Description
Context:
- An 11-year-old boy died of H5N1 avian influenza in Delhi.
- This is the first recorded death due to the bird flu in India this year.
- In January, bird flu was confirmed in several states with thousands of birds, including migratory species, being found dead.
What is bird flu?
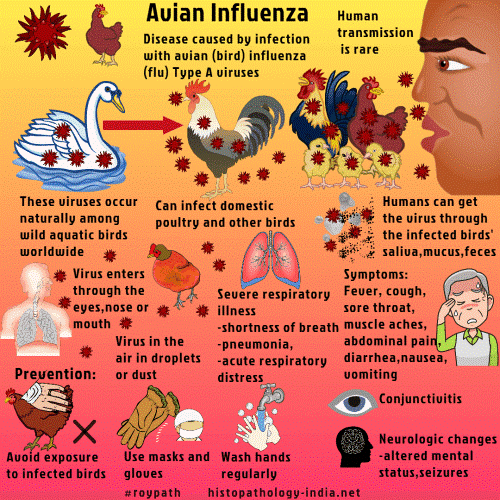
- Bird flu or avian influenza is a disease caused by avian influenza Type A viruses found naturally in wild birds worldwide.
- The virus can infect domestic poultry including chickens, ducks, Turkeys and there have been reports of H5N1 infection among pigs, cats, and even tigers in Thailand zoos.
- Avian Influenza type A viruses are classified based on two proteins on their surfaces – Hemagglutinin(HA) and Neuraminidase(NA).
- There are about 18 HA subtypes and 11 NA subtypes. Several combinations of these two proteins are possible e.g., H5N1, H7N2, H9N6, H17N10, etc.
Bird flu: Infection in humans
- There have been reports of avian and swine influenza infections in humans including A(H1N1), A(H1N2), A(H5N1), A(H7N9), etc.
- The first report of human H5N1 infection was in 1997 and currently, over 700 human cases of Asian Highly Pathogenic Asian Avian Influenza A (HPAI) H5N1 virus have been reported to the World Health Organisation from 16 countries.
- The infection is deadly as it has a high mortality rate of about 60%.
- The most common route of virus transmission is direct contact — when a person comes in close contact with infected birds, either dead or alive.
- Humans can also be affected if they come in contact with contaminated surfaces or air near the infected poultry.
- There is no sufficient evidence suggesting the spread of the virus through properly cooked meat.
Symptoms of avian influenza
Signs and symptoms of avian influenza A virus infections in humans have ranged from mild to severe influenza-like illness.
* Fever, cough, sore throat, muscle aches, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting
* Severe respiratory illness (e.g., shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, pneumonia, acute respiratory distress, viral pneumonia, respiratory failure)
* Neurologic changes (altered mental status, seizures)
Risk groups
- Children and adults below 40 were seen to be the most affected and mortality was high in 10-19 years olds.
Bird flu: Human-to-human transmission
- Human-to-human transmission of the H5N1 virus a very rare.
- The transmission of the virus from birds to humans is rare and sustained human-to-human transmission of the H5N1 virus has not yet been established.
- But then people working closely with poultry must take precautionary measures and maintain proper personal hygiene.
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-what-is-h5n1-avian-influenza-its-symptoms-and-how-fatal-can-it-be-7415702/





