AIR SPOTLIGHT
GLOBAL INNOVATION INDEX

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context:
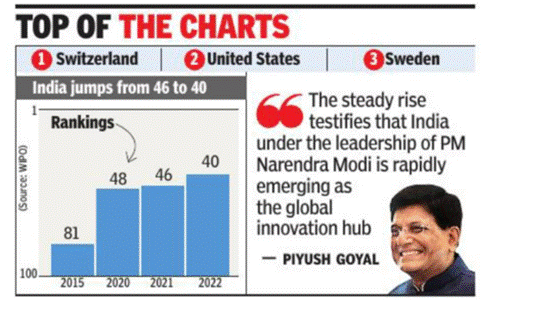
- India, for the first time, made it to the top 40 countries at the Global Innovation Index (GII).
GII:
- The Global Innovation Index is an annual ranking of countries by their capacity for, and success in, innovation. It was started in 2007 by INSEAD and World Business- a British magazine.
- It is published by the World Intellectual Property Organization, in partnership with Cornell University, INSEAD, and other organisations and institutions.
- It is based on both subjective and objective data derived from several sources, including the International Telecommunication Union, the World Bank and the World Economic Forum.
- The GII reveals the most innovative economies in the world, ranking the innovation performance of 132 economies.
- The 2022 edition of the GII tracks the most recent global innovation trends against the background of an ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, slowing productivity growth and other evolving challenges. Theme: What is the future of innovation-driven growth?
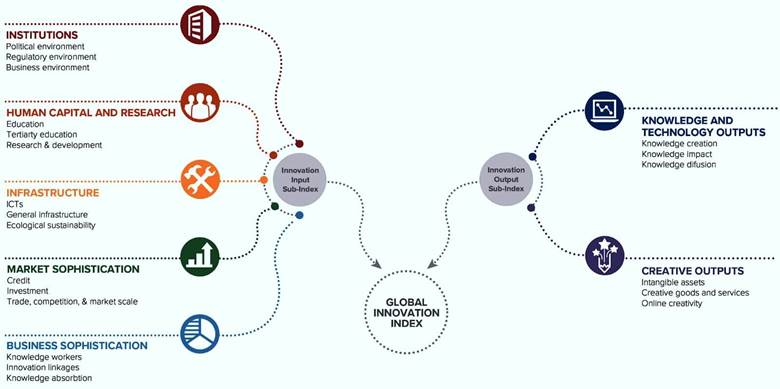
India’s ranking in GII 2022:
- India, for the first time, made it to the top 40 countries at the Global Innovation Index (GII). This was led by improvement in information and communication technologies (ICT) services exports, venture capital recipients’ value, and finance for startups.
- India’s ranking made it to the top most innovative lower middle-income economy in the world, overtaking Vietnam.
- In Central and Southern Asia, India ranked highest among three in the “most innovation economies” followed by Iran and Uzbekistan.
Indicators:
India continues to lead the world in the ICT services exports indicator with the first rank while holding top rankings in other indicators, including
- Venture capital recipients’ value (6th),
- Finance for startups and scaleups (8th),
- Graduates in science and engineering (11th),
- Labor productivity growth (12th) and
- Domestic industry diversification (14th).
Indian Innovation Index 2021:
About
- Prepared by NITI Aayog and the Institute for Competitiveness, the India Innovation Index is a comprehensive tool for the evaluation and development of the country's innovation ecosystem. It ranks the states and the union territories on their innovation performance to build healthy competition amongst them.
Report
- Manipur secured the lead in the Northeast and Hill States category, while Chandigarh was the top performer in the Union Territories and City States category.
- Karnataka has held first position, under the Major States category, in all three editions of the Index so far.
- Karnataka was followed by Telangana, Haryana, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu. Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Bihar and Gujarat were at the bottom of the index.
- Pointing out that India’s average innovation score is insufficient, given the country’s ambitious targets to be named among the top 25 nations in the Global Innovation Index, the report has recommended some measures such as: increasing Gross Domestic Expenditure on R&D (GDERD), promoting private sector participation in R&D and closing the gap between industry demand and what the country produces through its education systems.
- Finding: countries that spend less on GDERD fail to retain their human capital in the long run and the ability to innovate is dependent on the quality of human capital; India’s GDERD as a percentage of GDP stood at about 0.7%.
- Therefore, GDERD needs considerable improvement and should touch at least 2%, which would play an instrumental role in India achieving the goal of 5 trillion economy. The private sector needs to pick up pace in R&D.
- Public expenditure is productive up to some extent; once the growth follows a trajectory, it is desirable to shift to R&D mostly drive by the private sector. Therefore, it is important for India to find that inflexion point after which private sector takes over the government sector.
Reasons for India’s growth:
- The enormous intellectual capital, the active start-up environment, and the great work done by public and private research groups are all contributing to the GII ranking's steady development.
- Scientific departments such as the Department of Atomic Energy, the Department of Science and Technology, the Department of Biotechnology and the Department of Spacehave all contributed to the National Innovation Ecosystem’s enrichment.
- NITI Aayoghas been working relentlessly to guarantee that national initiatives to introduce policy led innovation in sectors like electric vehicles, biotechnology, bio space, alternative energy sources and others are optimised.
- The India Innovation Index, whose most recent edition was released last year by the NITI Aayog, has been generally hailed as a significant step toward decentralising innovation across India's states.
- The NITI Aayog, which includes the GII, has maintained a steady focus on monitoring and reviewing India's place in worldwide rankings.
Challenges to Innovation in India:
- Institute – Industry gap:
- Steps like the Atal Innovation Missionand collaboration with institutions in Switzerland and the United Kingdomare helping but we still have a long way to go before we can close the gap fully.
- Growth necessitates a significant shift in the Indian educational system.
- Top Indian universities are still mostly focused on education.
- Universities conduct research that is unrelated to industry or real-world challenges.
- Focus on R&D:
- India producesmost engineers in the world but the number of innovations and start-ups does not reflect this.
- Interdisciplinary and multinational interactions are essential to achieve optimum impact and outcomes.
- Another area where India lags is research and development spending.
- Investments in research are made on trust, with a modest level of risk.
- Building up Infrastructure:
- This is an area where India lags behind the rest of the world.
- The organisers can only provide good and efficient infrastructure if they are aware of the needs of the innovators and scientists.
Innovation in India- opportunities and challenges:
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT
- There is a positive relationship between per capita R&D and per capita GDP, whereby countries that have high per capita R&D expenditure tend to have higher per capita GDP as well.
- However, in India, R&D investment has been relatively low. In the past few years, R&D investment in the country has declined from 0.8% of the GDP in 2008–09 to 0.7% in 2017-18.
- This is lower than the other BRICS nations—Brazil spends about 1.2%, Russia about 1.1%, China just above 2%, and South Africa around 0.8%, with the world average being about 1.8%.
- On the other hand, developed countries like the United States, Sweden, and Switzerland spend about 2.9%, 3.2% and 3.4%, respectively. Among all nations, Israel spends the most, 4.5%, of its GDP on R&D
- One reason for the low spending on R&D in developing countries like India is that investments in R&D take time to produce results.
- Although inventions take time, nonetheless innovative thinking can be applied in dealing with such issues as well.
- The example of Grameen Bank is one such example where a small idea turned into a huge success both financially and helping poor communities. Thus, it becomes important to bring ‘research’ into these issues and not to restrain to spend in R&D, be it idea or product.
COMPOSITION OF R&D
- Another source of concern is the composition of the current R&D expenditure.
- The government spends the most on R&D (over 60%).
- Low private participation is one of the key hindrances in India’s overall low R&D expenditure
- About 45% of the government expenditure is dedicated to defence and space research, leaving the rest for other sectors to compete.
FIRM SIZE
- The problem of the ‘missing middle’ is another area that warrants attention.
- India is a country where the manufacturing sector is peculiarly structured, with either a very small-sized firm (less than 50 employees) or a very large-sized firm (more than 500 employees) and a clear ‘missing middle’.
- This structure causes a number of problems, one of them being a vast difference in productivity, whereby the large-sized firms are 10 times more productive than the small-sized firms. This difference also shows up in innovation.
LABOUR MARKET
- There exists a positive relationship between innovation and employment.
- Moreover, it is not just labour availability and the quality of labour but also labour legislations that affect innovation.
- A right balance between labour laws that doesn’t compromise on labour standards which also promote an environment that is conducive to nurture innovation is something that should be strived for.
DEMOGRAPHIC DIVIDEND
- Currently, more than 60% of India’s population is in the working age group (15–59).
- The energy and potential of this age group can be rightly channelized towards innovation. There is always an element of risk involved in innovation.
- But most Indians tend to be risk-averse, which is tied to a fear of and intolerance for failure, making it difficult to generate innovative ideas or promote existing ones
MARKET DEMAND
- It is observed that there is a mismatch between what is taught at the university level and what is required at the industrial level
- To better understand the potential of Indian research one need only look at the number of patents filed in the country over the years. The number of patents filed has increased at a compound annual growth of 3.63% in the last decade.
VENTURE CAPITAL
- Venture capital provides not only the funds necessary to run a business but also the required personnel and expertise to utilise the same.
- In India, the amount of funding received through venture capital and private equity flow has risen from ₹4 billion to ₹1,327 billion in the last two decades
Way Forward:
- First, GERD needs considerable improvement and should touch at least 2%, which would play an instrumental role in India achieving the goal of a 5 trillion economy and further influence its innovative footprint across the globe.
- Second, the role of the private sector in research and development needs to pick up pace.
- Third, intangible assets like patents and trademarks filing process are complex and face procedural delays. For Intangibles to create spill-overs, it is important to encourage more start-ups to file patents across India.
- Fourth, we are yet to take full advantage of our demographic dividend. About 60% of the population lies in the working age category, there lies a huge scope for innovation within the country, whereby the energy and potential of this age group can be channelized.
- Fifth, one needs to sincerely fill the gap between industry demand and what we produce through our education systems. Universities have the potential to become the go-to-place for industries, for any sort of innovation.
- Sixth, India is among the top 10 performing developing economies in stimulating global trade in creative goods. India needs to undertake efforts in creative goods and services, which have been ignored for a long time.
- And finally, we need to break silos and start working in tandem, i.e., no state/UT can thrive alone endlessly without taking care of its peers. This involves learning from peers, and providing adequate support to other states/UTs to ensure inclusive growth. This promotes the spirit of competitive federalism, which forces states/UTs to perform well, and ensures encompassing growth.
https://epaper.thehindu.com/Home/ShareArticle?OrgId=G9HA2FC55.1&imageview=0
https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/economy/indicators/india-breaks-into-top-40-innovative-nations-ranking/articleshow/94540108.cms
https://indianexpress.com/article/opinion/building-a-vibrant-science-ecosystem-7143793/
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/sti-policy-science-technology-innovation-policy-atmanirbhar-bharat-5th-national-sti-policy-7135888/
https://www.niti.gov.in/sites/default/files/2022-07/India-Innovation-Index-2021-Web-Version_21_7_22.pdf

NEWS IN BRIEF
PRELIMS SPECIAL
RUSSIAN ANNEXATION

Copyright infringement not intended
Context:
- Russia has vetoed the Western bid in the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) to condemn its annexation of Ukrainian territory. Among the 15 nations of the Council, 10 voted in favour of the resolution, and four India, China, Gabon, and Brazil abstained.
- President Vladimir Putin hosted a signing ceremony in the Kremlin to incorporate four Ukrainian regions into Russia, a major step towards formally annexing around 15% of Ukraine.
Details:
- Russian-backed separatists and Russian-installed officials in the four partially Russian-controlled regions of Ukraine declared that voters had chosen to join Russia, in hastily organised “referendums” that the West said were illegal shams.
- Kherson region, Zaporizhzhia, Donetsk People’s Republic and Luhansk People’s Republic will now forever be part of Russia
- For Russia to formally annex the territories, some sort of treaty will be signed and then ratified by the Russian parliament, which is controlled by Putin allies. Moscow will then consider the areas part of Russia, and the “umbrella” of its nuclear defences will extend to them.
- Furthermore, their populations will be eligible to be drafted to fight for Russia against Ukraine, as men in the DNR and LNR, set up with Russian backing in 2014, already do.
- Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky has repeatedly said that “pseudo-referendums” on annexation by Russia will destroy any chance of peace talks.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=India-abstains-on-UNSC-resolution-condemning-Russia%26%2339%3Bs-referenda-and-annexation-in-Ukraine&id=448631
https://t.me/+hJqMV1O0se03Njk9
VANDE BHARAT EXPRESS

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi flagged off Vande Bharat Express train between Gandhinagar and Mumbai.
Vande Bharat Express
- The Vande Bharat Express offers a myriad of superior amenities which will provide passengers with aircraft like travelling experience.
Features
- Advanced state-of-the-art safety features including Kavach technology - an indigenously developed Train Collision Avoidance System.
- The train has been provided with bogies having fully suspended traction motors for 160 kmph operational speed along with the advanced state-of-the-art suspension system ensuring a smooth and safe journey and enhanced riding comfort for passengers.
- The train has been designed to increase Indian Railways' Green footprint by dispensing with the power cars and saving about 30 per cent of electricity with the advanced regenerative braking system.
- In any emergency situation, loco pilot and train guard can easily communicate with each other as well as passengers, the loco pilot of the Vande Bharat Express.
- The new Vande Bharat trains would have improved features including reclining seats, automatic fire sensors, CCTV cameras, on-demand content with wifi Facility, three-hour battery backup and GPS systems to make travelling safer and more comfortable.
- It also has a photocatalytic ultraviolet air purification system in the roof-mounted package unit (RMPU) for air purification.
- The weight of the train has been reduced by 38 tonnes to 392 tonnes and it can continue functioning even with two feet of flood waters on the tracks. These are made of stainless steel. Due to less weight, the passengers would feel extra comfortable even at high speed.
https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=newssearch&cd=&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=2ahUKEwjXk7f9g8j6AhXdT2wGHX9hBDYQxfQBKAB6BAgFEAE&url=https%3A%2F%2Fnewsonair.com%2F2022%2F10%2F01%2Findia-gets-its-3rd-vande-bharat-named-vande-bharat-2-0%2F&usg=AOvVaw1YhEm2ZMLumvqebAki9xmB
https://t.me/+hJqMV1O0se03Njk9
REPO RATE
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- The repo rate, the rate at which RBI lends money to commercial banks, has been hiked by 50 basis points.
Policy Rates
- Bank rate – The interest rate at which RBI lends long term funds to banks is referred to as the bank rate. However, presently RBI does not entirely control money supply via the bank rate. It uses Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) – repo rate as one of the significant tools to establish control over money supply. Bank rate is used to prescribe penalty to the bank if it does not maintain the prescribed SLR or CRR.
- Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) – RBI uses LAF as an instrument to adjust liquidity and money supply. The following types of LAF are:
- Repo rate: Repo rate is the rate at which banks borrow from RBI on a short-term basis against a repurchase agreement. Under this policy, banks are required to provide government securities as collateral and later buy them back after a pre-defined time.
- Reverse Repo rate: It is the reverse of repo rate, i.e., this is the rate RBI pays to banks in order to keep additional funds in RBI. It is linked to repo rate in the following way: Reverse Repo Rate = Repo Rate – 1
- Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) Rate: MSF Rate is the penal rate at which the Central Bank lends money to banks, over the rate available under the rep policy. Banks availing MSF Rate can use a maximum of 1% of SLR securities. MSF Rate = Repo Rate + 1
https://newsonair.com/2022/09/30/rbi-hikes-the-repo-rate-by-50-basis-point-real-gdp-for-2022-23-projected-to-grow-at-7-0/
https://t.me/+hJqMV1O0se03Njk9
NORD STREAM PIPELINE LEAKAGES

Copyright infringement not intended
Context:
- Sweden’s coast guard said that it discovered the fourth leak in the two damaged offshore pipelines that comprise the crucial Nord Stream pipelines (Nord Stream 1 and Nord Stream 2), designed to carry gas from Russia to Europe via the Baltic sea.
- The presently unexplained leak is the second of its kind to be discovered in Swedish waters, while two other leaks were found near Denmark earlier this week, Reuters reported.
Details:
- Nord Stream 1 is a 1,224 km underwater gas pipeline running from Vyborg in northwest Russia to Lubmin in northeastern Germany via the Baltic Sea.
- The majority owned by the Russian energy giant Gazprom, it is the primary network through which gas reaches Germany.
- Most of the gas goes directly to Germany, while the rest travels west and southwards through onshore links to other countries and into storage caverns, according to Reuters.
- Gazprom and five other European firms decided to build Nord Stream 2 in 2015, valued at around $11 billion.
- The 1,200-km pipeline was to run from Ust-Luga in Russia to Greifswald in Germany through the Baltic Sea and carry 55 billion cubic metres of gas per year. It was meant to run along with the Nord Stream 1 system.
- Germany is Russia’s biggest European gas consumer, and most of it comes through the Nord Stream.
- The pipelines have been at the centre of tensions lately. Russia has been accused of leveraging Europe’s dependency on its energy, as retaliation against the Western sanctions imposed on it since the Ukrainewar began.
- The leaks occurred a day before the ceremonial launch of the Baltic Pipe, which carries gas from Norway to Poland, a project that is part of Poland’s attempt to reduce its dependence on Russian energy, according to Reuters.
- While investigations have not yet revealed the cause behind the leaks, leaders from Europe and the United States suspect foul play. They alleged that it was an act of sabotage with three separate leaks and explosions occurring on the very same day.
- While the EU and the United States have stopped short of explicitly blaming Russia so far, Ukraine and Poland have not been so cautious.
- Moscow has, however, called the allegations against it “predictably stupid and absurd”, blaming the US and its collaborators for the attacks – a charge Washington has denied.
https://newsonair.gov.in/Main-News-Details.aspx?id=448706
https://t.me/+hJqMV1O0se03Njk9
SWACHH SURVEKSHAN 2022
Copyright infringement not intended
In News
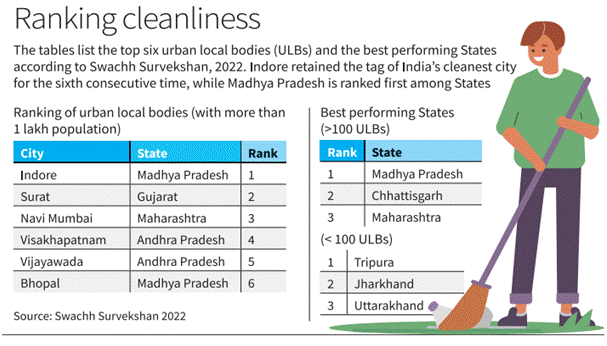
- Indore is the cleanest city in India, while Madhya Pradesh is the cleanest State in the country.
- Surat (Gujarat) is the 2nd cleanest city.
- Chhattisgarh is the 2nd cleanest State.
- Tirupati received the best city award in the Safai Mitra Suraksha category.
- Haridwar (Uttarakhand) received the best Ganga town award in more than one lakh population cities categories.
Details
- The field assessment for Swachh Survekshan was launched on 1st March 2022 by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
- Swachh Survekshan 2022 is targeted toward capturing the initiatives of cities for the overall welfare and well-being of Sanitation workers.
- This year another new indicator ‘Swachh Technology Challenge’ has been added.
- To expand the Survekshan footprint, district rankings have been introduced.
- The scope of the survey has been expanded to now cover 100% of wards, as compared to 40% in previous years.
Swachh Survekshan
- Swachh Survekshan was initiated by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs in 2016 as a competitive framework to encourage cities to improve the status of urban sanitation.
- Swachh Survekshans are conducted under the Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban).
- It has promoted a spirit of healthy competition among cities and towns of India.
- The Primary goal of Swachh Survekshans is to encourage large-scale citizen participation and create awareness amongst all sections of society about the importance of working together towards making towns and cities better places to reside in.
- The performance of each city is evaluated on six parameters:
- Municipal solid waste, sweeping, collection and transportation.
- Municipal solid waste, processing, and disposal of solid waste.
- Open defecation free and toilets.
- Capacity building and e-Learning.
- Provision of public toilets and community toilets.
- Information, education and communication, and behaviour change.
https://epaper.thehindu.com/Home/ShareArticle?OrgId=G25ABLH25.1&imageview=0
https://t.me/+hJqMV1O0se03Njk9











