



Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: THE HINDU
India is strategically positioning itself as a global power by leveraging its economic strengths, civilizational heritage, and unique ability to engage with a complex, multi-polar world amidst geopolitical shifts, economic uncertainty, and technological change.
|
Read all about: INDIA'S STRATEGY AGAINST US PRESSURE l CHINDIA: NEW ERA OF INDIA-CHINA DIPLOMACY |
Geopolitical Volatility
Rising U.S.–China rivalry, Russia–Ukraine conflict, and tensions in the Indo-Pacific (e.g., Taiwan, South China Sea) create global instability.
The UN reported 56 active conflicts in 2024, the highest since World War II (Source: Institute for Economics & Peace).
Economic Shifts
Global inflation (5.8% in 2024), energy crises due to supply chain disruptions, US tariffs, and recession risks in major economies threaten trade and investment (Source: World Economic Outlook).
Climate Challenges
Extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and water scarcity impact 3.6 billion people globally (Source: UN).
Top 10 climate disasters cost the world more than $228 billion in 2024. (Source: Times of India).
Tech Disruptions
AI, 5G, and cyber threats reshape economies and security.
India detected an average of 761 cyberattack attempts per minute in 2024 (Source: Data Security Council of India)
India, with a GDP of $4.18 trillion in 2025, aspires to be a $7 trillion economy by 2030. Its strategic ambitions include:

The uncertain world tests India’s ability to maintain strategic autonomy while addressing domestic and global challenges.
Indo-Pacific Tensions
China’s assertiveness in the South China Sea and Taiwan Strait threatens regional stability.
India’s Quad membership counters China’s maritime dominance, with joint naval exercises like Malabar 2024 enhancing interoperability.
India balances strategic autonomy with partnerships, engages in Quad for Indo-Pacific security while using BRICS and SCO to advocate Global South interests, avoiding alignment with any single bloc.
Border Disputes
The India–China border standoff along the Line of Actual Control (LAC), despite 2024 disengagements in Depsang and Demchok, remains a flashpoint. Pakistan’s cross-border terrorism adds pressure.
Regional Instability
Conflicts in the Middle East (e.g., Gaza, Israel-Iran) disrupt India’s trade and endanger over 9 million diaspora living in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC).
Inflation and Energy Crises: Global inflation and oil price volatility raise India’s import bill.
Recession Risks: A projected 2.3% global growth slowdown in 2025 (Source: World Bank), and USA 50% tariffs threatens India’s exports, particularly in IT, textiles, and pharmaceuticals.
Supply Chain Disruptions: Semiconductor shortages and shipping delays hinder India’s manufacturing goals.
Self-Reliance: Initiatives like Atmanirbhar Bharat and Make in India boosted domestic production, with electronics manufacturing rising to $115 billion in 2024.
Trade Diversification: India signed Free trade Agreement (FTA) with Australia, UAE, EFTA, UK, to diversify export markets and reduce dependency of few countries (eg. USA, China).
Tech Diplomacy: India’s digital infrastructure (e.g., UPI) positions it as a tech leader, specially in Global South.
India leverages trade agreements, digital innovation, and self-reliance to strengthen soft power, projecting resilience and stability in a turbulent global economy.
Modernization: The 2025-26 defence budget of ₹6.81 lakh crore funds indigenous projects like Tejas aircraft and Arjun tanks, to reduce import reliance.
Space Security: India is accelerating its space surveillance capabilities following Operation Sindoor, planning to launch 52 dedicated military satellites by 2029. (Source: Times of India)
Defence self-reliance aligns with economic goals, reducing dependence on foreign suppliers (e.g., Russia, U.S.) and enhancing India’s strategic leverage.
Technology
AI and 5G adoption face cyber threats, in June 2025, 12.4% of the devices running on the Windows operating system in India experienced malware detections, the highest worldwide, according to the Acronis Cyberthreats Report.
Climate Change
In 2024, India experienced extreme weather events on 322 out of 366 days (Source: Down To Earth).
The UN Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP) reported that India suffered $87 billion in economic losses from extreme weather events in 2021.
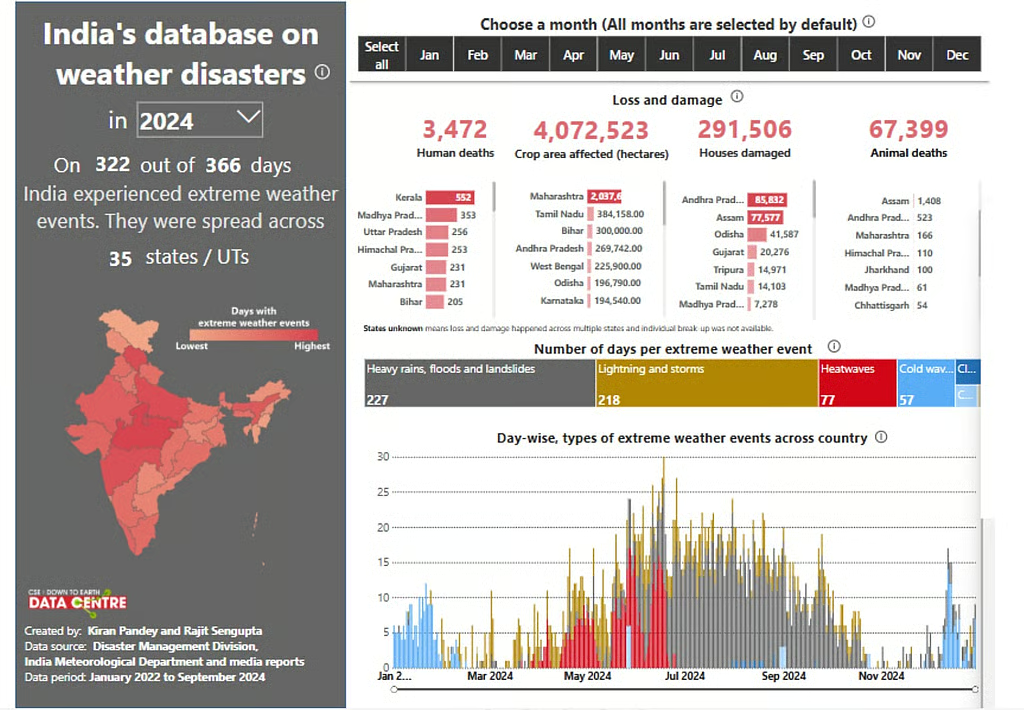 India leverages technology (e.g., AI in agriculture, UPI) and green diplomacy (e.g., International Solar Alliance) to build resilience, positioning itself as a leader in non-traditional security.
India leverages technology (e.g., AI in agriculture, UPI) and green diplomacy (e.g., International Solar Alliance) to build resilience, positioning itself as a leader in non-traditional security.
Culture and Diaspora: Yoga, Bollywood, and 32 million diaspora amplify India’s cultural reach, with 2025’s International Yoga Day celebrated in 190 countries with the theme “Yoga for One Earth, One Health.”.
Development Assistance: India supplied over 30 crore doses of vaccine to 99 countries and 2 United Nations entities under the Vaccine Maitri initiative (Source: MEA).
Education and Media: Indian universities hosted 64,000 foreign students in 2023-4 (Source: The Hindu). OTT platforms globalized Indian content.
Soft power complements India’s hard power limitations, cultivating goodwill.
Economic Dependence: Over $915 billion imports (2024) and reliance on foreign energy (over 85% of oil imports) limit autonomy.
Geopolitical Pressure: 50% USA tariffs on India, U.S. sanctions over Russian oil, and China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) dominance in Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) challenge India’s multialignment.
Strengthen Regional Partnerships: Expand FTAs, deepen ties with ASEAN, African Union, and SCO to secure trade and security interests.
Enhance Self-Reliance: Scale up indigenous defence (e.g., DRDO’s hypersonic missile tests in 2024) and tech innovation (e.g., 6G trials).
Diversify Energy: Expand renewable energy to reduce external dependence.
Amplify Soft Power: Use diaspora networks and cultural exports to shape global narratives.
Conclusion
India’s rise in an uncertain world depends on balancing strategic autonomy with global partnerships, leveraging its $4.1 trillion economy to shape a multipolar order while addressing domestic limitations.
Source: THE HINDU
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. India's foreign policy in the 21st century is characterized by 'multi-alignment' rather than 'non-alignment'. Critically analyze 250 words |
Strategic autonomy refers to India’s ability to make independent foreign policy and security decisions without undue reliance on or influence from any single global power, balancing multiple partnerships to safeguard national interests.
India maintains defense and energy ties with Russia while deepening strategic, economic, and technological cooperation with the U.S., balancing commitments to preserve autonomy and avoid over-dependence.
Economic resilience allows India to reduce dependency on foreign aid, invest in defense and infrastructure, and negotiate global partnerships from a position of strength.
© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved