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=President-Droupadi-Murmu-inaugurates-Gaj-Utsav-at-Kaziranga-in-Assam&id=458940

WORLD HEALTH DAY
Context
- Every year this day is organised on 7th April to coincide with the setting up of the World Health Organisation, WHO in 1948.
Details
- April 7th is marked as World Health Day, to commemorate the foundation of the World Health Organization (WHO) in 1948.
- The theme this year is Health for All.
- In 1948, the WHO held the First World Health Assembly.
- This year the world health body is observing its 75th anniversary.
- The World Health Day is held to mark WHO's founding and is seen as an opportunity by the organization to draw worldwide attention to a subject of major importance to global health each year.
- The WHO organizes international, regional and local events on the Day related to a particular theme.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=World-Health-Day-being-celebrated-today&id=458952

ALULA DECLARATION
Context
- Two official delegations from the United Arab Emirates and the State of Qatar held their fourth joint meeting in the UAE capital, Abu Dhabi, to follow up on the implementation of the "AlUla Declaration."
About
- The AlUla Declaration, which was signed on January 5, 2021, marked the conclusion of the Gulf Cooperation Council summit held in AlUla, Saudi Arabia.
- The declaration resolved the dispute with Qatar and called for unity and the strengthening of relations among GCC countries.
- It also affirmed the GCC member states' commitment to achieving coordination and integration in all fields to eventually form a union of states.
READ: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/gulf-cooperation-council-gcc
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Review-meeting-of--AlUla-Declaration-held-at-Abu-Dhabi&id=458916
BARREN MASSACRE
Context
- Several protest marches were taken out and programmes organised in Bangladesh to mark the 33rd anniversary of the Baren Massacre.
About
- The Baren Township conflict also known as the Baren Uprising was an armed conflict that took place between ethnic Uyghur militants fighting for East Turkestan independence and Chinese government forces in 1990 between 5 April and 10 April in the township of Baren.
- On 5 April 1990, the Chinese government brutally quelled an uprising by the Uyghurs which took place at Akto County, Kizilsu Kirghiz prefecture. Several Uyghurs were killed in the government operation. Uyghurs call it the ‘Baren Massacre’.

https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Bangladesh%3a-Protests-organised-on-the-33rd-anniversary-of-Baren-Massacre-of-Uyghurs-in-China&id=458932






