



Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: THE HINDU
Prime Minister Narendra Modi's official visit to Oman is expected to conclude with the signing of the Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA).
Ancient Trade
Archaeological evidence shows maritime trade dating back 5,000 years to the Indus Valley Civilisation, connecting ports like Lothal to ancient Omani regions known as Magan.
Medieval & Colonial Eras
In the 18th century, Tipu Sultan of Mysore established diplomatic missions to Oman. Omani rulers later collaborated with Indian powers like the Marathas to counter European dominance in the Indian Ocean.
Establishment of Diplomatic Ties
Formal diplomatic relations were established in 1955. India opened a consulate in Muscat, which was later upgraded to an embassy in 1971. Oman established its embassy in New Delhi in 1972.
The relationship was elevated to a Strategic Partnership in 2008 during the visit of the then Prime Minister of India to Oman.
 Why is Oman Important to India?
Why is Oman Important to India?
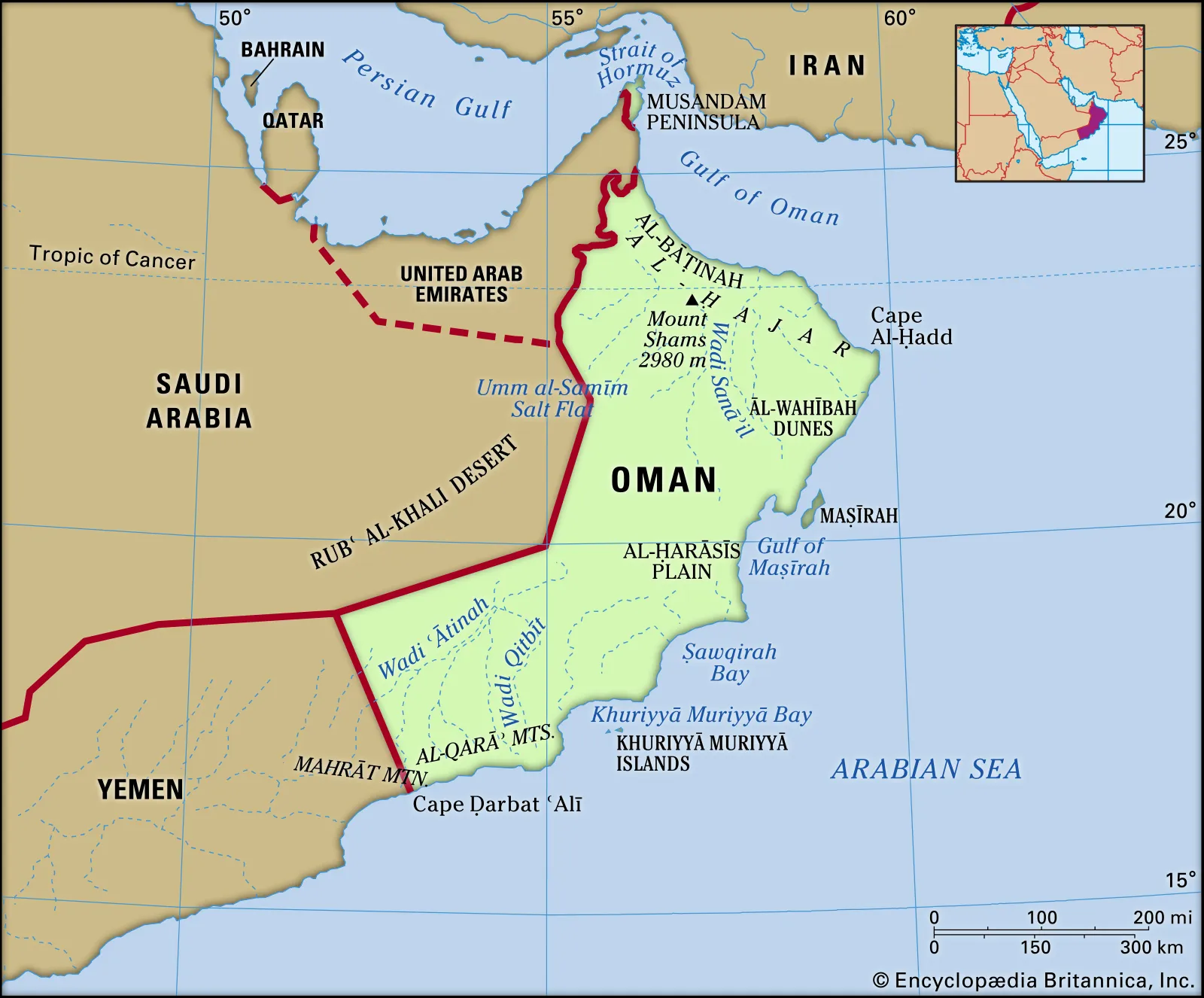
Strategic Location: Oman's strategic location at the Strait of Hormuz and the Persian Gulf, crucial for global oil trade, offers India a vital point for monitoring maritime activities in the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean.
Defence and Security Cooperation: Oman is the first Gulf country with which India conducts joint military exercises across all three services—Army (Al Najah), Navy (Naseem al-Bahr), and Air Force (Eastern Bridge).
Access to Duqm Port: A 2018 agreement grants the Indian Navy access to Oman's deep-sea port of Duqm for logistics and maintenance, expanding India's operational reach and maritime surveillance in the Western Indian Ocean.
Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA): In December 2025, the Cabinet approved the India-Oman CEPA, making Oman the second Gulf nation to sign such a deal after the UAE.
Energy Security: Oman is a reliable source of energy for India's growing economy, supplying crude oil and LNG.
Gateway to the GCC: Oman is a key partner for India in regional bodies, including the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), the Arab League, and the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA).
Large Indian Diaspora: Approximately 6.7 lakh Indians live in Oman, serving as a bridge for people-to-people diplomacy.
Economic Diversification
As Oman seeks to diversify its economy away from hydrocarbons under its 'Vision 2040' plan, India offers a massive market for its non-oil exports and a source of investment and technology in key sectors like manufacturing, logistics, IT, and tourism.
Trade and Investment
The bilateral trade reached $10.61 billion in the fiscal year 2024-25. Indian investments have contributed an estimated $7.5 billion to Oman’s economy over time. (Source: DD NEWS)
Food Security
India is a reliable partner for ensuring Oman's food security, being a major supplier of agricultural products like rice and other food items.
Security and Stability
India's role as a net security provider in the Indian Ocean region contributes to the stability and safety of maritime trade routes, which are vital for Oman's economy.
Skilled Human Resources
Indian expatriate community provides essential skilled and semi-skilled labor that supports various sectors of the Omani economy.
 What are the Challenges in the India-Oman Relations?
What are the Challenges in the India-Oman Relations?
Omanisation Policy Hurdle
Oman's policy to reserve jobs for its citizens ("Omanisation") is the sticking point in finalizing the CEPA. India wants these employment quotas frozen at their current levels to protect opportunities for its large expatriate workforce.
Trade Concentration
Over 70% of India's imports from Oman are oil and petroleum products, making the trade relationship vulnerable to global energy market volatility and limiting diversification.
China's Growing Influence
China is Oman's top oil importer and is expanding its influence through the Belt and Road Initiative, creating a major power competition for strategic space in the Indian Ocean Region.
Regional Instability
Conflicts in West Asia, such as the Houthi attacks on Red Sea shipping, create security concerns and force India to navigate a complex diplomatic path to protect its interests without joining Western military coalitions.
Labor and Diaspora Issues
The "Kafala" labor sponsorship system leaves blue-collar Indian workers vulnerable to exploitation. Ensuring wage protection and safe housing remains an ongoing challenge.
Fast-Track CEPA Implementation: Signing and effective implementation of the CEPA to boost trade and investment.
Deepen Maritime Cooperation: Move beyond port access to enhance joint patrols, information sharing, and coordinated anti-piracy and HADR (Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief) operations from Duqm.
Focus on Future-Oriented Sectors: Build partnerships in green energy, particularly green hydrogen, where both nations have shown interest. Enhance collaboration in space technology, digital payments, and food security.
Align with Oman Vision 2040: Indian businesses should seek investment opportunities in Oman's priority sectors like logistics, tourism, fisheries, and mining to align with its economic diversification goals.
Enhance People-to-People Connect: Promote greater collaboration in education, health, and skill development to further strengthen the deep-rooted cultural ties.
Connectivity & Digital: Strengthening port logistics (Sohar, Duqm) and expanding India's Digital Public Infrastructure (RuPay launch, UPI discussions) for seamless remittances.
The India-Oman relationship, a model of stability and trust, has evolved from a trading partnership into a comprehensive strategic alliance, driven by shared interests in security and economy.
Source: THE HINDU
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Which of the following countries does not share a land border with Oman? A) Yemen B) Saudi Arabia C) United Arab Emirates D) Qatar Answer: D Explanation: Oman shares land borders with the United Arab Emirates (northwest), Saudi Arabia (west), and Yemen (southwest). |
Oman is strategically crucial due to its location at the mouth of the Strait of Hormuz, overlooking key global shipping lanes. It provides India with access to the Duqm Port, enhancing India's naval presence in the Indian Ocean Region and acting as a vital pillar of India's West Asia policy.
The three main bilateral exercises are:
- Naseem Al Bahr: A joint naval exercise.
- Al Nagah: A joint army exercise.
- Eastern Bridge: A joint air force exercise.
The key challenges include navigating regional instability in West Asia, Oman's economic vulnerability due to its dependence on oil revenues, and balancing the growing economic influence of China in Oman, particularly through its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved