INDIA-DENMARK, BILATERAL TIES AND NORDIC SUMMIT SIGNIFICANCE

Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi met with Mette Frederiksen, his Danish counterpart, and the two leaders are anticipated to address a wide variety of matters of mutual interest in order to strengthen the bilateral relationship.
Background
During a virtual meeting in September 2020, a "Green Strategic Partnership" was formed. During Prime Minister Frederiksen's visit to India in October 2021, this partnership was transformed into a results-oriented five-year action plan.
The History of bilateral relations
- The earliest encounter between the two countries occurred in the 17th century, when a Danish colony was formed at Tranquebar, now in Tamil Nadu, in 1620.
- Different trade posts were built by the Danish in other regions of India, including Serampore in West Bengal. The Nicobar Islands were a Danish colony as well.
- In 1845, the British bought all of Denmark's possessions, including the Nicobar Islands, which they bought in 1868.
- Regular high-level contacts characterise India-Denmark diplomatic relations, which were formed in September 1949 and are founded on historical ties, shared democratic traditions, and a shared goal for regional and international peace and stability.
- Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru's visit to Denmark in 1957, just after India's independence, lay the groundwork for a close relationship between the two countries.
- The non-extradition of Niels Holck Nielsen, a Danish national implicated in the Purulia Arms Dropping Case in 1995, harmed relations in 2011.
Joint Commission
- The joint commission between India and Denmark conducted its first meeting in New Delhi in 2010.
- The two countries addressed critical areas of bilateral cooperation, as well as regional and global problems of mutual interest.
- Three new Joint Working Groups on Shipping, Food, Agriculture, and Fisheries were established.
- The two sides also decided to turn the three joint committees created before, namely
- Biotechnology;
- New and Renewable Energy; and
- Labor Mobility, into Joint Working Groups.
India-Nordic summit
- The only nations have summit-level encounters with Nordic countries are India and the United States.
- The inaugural India-Nordic Summit was held in Stockholm in 2018.
- The six nations' commitment to global security, economic growth, innovation, and climate change was reaffirmed at this summit.
- The Summit contributes to the expansion of India's diverse collaboration with the Nordic area.
- The theme of this year's summit was post-pandemic economic recovery, climate change, innovation and technology, renewable energy, the shifting global security picture, and India-Nordic collaboration in the Arctic.
- In the areas of sustainability, renewable energy, digitalization, and innovation, the Nordic nations are essential partners for India.
- Regional and international issues were also considered.
- The Summit's main focus was on how to go forward with the bilateral engagement agenda between India and the Nordic nations.
Way Forward
- For India and the region, this cooperation has the potential to be transformative.
- For the time being, India's only Green Strategic Partnership is with Denmark, but this move toward sustainable development is critical since it can help India reach similar agreements with other countries in the area and beyond.
- The Nordic nations (Norway, Sweden, Iceland, Finland, and Denmark) have a combined GDP of billions of dollars.
- India and the Nordic nations have a substantial total bilateral trade in products and services.
- These nations are among the highest achievers in a number of fields, including innovation, renewable energy, green technology, and education.
- As a result, India must preserve positive ties with these countries.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=PM-Modi-says%2C-2nd-India-Nordic-Summit-a-great-platform-to-discuss-ways-to-boost-ties-with-Nordic-nations&id=440317
https://indianexpress.com/article/india/narendra-modi-europe-visit-live-updates-india-nordic-summit-denmark-france-emmanuel-macron-7900230/
https://www.deccanchronicle.com/nation/politics/040522/india-denmark-sign-9-pacts-to-ramp-up-trade.html
https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/india/the-second-india-nordic-summit-a-huge-impetus-to-regional-partnership/articleshow/91219271.cms
NEWS IN BRIEF: PRELIMS SPECIAL
National Commission for Minorities

- Iqbal Singh Lalpura, Chairman of the National Commission for Minorities, has stated that the commission has made many initiatives to ensure the welfare of minority populations.
- The objective of the commission is to give education and job possibilities to this group of people.
- The National Commission for Minorities (NCM) was established in 1992 as a result of the National Commission for Minorities Act.
- It oversees the implementation of minorities' protections enshrined in the Constitution and laws passed by Parliament and state legislatures.
- The NCM is made up of a Chairperson, a Vice-Chairperson, and five members, all of whom must be from minority communities.
- Each Member is elected for a three-year term beginning on the day he or she is sworn in.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Chairman-of-National-Commission-for-Minorities-says-commission-has-taken-several-steps-for-welfare-of-minority-communities&id=440312
Kisan Drones

- Agriculture Minister Narendra Singh Tomar has announced that the government will provide a 50% subsidy to SC-ST, small and marginal farmers, and women in northeastern regions who wish to purchase drones.
- Kisan Drones will be pushed for crop evaluation, digitalization of land records, and spraying of pesticides and fertilisers in order to strengthen the agricultural industry in the nation.
- Kisan Drone will usher in a new edge revolution by using high-capacity drones to transport veggies, fruits, and seafood directly from farmers to markets.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Govt-to-provide-50%25-subsidy-to-SC-ST%2c-small-and-marginal%2c-women-and-farmers-of-northeastern-states-to-buy-drones%2c-says-Agriculture-Minister&id=440223
Triangular Development Cooperation and Renewable Energy Partnership
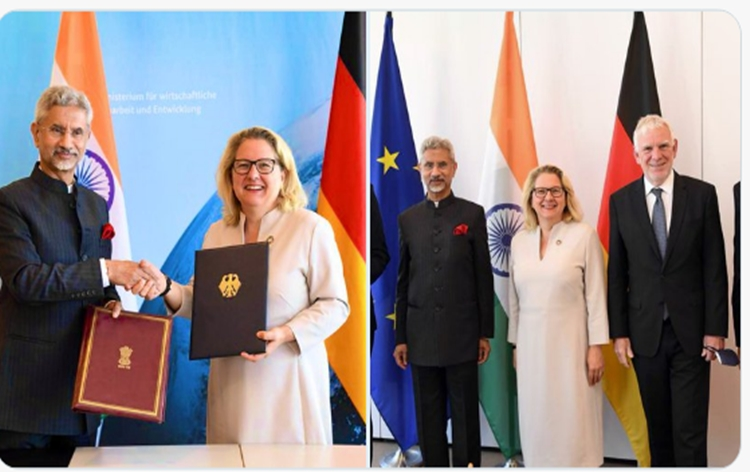

- S. Jaishankar, Minister of External Affairs, met with Svenja Schulze, German Minister for Economic Cooperation and Development, in Berlin.
- India and Germany signed a collaborative statement on agroecology and natural resource sustainability.
- Joint research, information exchange, and innovation between academic institutions in both nations and practitioners, especially farmers, will be fostered as a result of this.
- Encouragement of exchanges, partnerships, and research engagement with the commercial sector will aid in the transfer of technology and scientific information.
- Germany's Federal Ministry of Economic Support and Development will offer up to 300 million euros for financial and technical cooperation for projects under this programme by 2025.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=India%2c-Germany-sign-agreements-on-Triangular-Development-Cooperation-and-Renewable-Energy-Partnership&id=440226
ALH Mk III

- Today marks the four-year anniversary of the Unnat Bharat Abhiyan 2.0.
- In the Coast Guard Air Enclave at Nedumbassery in Kochi, the Coast Guard commissioned its second Air Squadron, 845 Squadron (CG).
- It is equipped with the Advanced Mark III (ALH Mark III) helicopters, which were created in-house.
- The commissioning represents a huge step toward self-sufficiency in search and rescue operations as well as long-range marine surveillance.
- Four helicopters have been stationed in Kochi to cover all of Karnataka's, Kerala's, and Lakshadweep's coastlines.
- Hindustan Aeronautics Limited manufactures the ALH MK III aircraft, which represents a huge step toward self-reliance in the sector of military aviation, in keeping with the government's aim for 'Aatmanirbhar Bharat.'
- Over 300 of these aircraft have been supplied by HAL and are now in service with the Armed Forces.
- Among its versions, the MK III is a marine role variant that includes cutting-edge sensors and armaments to boost India's maritime power.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Indian-Coast-Guard-commissions-its-second-ALH-Mk-III-Squadron-in-Kochi&id=440331









