



Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: INDIAN EXPRESS
German Chancellor Friedrich Merz and PM Narendra Modi met in Gandhinagar, Gujarat, signing 19 pacts, including roadmaps for defence industrial cooperation and higher education.
|
Read all about: INDIA GERMANY RELATIONS l INDIA-GERMANY RELATIONS l INDIA-GERMANY RELATIONS EXPLAINED |
Joint Declaration on:
Announcements
India-Germany Strategic Partnership
The India-Germany Partnership is anchored by shared democratic values, a commitment to a rules-based international order, and strong economic and technological ties, crucial for addressing global challenges.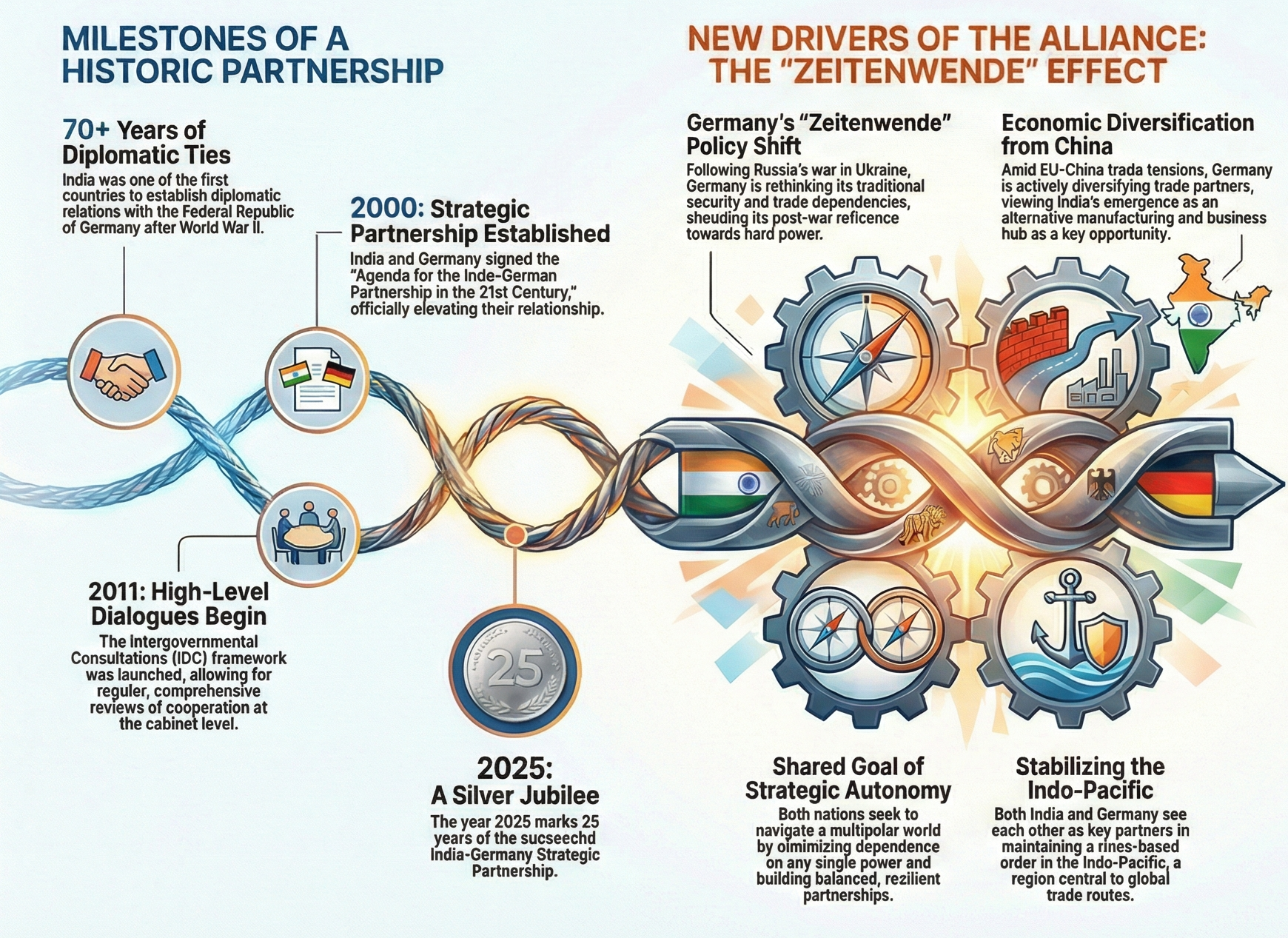
Evolution of the Bilateral Relationship
1951: India was one of the first countries to establish diplomatic relations with the Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany) after World War II.
Post-1990: German reunification and India's economic liberalization in 1991 opened new avenues for economic engagement.
2001: Relationship was officially elevated to a 'Strategic Partnership'.
2006: A Defence Cooperation Agreement was signed.
2011: Launch of Inter-Governmental Consultations (IGC) elevated the ties further, with both cabinets meeting every two years to coordinate policies.
 Key Pillars of Cooperation
Key Pillars of Cooperation
Economic and Commercial Ties
Bilateral Trade
India-Germany bilateral trade in goods and services surpassed $50 billion in 2024, amounting to over 25% of India’s trade with the EU. Germany was the 8th largest trading partner for India in 2024-25.
(Source: MEA)
German FDI in India
Germany is the 9th largest foreign direct investor in India. Cumulative German FDI from April 2000 to March 2025 was approximately $15.11 billion (Source: Indianembassy).
Key Sectors
Collaboration is strong in machinery, automotive components, chemicals, electronics, renewable energy, and services. Over 2,100 German companies operate in India (Source: Indo-German Chamber of Commerce).
Synergies
Strong alignment between India's 'Make in India' and 'Aatmanirbhar Bharat' initiatives and Germany's world-renowned 'Mittelstand' (SMEs) and 'Industry 4.0' leadership.
Green and Sustainable Development Partnership (GSDP)
Established during the 6th IGC in 2022, this pillar frames the joint approach to tackling climate change and advancing sustainable development.
Financial Commitment: Germany has pledged new and additional development assistance of €10 billion until 2030 to support India's green growth plans.
Key Areas of Focus:
Defence and Security Cooperation
Indo-Pacific Strategy: India is a central pillar in Germany's Indo-Pacific strategy. Germany has increased its presence in the region.
Maritime Security: Both nations share interests in ensuring open and secure sea lanes of communication and upholding international law (UNCLOS).
Defence Industrial Cooperation: Discussions for co-development and co-production of defence equipment, though Germany's strict arms export laws remain a challenge.
Counter-Terrorism: A Joint Working Group on Counter Terrorism actively shares intelligence and coordinates positions.
Multilateral Cooperation
India and Germany are strong proponents of multilateralism and work together to reform global governance institutions.
G4 Nations: Along with Brazil and Japan, India and Germany form the G4, which advocates for the reform of the UN Security Council and mutually supports each other's candidacies for permanent seats.
G20: Both countries coordinate closely within the G20 framework to address global economic, financial, and sustainable development challenges.
Rules-Based Order: A shared commitment to upholding a rules-based international order, democracy, and human rights forms the foundation of their global cooperation.
People-to-People Connect
Indian Diaspora: A vibrant Indian diaspora of over 280,000 people contributes to the German economy and society (Source: MEA).
Education: Germany is the top destination for Indian students, with around 50,000 making them the largest international student group. (Source: German Academic Exchange Service)
Skilled Mobility: The Migration and Mobility Partnership Agreement signed in 2022 aims to facilitate easier access to study, research, and work between the two countries.
Vocational Training: Germany's renowned dual-track vocational training system is a model for India's 'Skill India' mission, with several collaborations in place.
Economic Hurdles
Long-Pending India-EU Free Trade Agreement (FTA) remains a key obstacle to unlocking full economic potential. German businesses in India cite regulatory uncertainty and bureaucratic delays as concerns.
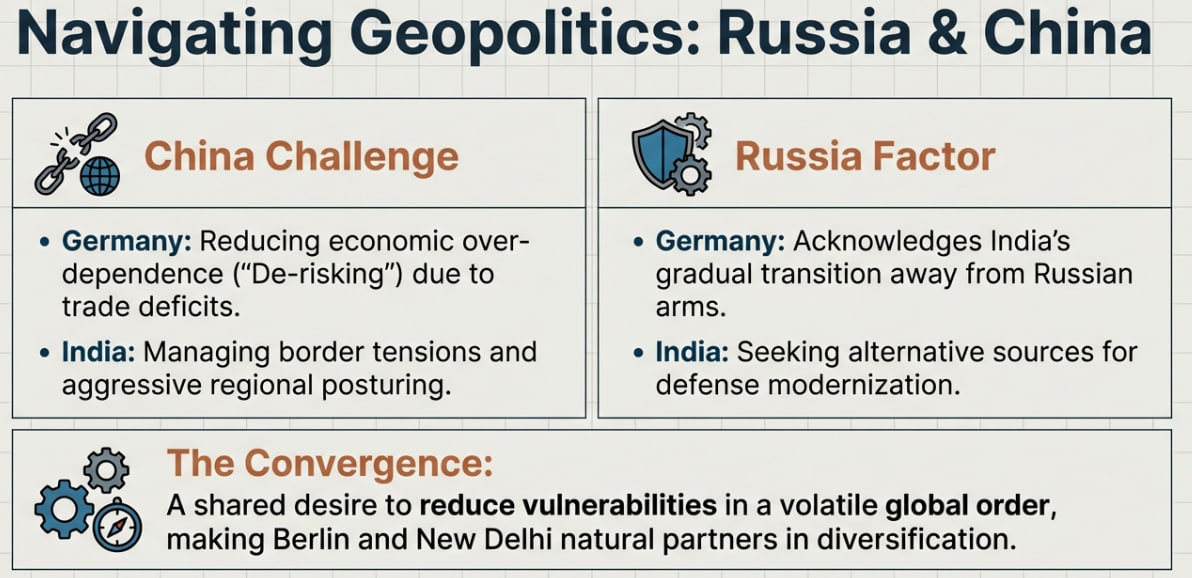
Geopolitical Stances
Russia-Ukraine conflict highlighted differing approaches. While Germany undertook a policy shift ('Zeitenwende') with a strong stance against Russia, India maintained its position of strategic autonomy, calling for dialogue and diplomacy.
Defence Export Controls
Germany's very strict arms export rules often hinder or complicate defense industrial collaboration due to the constraints they impose.
China Factor
While both countries share concerns about China's assertiveness, their approaches differ in tone and intensity, influenced by Germany's deep economic interdependence with China.
 Way Forward
Way Forward
Finalize the India-EU FTA: A successful conclusion of the trade agreement would provide a massive boost to bilateral trade and investment.
Enhance Defence Co-production: Move beyond a buyer-seller relationship to joint R&D, co-development, and co-production of advanced defence platforms, aligning with 'Aatmanirbhar Bharat'.
Lead in Green Technologies: Operationalize the Green Hydrogen Task Force to create resilient supply chains and position India and Germany as global leaders in the green transition.
Streamline Mobility: Effectively implement the Migration and Mobility Partnership to create a seamless talent corridor for students, researchers, and professionals.
Strengthen Indo-Pacific Coordination: Deepen maritime security cooperation and strategic dialogue to contribute to a free, open, and inclusive Indo-Pacific.
Utilize Untapped Opportunities
The India-Germany Strategic Partnership is a mature and vital collaboration founded on mutual economic interests, democratic values, and a shared commitment to a stable, rules-based global order.
Source: INDIAN EXPRESS
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. "The transition from a 'buyer-seller' relationship to a 'co-development' model marks a new era in India-Germany defense ties." Discuss. 150 words |
The India-Germany Strategic Partnership, established in 2000, is a comprehensive framework for cooperation between the two countries. It is built on shared democratic values and covers diverse areas including economy, defence, science and technology, climate change, and people-to-people ties. It is anchored by the unique Inter-Governmental Consultations (IGC), a biennial cabinet-level meeting.
The GSDP is a landmark initiative launched in 2022. Under this partnership, Germany has committed new and additional development assistance of €10 billion until 2030 to support India's climate action goals, such as achieving 500 GW of non-fossil fuel energy capacity. It focuses on renewable energy, sustainable urban development, and climate resilience.
The G4 is a grouping of four countries: India, Germany, Japan, and Brazil. Their primary objective is to mutually support each other's bids for permanent seats on a reformed and expanded United Nations Security Council (UNSC) to make it more representative of 21st-century geopolitical realities.
© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved