Description
GS PAPER III: Security challenges and their management in border areas - linkages of organized crime with terrorism.
Context: 78% companies worldwide expect another Solar Winds-style hack, one of the most large-scale supply chain attacks to date that affected over 18,000 organisations.
- It is noted that an increase in remote work and expansion in usage of cloud and digital technologies could boost cyberattacks.
- Remote workers are harder to secure.
- At least 95% companies perform various assessments of a vendor’s security but still the existing security checks failed to stop the SolarWinds attack.
What is this ‘SolarWinds hack’?
- FireEye called it a state-sponsored attack, although it did not name Russia.
- It said the attack was carried out by a nation “with top-tier offensive capabilities”, and “the attacker primarily sought information related to certain government customers.”
- It also said the methods used by the attackers were novel.
- FireEye named this cyberattack as Campaign UNC2452, was not lmited to the company but had targeted various “public and private organisations around the world”.
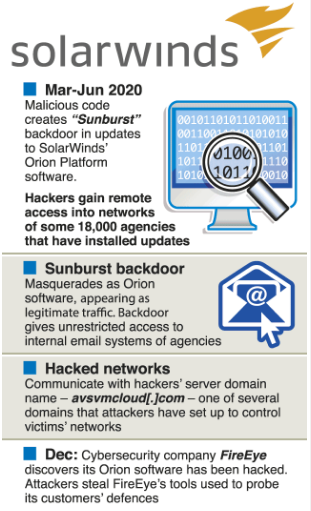


- This is being called a ‘Supply Chain’ attack: Instead of directly attacking the federal government or a private organisation’s network, the hackers target a third-party vendor, which supplies software to them.
What is Hacking?
- Hacking is an unauthorized entry into a network or a computer to steal or manipulate information, data or files.
- The person involved in this process is named as a hacker.
- Computer hacking is done using several types of programs such as Rootkit, Trojan, Keylogger etc.
- Hackers also employ techniques like browser hijacks, spoofing, phishing to capture user’s personal or financial details.
Well-known methods of hacking:
Phishing
- This implies replicating the original website so that the unsuspecting user enters the information like account password, credit card details, which the hacker seizes and misuses.
- The banking websites are the frequent target for this.
Virus
- These are released by the hacker into the files of the website once they enter into it.
- The purpose is to corrupt the information or resources on the website.
UI redress
- In this method the hacker creates a fake user interface and when the user clicks with the intent of going to a certain website, they are directed to another site altogether.
Cookie theft
- Hackers accesses the website using malicious codes and steal cookies which contain confidential information, login passwords etc.
DNS spoofing
- This basically uses the cache data of a website or domain that the user might have forgotten about.
- It then directs the data to another malicious website.
How to guard against hacking?
- Virtual Private Networks (VPN) is a protocol by which corporate networks connect to offsite and remote locations through a point to point tunnel like connectivity.
- Normally security firewalls are placed at multiple levels of the network and security policies are defined at the highest level leading to a near to 100 % security coverage.
- Download software from authorized websites.
- Do not click on random email attachments.
- Scan all types of hard drives before running
- Anti-hacking software.
https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/technology/78-companies-expect-another-solarwinds-style-hack-survey-finds/article34676536.ece?homepage=true