




Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
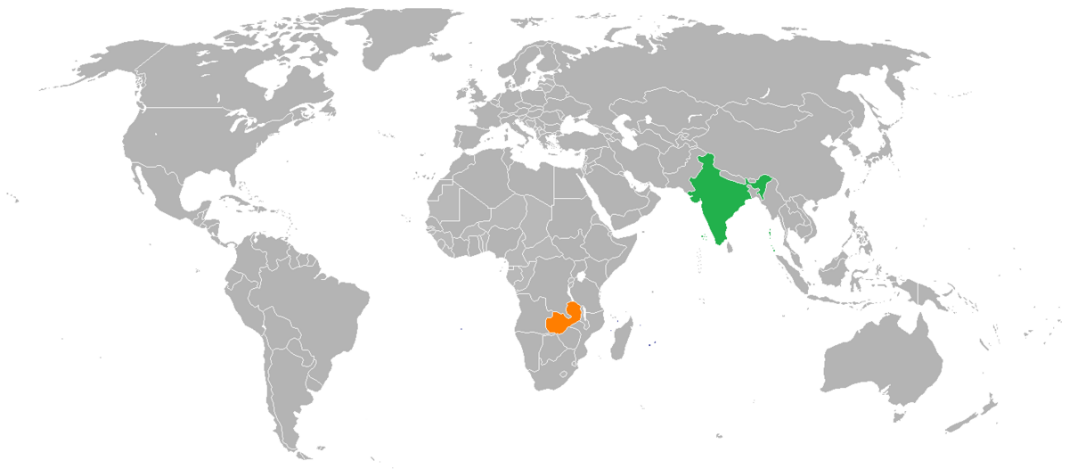
Copper Reserves in Zambia:
India Zambia Joint Working Group (JWG) Meetings:
Copper Demand in India:
India's Presence in Zambia's Copper Sector:
Foreign Investors in Zambia:
Interest from Indian Companies:
Upcoming JWG Meeting:
India-Zambia Relations: Key Points
Political Ties:
Bilateral Visits:
Development Cooperation:
Bilateral Trade:
Cultural Cooperation:
Zambia [Geography Perspective]
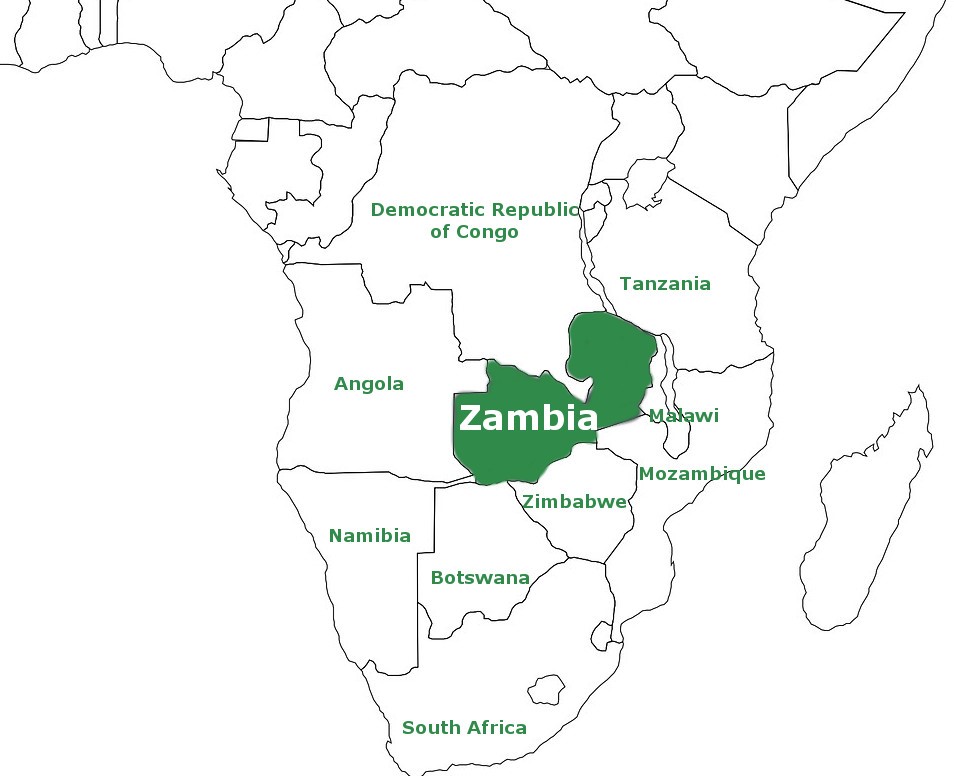
Location and Neighbors:
Capital and Major Cities:
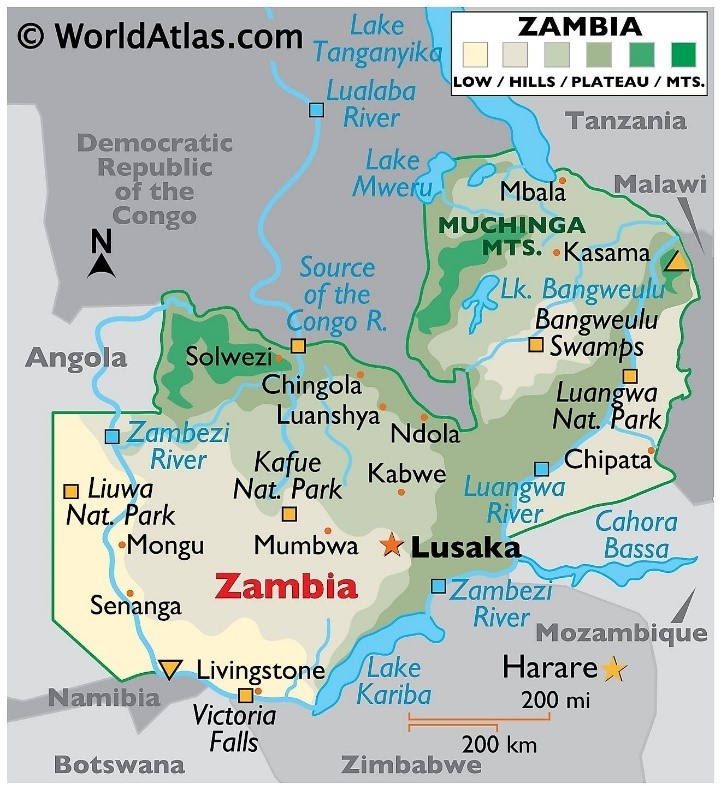
Physical Features:
Climate:
Natural Resources:
National Parks and Wildlife:
Economy:
Victoria Falls:
Political History:
Population and Languages:
Infrastructure:
Health Challenges:
Conclusion:
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Consider the following statements about Zambia: 1.Zambia shares its borders with Namibia, Mozambique, and Angola. 2.The Zambezi River forms the southern border of Zambia with Zimbabwe. 3.Kitwe is one of the major cities in Zambia. 4.The official language of Zambia is French. How many of the above statements are correct? a) Only 1 b) Only 2 c) Only 3 d) All Answer: c) Only 3 Explanation: Statement 1: Zambia is bordered by Namibia, Mozambique, and Angola. This statement is incorrect as Zambia is actually bordered by Tanzania, Malawi, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Botswana, Namibia, Angola, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Statement 2: The Zambezi River forms the southern border of Zambia with Zimbabwe. This statement is correct. Statement 3: Kitwe is one of the major cities in Zambia. This statement is correct. Statement 4: The official language of Zambia is French. This statement is incorrect as the official language of Zambia is English, and several indigenous languages are also spoken. Therefore, the correct answer is: c) Only 3 PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Discuss the potential implications of India's interest in Zambia's copper sector. Analyze the historical, political, economic, and cultural aspects of India-Zambia relations, emphasizing the role of Indian investments, bilateral trade dynamics, and the cultural cooperation between the two nations. |




© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved