SPOTLIGHT| Aditya L1 – India's First Solar Observatory Mission

Context
- India’s journey towards the sun began today as the maiden flight mission took off precisely at 11. 50 am at the Sathish Dhawan Space Centre Sriharikota.
Key Details:
- The space agency's Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC) carried out the operation.
- The spacecraft moving to L1 point has now moved from its previous orbit of 282 by 40,225 km to 245 by 22,459 km around Earth.
- The satellite will undergo four Earth-bound orbital manoeuvres before placing in the transfer orbit towards the Lagrange point L1 in 125 days.
- The third Earth-bound manoeuvre is scheduled for 10th September at 2.30 a.m.
- Aditya L1 mission will provide information on the Solar corona and conduct in-situ observations of the solar wind at L1 point which is about 1.5 million kilometers away from Earth.
- The Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle C57 successfully launched the Aditya L1 spacecraft on 2nd September.
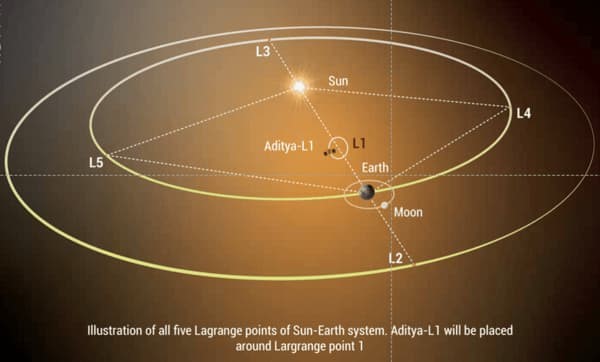
About Aditya- L1 Mission:
| Aditya's L1 mission is to study the solar winds and the sun's atmosphere. It carries seven payloads to observe the photosphere, chromosphere, and the outermost layers of the Sun, the Corona. |
- It will carry seven payloads to observe the photosphere, chromosphere, and the outermost layers of the Sun namely the Corona.
- This will help us understand the problems of coronal heating. Coronal mass ejection, pre-flare and flare activities, dynamics of weather and the study of the propagation of particles and fields in the interplanetary medium.
- Lagrange points are named in honor of Italian-French mathematician Joseph-Louis Lagrange. Of the five Lagrange points, three are unstable and two are stable.
- The unstable Lagrange points – labeled L1, L2 and L3 – lie along the line connecting the two large masses.
- The Indian Space Research Organisation will be on par with NASA, the European Space Agency, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency and the Chinese Academy of Sciences which have launched Solar observation missions.

The major science objectives of Aditya-L1's mission are:
- Study of Solar upper atmospheric (chromosphere and corona) dynamics.
- Study of chromospheric and coronal heating, physics of the partially ionized plasma, initiation of the coronal mass ejections, and flares.
- Observe the in-situ particle and plasma environment providing data for the study of particle dynamics from the Sun.
- Physics of solar corona and its heating mechanism.
- Diagnostics of the coronal and coronal loops plasma: Temperature, velocity and density.
- Development, dynamics, and origin of CMEs.
- Identify the sequence of processes that occur at multiple layers (chromosphere, base and extended corona) which eventually leads to solar eruptive events.
- Magnetic field topology and magnetic field measurements in the solar corona.
- Drivers for space weather (origin, composition and dynamics of solar wind)
Payloads of Aditya L1:
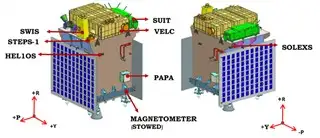
The instruments of Aditya-L1 are tuned to observe the solar atmosphere mainly the chromosphere and corona. In-situ instruments will observe the local environment at L1. There are a total of seven payloads on-board with four of them carrying out remote sensing of the Sun and three of them carrying in-situ observation.
|
Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC)
|
- Corona/Imaging & Spectroscopy.
|
|
Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT)
|
- Photosphere and Chromosphere Imaging- Narrow & Broadband.
|
|
Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer (SoLEXS)
|
- Soft X-ray spectrometer: Sun-as-a-star observation.
|
|
High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer (HEL1OS)
|
- Hard X-ray spectrometer: Sun-as-a-star observation.
|
|
Aditya Solar Wind Particle Experiment (ASPEX)
|
- Solar wind/Particle Analyzer Protons and heavier Ions with directions.
|
|
Plasma Analyser Package for Aditya (PAPA)
|
- Solar wind/Particle Analyzer Electrons and heavier Ions with directions
|
|
Advanced Tri-axial High-Resolution Digital Magnetometers
|
- In-situ magnetic field (Bx, By and Bz).
|
Significance of the Mission:
Advancement in Solar Physics:
- Aditya-L1's observations and data will contribute to advancements in solar physics, plasma dynamics, and magnetism, enriching our understanding of stellar astrophysics.
Space Exploration Endeavors:
- The mission sets a precedent for India's space exploration initiatives, enabling future solar and space-based research missions.
Coronal Heating and Eruption Mechanisms:
- Aditya-L1 aims to uncover the mechanisms behind coronal heating, coronal mass ejections, and solar flares, providing insights into the complex interactions within the Sun's atmosphere.
Space Weather Prediction:
- By studying space weather impacts and solar events, the mission intends to enhance space weather prediction models, offering the potential to mitigate their effects on Earth's technological infrastructure.
Solar Wind and Magnetic Field Studies:
- The mission will contribute to understanding the solar wind's composition, dynamics, and magnetic field topology, shedding light on their roles in driving space weather.
Limitations of the Mission:
Orbital Perturbations:
- While Lagrange points offer stability, they are not completely free from disturbances. Orbital perturbations from other celestial bodies and non-gravitational forces can affect objects stationed at these points.
Energy Requirements:
- Positioning and maintaining objects at Lagrange points require careful fuel management due to the need to counteract gravitational influences and maintain desired orbits.
Position and Characteristics
|
L1: Located on the line connecting the two massive bodies, closer to the larger body. Objects placed at L1 move in sync with the Earth's orbital motion, making it suitable for space observatories like the James Webb Space Telescope.
|
|
L2: On the line connecting the two bodies, beyond the larger body. Objects at L2 enjoy a constant view of the night sky and are used for solar and Earth observations.
|
|
L3: Opposite to the larger body, forming a straight line with the two massive bodies. It's unstable, making objects there prone to perturbations and drift.
|
|
L4 and L5: Form equilateral triangles with the two massive bodies. Objects at these points tend to accumulate over time due to gravitational forces, forming regions known as Trojan asteroids or Lagrange point clouds.
|
Closing thoughts
- The Aditya-L1 mission represents India's foray into solar research and exploration, promising valuable insights into the Sun's intricate dynamics and their impacts on our technological environment.
- By studying the Sun's upper atmospheric behavior, space weather phenomena, and solar particle interactions, Aditya-L1 aims to unravel longstanding mysteries while contributing to global scientific knowledge and the advancement of space technology.
https://newsonair.gov.in/Main-News-Details.aspx?id=467280#:~:text=Aditya%20L1%20mission%20will%20provide,L1%20spacecraft%20on%202nd%20September.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=India%E2%80%99s-first-solar-observatory-mission%2C-Aditya-L1%2C-successfully-launched-from-Sriharikota-Space-Centre&id=467119
https://newsonair.com/2023/09/02/aditya-l1-indias-first-space-mission-to-study-sun-to-be-launched-from-sriharikota-this-morning/
https://www.isro.gov.in/Aditya_L1.html
.jpg)
ASEAN-India Summit
Context
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi will embark upon a two-day visit to Indonesia to attend the 20th ASEAN-India Summit and 18th East Asia Summit.
Details
- The two Summits will be hosted in Jakarta by Indonesia the current Chair of ASEAN.
- The 20th ASEAN-India Summit is the first one after the elevation of the India-ASEAN relationship to a comprehensive strategic partnership last year.
- ASEAN-India relations and provide them with further direction.
- India's relations with ASEAN are a Central Pillar of Act-East Policy as well as India's vision of the wider Indo-Pacific.
- India is the founding member of the East Asia Summit.
About ASEAN:
- The Association of Southeast Asian Nations, or ASEAN, was established on 8 August 1967 in Bangkok, Thailand, with the signing of the ASEAN Declaration (Bangkok Declaration) by the Founding Fathers of ASEAN, namely Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore and Thailand.
- Brunei Darussalam then joined on 7 January 1984, Vietnam on 28 July 1995, Lao PDR and Myanmar on 23 July 1997, and Cambodia on 30 April 1999, making up what is today the ten Member States of ASEAN.
- The motto of ASEAN is “One Vision, One Identity, One Community”.
- 8th August is observed as ASEAN Day. ASEAN Secretariat – Indonesia, Jakarta.
About East Asia Summit:
|
About
|
- The East Asia Summit (EAS) is a regional forum held annually by leaders of, initially, 16 countries in the East Asian, Southeast Asian, South Asian and Oceanian regions, based on the ASEAN Plus Six mechanism.
|
|
Purpose
|
- It is the only leader-led forum at which all key partners meet to discuss political, security and economic challenges facing the Indo-Pacific, and has an important role to play in advancing closer regional cooperation.
|
|
First Summit
|
- The first summit was held in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia on 14 December 2005.
|
|
Six priority areas of cooperation
|
- Environment and energy, education, finance, global health issues and pandemic diseases, natural disaster management, and ASEAN Connectivity.
|
|
The theme of the 20th summit
|
- ASEAN Matters: Epicentrum of Growth.
|
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=PM-Modi-to-attend-ASEAN-India-Summit-and-East-Asia-Summit-in-Jakarta-on-Thursday&id=467333

Country's first solar city
Context
- In Madhya Pradesh, the country's first solar city Sanchi will be inaugurated today by state Chief Minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan.

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement is not intended
Details:
- Annually about 13 thousand 747 tonnes of carbon dioxide emissions will be reduced in Sanchi Solar City, which is equivalent to more than 2 lakh adult trees.
- Along with this, there will be a saving of more than 7 crore rupees annually in the energy-related expenditure of the government and the citizens.
- It is noteworthy that Prime Minister Narendra Modi has set a target of developing a solar city in every state of the country by 2070.
- An effort has also been made to attract tourism by reducing environmental pollution through eco-friendly facilities in Sanchi. Battery-operated e-rickshaws and garbage vehicles will also run in the city. E-vehicle charging stations have also been installed.
About Sanchi, a global heritage site
- Sanchi, also spelled Sanci, historic site, in west-central Madhya Pradesh state, central India.
- It lies in an upland plateau region, just west of the Betwa River and about 5 miles (8 km) southwest of Vidisha.
- On a flat-topped sandstone hill that rises some 300 feet (90 meters) above the surrounding country stands India’s best-preserved group of Buddhist monuments, collectively designated a UNESCO World Heritage site in 1989.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Country%26%2339%3bs-first-solar-city-to-be-inaugurated-in-Sanchi-of-Madhya-Pradesh-today&id=467334

Black Sea Grain deal
Context
- Russian President Vladimir Putin has refused to restore the Black Sea Grain deal.
Details
- Turkish President Tayyip Erdogan on Monday (September 4) said he was confident Russia would “soon” revive the Black Sea grain deal, which was signed in July 2022 and assured safe passage to ships carrying grain from Ukraine. In July this year, Russia refused to extend the deal.
About the Black Sea Grain deal:
|
Negotiated
|
- The Black Sea grain initiative was negotiated in July 2022 between Turkey, the UN and Russia as a way of ensuring that Ukraine, one of the breadbaskets of the world, could ensure that its grain could leave its southern ports via the Bosphorus.
|
|
Trade
|
- The grain could not be exported in the quantities required using the alternative methods of road or rail through Poland or by canal and river through Romania.
|
|
Member
|
- Turkey was involved due to the close relationship between its president, Recep Tayyip Erdoğan, and Vladimir Putin and because under the Montreux convention signed in 1936, it oversees maritime traffic in the Bosphorus and Dardanelles straits.
|
|
Did it succeed?
|
- Despite the acute lack of trust, 33m tonnes of grain left Ukraine’s ports in the year to July. The UK says about 61% of that has gone to low- and middle-income countries, and 65% of wheat alone.
- The World Food Programme bought about 750,000 tonnes of Ukrainian grain that was shipped immediately to places such as Afghanistan, Ethiopia, Somalia and Sudan.
- Partly as a result of this, the price of grain stabilised at $800 (£620) per tonne, down from a high of $1,360.
|
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Russian-President-Vladimir-Putin-refuses-to-restore-the-Black-Sea-Grain-deal&id=467293

B20 Summit 2023
Context
- In a thought-provoking discussion on Akashvani's Spotlight program, experts shed light on the significant implications of the B20 Summit 2023, hosted by India under the G20 umbrella.

Details:
- The B20 Summit, organized by the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) ahead of the G20 Summit, bears the theme 'Responsible, Accelerated, Innovative, Sustainable, and Equitable.'
- Jiten Kumar Jain emphasized that this is a pivotal moment for Indian businesses and the IT industry.
- India's remarkable growth, technology leadership, and a surge in unicorn startups have positioned it as a global leader.
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi's insights into upcoming policies for cryptocurrencies and AI signal India's commitment to shaping the future of these technologies.
About the B-20 Summit:
|
About
|
- The Business 20 (B20) is the official G20 dialogue forum with the global business community.
|
|
Established
|
- Established in 2010, B20 is among the most prominent Engagement Groups in G20, with companies and business organizations as participants.
|
|
Theme
|
- Its theme is A.I.S.E – Responsible, Accelerated, Innovative, Sustainable and Equitable Businesses.
- It is being attended by over 1,500 delegates from about 55 countries.
|
|
Role
|
- B20 Summit India brings policymakers, business leaders and experts from across the world to deliberate and discuss the B20 India Communique.
- The B20 India Communique includes 54 recommendations and 172 policy actions for submission to the G20.
|
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=B20-Summit-2023%3a-India%26%2339%3bs-Vision-for-Ethical-AI-and-Cryptocurrency-Regulation&id=467251










