



Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: THESTATESMAN
India's research ecosystem is rapidly evolving, driven by government initiatives and a growing startup culture, despite persistent challenges such as low private investment and a fragmented research landscape.
India's research ecosystem is marked by significant achievements and persistent weaknesses.
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Chronic Underfunding
With low R&D spending, the research ecosystem is starved of funds. This limits the ability of universities to acquire state-of-the-art equipment, provide competitive salaries, and undertake ambitious, long-term projects.
Low Private Sector Contribution
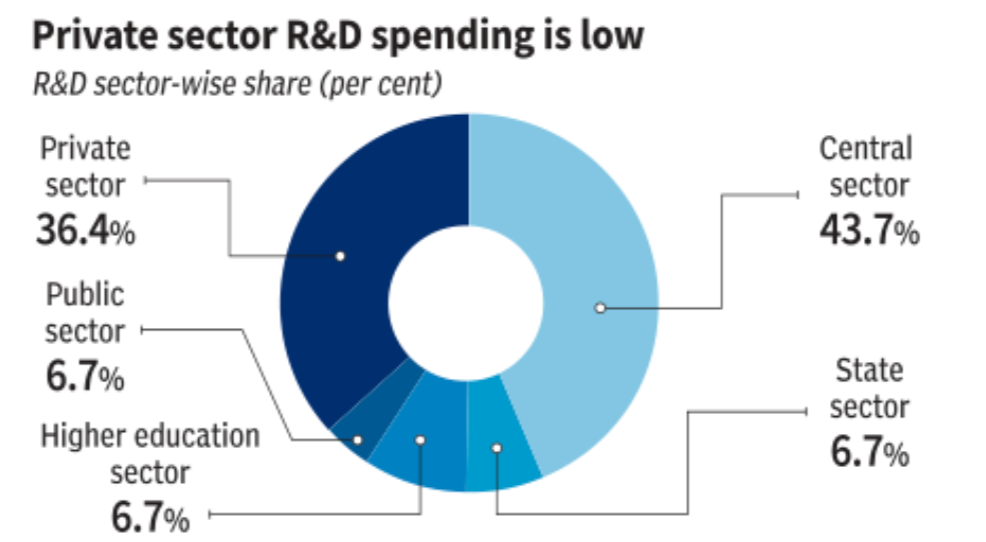
Private sector contributes only about 36% of the total R&D expenditure in India, this is lower than global leaders like the US and China, where industry drives over 70% of R&D investment, linking research directly to market needs.
 Gap in Innovation
Gap in Innovation
Gap exists between academic research and its commercial application. While India generates a high number of patents, their commercialization rate is low. This failure to translate lab-based innovations into market ready products is a major bottleneck.
 Bureaucratic Hurdles
Bureaucratic Hurdles
Researchers spend excessive time navigating complex administrative and financial procedures. Delays in receiving sanctioned funds are common, which disrupts project timelines and discourages ambitious research.
Significant "Brain Drain"
Many of India’s top scientists and engineers move abroad for better research infrastructure, higher pay, and greater academic freedom. This outflow of talent deprives the country of its best minds "Brain Drain".
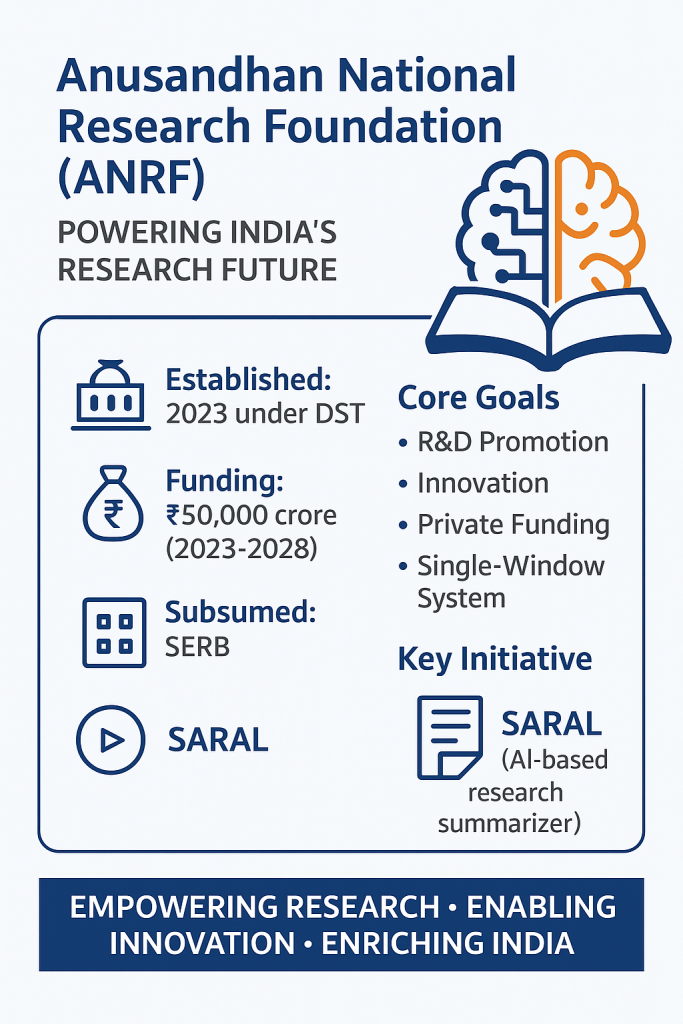
Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF): Established as an apex body to streamline and boost research funding. It provide high-level strategic direction and consolidate funding previously managed by different agencies to promote a culture of research across all institutions.
 Strategic Policies and Missions
Strategic Policies and Missions
IMPRINT Initiative: A joint effort by IITs and IISc, this scheme aims to convert research into viable technology in ten key engineering domains, directly addressing the industry-academia gap.
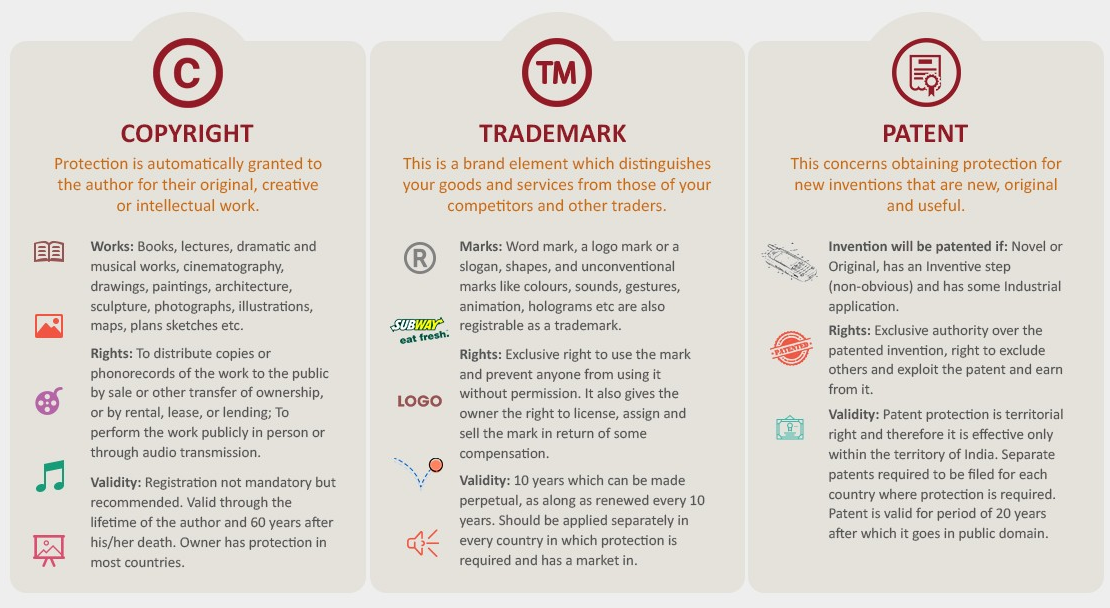
Strengthening IPR Framework: India's National IPR Policy and adherence to the WTO's TRIPS agreement aim to create a more robust environment for protecting and commercializing intellectual property.
Boost R&D Investment
India must set a clear national target to increase its Gross Expenditure on R&D (GERD) to at least 2% of GDP within the next decade, with a focus on stimulating private sector investment to contribute over half of this amount.
Promoting Strong Public-Private Synergy
Establish Public-Private Innovation Hubs in key sectors like AI, semiconductors, and green energy to share resources and co-develop solutions.
Incentivize Corporate R&D through targeted tax benefits tied to measurable outcomes like patents and product development.
Bridge the Academia-Industry Gap
Academic performance metrics must be reformed to give equal weightage to patents, technology transfers, and entrepreneurship alongside publications. Promote programs that allow researchers to work temporarily in industry and vice-versa.
Develop and Retain Talent
Implement the vision of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 to promote critical thinking over rote learning. Launch well-funded national postdoctoral fellowships and create attractive schemes to bring back top Indian talent from abroad.
Democratize Infrastructure
Create a national network where researchers from any institution can access high-end equipment and facilities in exclusive labs on a time-sharing basis.
United States (Private-Sector Led)
The US R&D ecosystem is dominated by private companies, which account for over 70% of its R&D spending.
India must create influential financial and regulatory incentives to make R&D a core business strategy for its corporate sector.
South Korea (Strategic Government Direction)
South Korea transformed its economy with government strategic support, long-term investments in specific sectors (like electronics and semiconductors) and encouraging its large conglomerates (chaebols) to build global R&D leadership.
The Indian government, through ANRF, can identify and fund mission-mode projects in high-potential areas.
Germany
Germany's Fraunhofer Society is a world-renowned model for applied research. It acts as a bridge, taking academic discoveries and developing them into market-ready technologies for industry.
India needs to build a network of similar translational research institutions to close the academia-industry gap.
Israel
Israel has successfully leveraged its defense and public sector needs to create a prosperous startup ecosystem. Government defense contracts lead to advanced technologies that are later commercialized
India can use its public procurement power, especially in defense, space, and healthcare, to create a market for domestic innovation.
India must strengthen its research ecosystem by increasing R&D spending, enhancing infrastructure, promoting robust academia-industry collaboration, curbing brain drain, and building strategic partnerships, thereby creating a more innovative, inclusive, and globally competitive research environment.
Source: THESTATESMAN
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Critically analyze the structural challenges facing India's research ecosystem. 150 words |
ONOS aims to democratize knowledge by providing centralized, free access to leading global scientific and academic journals for higher education institutions.
The India Research Tour 2025 is a nationwide outreach initiative launched by the Indian Council of Social Science Research (ICSSR) in collaboration with Springer Nature. The tour aims to promote research integrity, inclusivity, and innovation across India's research institutions.
The Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) was established through the Anusandhan National Research Foundation Act, 2023. It serves as the apex body for guiding and regulating research and development (R&D) across various sectors in India, including natural sciences, engineering, technology, agriculture, and health tech.
© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved