



Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: INDIA TODAY
U.S. President Donald Trump's warning of a 25% tariff on all U.S. trade for countries doing business with Iran challenges India's strategic relationship with Iran and its Chabahar Port ambitions.
|
Read all about: India-Iran Relations l Chabahar Port Operation l US-Iran Nuclear Talks l India's Strategy on US Tariffs l India's Strategy Against US Pressure |
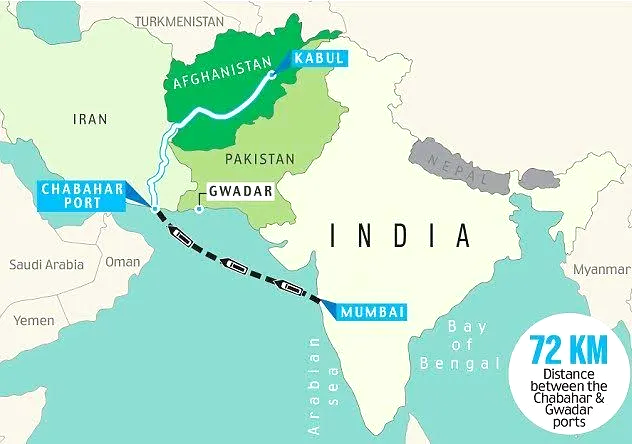
What is India-Iran Chabahar Port Agreement?
Location: Chabahar is a deep-water port in southeastern Iran on the Gulf of Oman. It is Iran's only oceanic port, providing direct access to the Indian Ocean.
 Long-Term Contract: In May 2024, India and Iran signed a 10-year contract for India to develop and operate the Shahid Beheshti terminal at the port. This agreement is managed by India Ports Global Ltd (IPGL).
Long-Term Contract: In May 2024, India and Iran signed a 10-year contract for India to develop and operate the Shahid Beheshti terminal at the port. This agreement is managed by India Ports Global Ltd (IPGL).
Financial Commitment: India committed to invest $120 million for port equipment and offered a $250 million credit line for related infrastructure.
Gateway to Central Asia
It provides India with a trade route to Afghanistan and landlocked Central Asian countries, completely bypassing Pakistan.
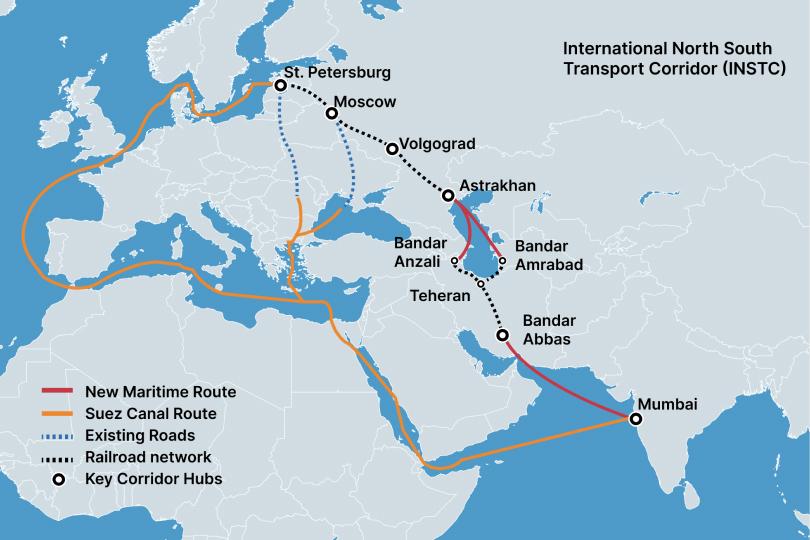
Pillar of the INSTC
Chabahar is a key node in the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC), a 7,200-km multi-modal route connecting India with Russia and Europe.
The INSTC is projected to be 30% cheaper and 40% shorter than the traditional Suez Canal route. (Source: Federation of Freight Forwarders' Associations)
 Counterbalancing China
Counterbalancing China
The port is strategically important for India as a countermeasure to China's Gwadar port, allowing India to monitor Chinese activities and counter Beijing's "String of Pearls" strategy in the Indian Ocean.
Humanitarian Operations
The port has served as a dependable route for aid, facilitating India's shipment of millions of tonnes of wheat and pulses to Afghanistan, and pesticides to Iran.
Recent warnings of a potential 25% tariff on countries trading with Iran by the US have put the project's viability at risk.
Benefit the China: An Indian withdrawal would be detrimental to both Indian and US interests because it would create a vacuum that China would fill.
Economic Risk: A 25% tariff severely harms Indian exporters, as the US is the largest trading partner. India's trade with the US ($132.2 billion in FY25) far outweighs trade with Iran ($1.68 billion in FY 25).
Test of Strategic Autonomy: India needs to maintain a careful balance between its alliance with the US and its own regional priorities to protect its reputation as a credible, independent global power.
India's past actions in similar situations show a flexible approach, balancing pragmatism with strategic defiance.
Iranian Oil Imports (2018-19)
India stopped importing crude oil from Iran in 2019 to comply with US sanctions and protect its strategic relationship with the US, viewing it as a pragmatic decision despite the resulting higher economic costs.
S-400 Missile Deal with Russia
India prioritized its core national security interests and sovereign decision-making by proceeding with the purchase despite the threat of US sanctions under CAATSA (Countering America's Adversaries Through Sanctions Act), a case of strategic defiance.
Intensive Diplomacy
India engaging with the US to secure sanctions waiver, emphasizing Chabahar's importance for regional stability, humanitarian aid to Afghanistan, and as a check on Chinese influence.
De-risking the Project
India has reduced its direct financial risk through a change in financial obligation and may explore new management frameworks to protect government entities from potential sanctions.
Strengthening Regional Partnerships
Work with Afghanistan and Central Asian nations to increase port traffic and build a wider coalition of stakeholders who benefit from its operation.
Chabahar port tests India's strategic autonomy. Future success requires skillful US diplomacy, innovative de-risking, and strong commitment to regional partners, crucial for long-term economic and strategic regional goals.
Source: INDIA TODAY
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Analyze the strategic importance of the Chabahar Port for India's connectivity goals and how US sanctions threaten its viability. (250 Words) |
Chabahar Port is strategically crucial for India as it provides a direct sea-land access route to Afghanistan and the resource-rich Central Asian republics, bypassing Pakistan. It is a key component of the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) and serves as a vital channel for humanitarian aid to Afghanistan.
The INSTC is a 7,200-km multi-modal network of ship, rail, and road routes for moving freight between India, Iran, Afghanistan, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Russia, Central Asia, and Europe. It is projected to be more time and cost-effective than the traditional Suez Canal route.
India has adopted a multi-pronged approach. It has reduced its direct sovereign exposure by fulfilling financial commitments early and altering the management structure of the port operations. Diplomatically engaging with the US to secure a sanctions waiver, while also downplaying its minimal trade volume with Iran.
© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved