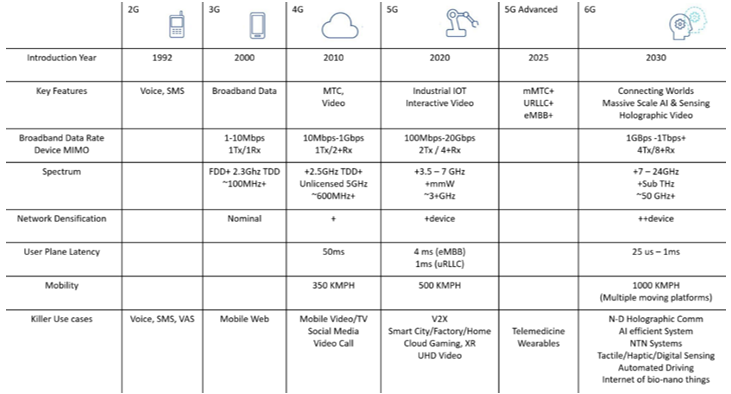
PERSPECTIVE: INDIA'S 6G VISION

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi has praised the rollout of 5G telecom networks in the country and the progress of the technology sector, calling them crucial for India’s transition to a developed economy.
Details:
- At the India Mobile Congress, the Prime Minister celebrated the nation's progress, emphasizing that India's momentum didn't stop at the success of 5G and took on the work of taking it to every individual.
- He underlined that 5G technology has helped India improve its ranking in terms of broadband speed to 43rd position from previous rank of 118th position globally.
- He also expressed confidence that India will take the lead with 6G technology.
- He recalled that From being a mobile phone importer, India has now become the second-largest mobile manufacturer in the world.
- The Prime Minister said that in the development of digital technology, India is behind no developed nation.

INTRODUCTION:
- India is already moving beyond the deployment of 5G technology to create and install its faster and superior successor: the sixth generation of telecom networks, or 6G.
- TIG-6G, the Technology Innovation Group on 6G, has developed the Bharat 6G Vision, a strategy to create 6G technology in India by 2030.
- The objective of this vision is to create and deploy 6G network technologies that provide secure, intelligent, and pervasive connectivity, enabling people all over the world to live better lives.
- The Vision statement emphasises India's commitment to socioeconomic prosperity, as well as the potential benefits of India’s pioneering 6G technology, which enables ultra-low latency and speeds of up to 1 terabit per second. This might be a game changer for the Indian economy.
| The Bharat 6G Vision is founded on the principles of affordability, sustainability, and ubiquity. It assures that India takes its due place in the world as a leading supplier of modern telecom technology and solutions that are affordable and contribute to the global good. |
Bharat 6G Mission:
- India just introduced 5G, which at its peak can deliver internet speeds of up to 10 gigabits per second; at the same time, 6G promises ultra-low latency with speeds of up to 1 terabit per second.
- In other words, 6G users will be able to download more than 100 films per minute due to 6G's ability to sustain high data speeds of 1 terabit per second.
- In addition, 6G will be able to use cases such as digital twins, holograms, and genuinely immersive extended reality applications, among many other characteristics.
- It is regarded as the first technology to provide integration between terrestrial and non-terrestrial networks, implying that a single device will be capable of operating across several technologies.
- It will connect billions of machines and gadgets, ushering in a significant shift in bringing the virtual and real worlds together.
| Several countries see India as a promising destination for investments in the 6G technology sector, owing to the country's large market size, the potential for a significant return on investment, and favourable government policies allowing for 100% Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in the telecom sector via the automatic route. |
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU):
- The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has accepted the 6G Vision Framework. India, through the Department of Telecommunications and the Ministry of Communications, played an important role in developing the Framework.
- 6G standardization has successfully adopted ubiquitous connectivity, ubiquitous intelligence, and sustainability as essential components of 6G Technology, which has also improved India's standing in the global telecommunications industry.
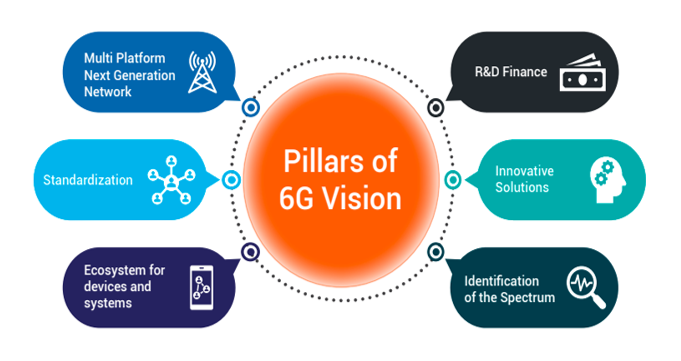
Objectives:
- To enable India to become a major provider of IP, goods, and services for cost-effective 5G, 6G, and other telecom solutions in the future.
- To implement 6G technologies by 2030 so that India can use them as a powerful force multiplier.
- To encourage and support Indian participation in organisations that develop standards.
- To form alliances with other international technological alliances and organisations as well as comparable 6G Global Alliances.
- To take into account India's priorities for contribution to 6G and other upcoming global technological standards, deployments, products, operations, and services.
- To support the ecosystem for, among other things, end-to-end solutions, use cases, pilots, research, design, prototyping, development, proof of concept testing, IPR creation, field testing, security, and manufacturing of telecom goods.
- To research, suggest, and enable the inclusion of national standards in Indian and international standardisation organisations.
- To develop suggestions for improving India's readiness for the implementation of the Bharat 6G Vision.
Potential 6G Use cases:
Healthcare:
- 6G will enable hospitals to access patients on demand and in an emergency. Future ambulances will be fully AI-enabled and connected to the infrastructure.
- As a result, Hospital-to-Home (H2H) will be implemented as a mobile hospital on an intelligent vehicle platform with little reliance on hospitals, including doctors and nurses.
Agriculture:
Smart Agriculture using 6G-IoT and AI
- To create an intelligent predictive system using IoT and AI/ML approaches to anticipate yield, irrigation schedule, pesticide schedule, and crop health information.
Defence & Internal Security:
Battlefield Surveillance
- With the integration of sensors, drones, and satellites, an unmanned surveillance grid mapping every inch of the border (high-accuracy localisation) will improve operational efficiency by delivering real-time inputs to commanders in field formations.
Security protocol
- In collaboration with academia and industry, a new protocol for authentication and key management in 6G may be created.
Education
- There are numerous prospects in the Education sector, such as remote learning. However, another major aspect is an effective infrastructure for exam administration. 6G will allow video to transfer at such a high speed and adjacent edge processing will aid in compliance management. All major examinations, including JEE and NEET, can use 6G in exam administration.
Metaverse
- Metaverse requires a real-time experience between what a person does and what their avatar performs, with no lag, hence very low latency. This necessitates super-fast, super-reliable, and everywhere network connectivity. Additionally, support the transition from 2D to 3D, holographic displays as processing power advances.

Government Initiatives:
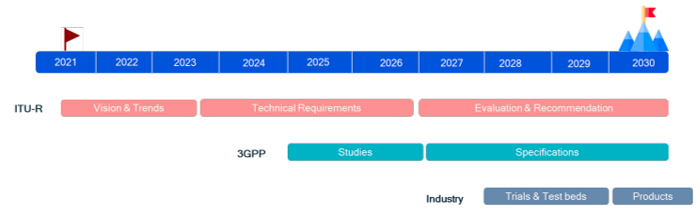
Roadmap for 6G Development (Tentative)
- The Mission can be divided into two phases-Phase 1 from 2023-2025 (2 years) and Phase 2 from 2025-2030 (5 years). The government has spent US$ 27.17 million (Rs. 2,240 million) on a new 6G Test Bed that was created.
| India's core digital economy expanded from 5.4% of GVA in 2014 to 8.5% in 2019, with a digitally dependent economy predicted to be about 22% of GDP in 2019. India's digital economy developed 2.4 times faster than the Indian GDP, with strong forward connections to non-digital sectors. |
Rationale behind the early approach towards 6G:
Assuming Leadership in Wireless Data Usage:
- The government is committed to elevating India's standing in wireless data usage by actively encouraging local manufacturing of telecom equipment.
- This approach aims to foster self-reliance, support Indian companies, and empower engineers to actively contribute to international discussions around the standardization of 6G technologies.
Avoiding Delays and Global Competitiveness:
- Learning from the delayed adoption of 5G, the government is determined to avoid falling behind other nations in rolling out 6G.
- By taking an early approach, India seeks to stay competitive on the global stage, ensuring that it is at the forefront of technological advancements in the telecommunications sector.
Addressing the Surge in Data Demand:
- Recognizing the surge in demand for data services and the limitations of lower frequencies in existing 4G networks, the government sees the early adoption of 6G as a strategic move to match and fulfill the escalating demand for data traffic effectively.
Promoting Research and Development (R&D):
- To drive innovation in 6G technologies, the government is committed to supporting research and development. This involves leveraging the expertise and talent in both academia and private companies, fostering an environment conducive to groundbreaking advancements in the field.
Achieving Connectivity Goals:
- 6G technology is seen as a critical enabler in achieving ambitious connectivity goals set by the government.
- This includes ensuring that every individual has access to a minimum of 100 Mbps broadband, providing each gram panchayat access to half a terabit per second of connectivity, and installing over 50 million internet devices across the nation at a density of 13 per square kilometer.
- This proactive approach underscores the government's commitment to comprehensive and widespread digital connectivity.
.jpg)
Conclusion
- India's pursuit of 6G technology is a key step towards becoming a digitally enabled society. India, with its enormous population and fast-expanding digital infrastructure, stands to benefit greatly from the development and implementation of 6G technology.
- However, the widespread adoption of 6G in India will necessitate major investment in research and development, as well as infrastructure modifications to accommodate the new technology.
- Collaborative efforts between the government and industry leaders are critical to maintaining India's position as a technical innovator and preparing the country for the arrival of 6G technology.
- By implementing suitable investments and policies, India can continue to lead the global technology scene and benefit from the possibilities of 6G for many years to come.
CITATIONS:
https://sansadtv.nic.in/show_type/perspective
https://www.ibef.org/blogs/bharat-6g-vision
https://www.rcrwireless.com/20230323/network-infrastructure/india-government-unveils-national-6g-vision
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1935884
https://epaper.thehindu.com/ccidist-ws/th/th_delhi/issues/31037/OPS/GI7B2JT6H.1+G9CB2K5RR.1.html
https://vikaspedia.in/e-governance/mobile-governance/bharat-6g







