



Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: PIB
The Economic Survey 2025-26 presents a comprehensive analysis of the Indian economy, highlighting robust growth and strong macroeconomic fundamentals amidst global challenges.
Robust GDP Growth
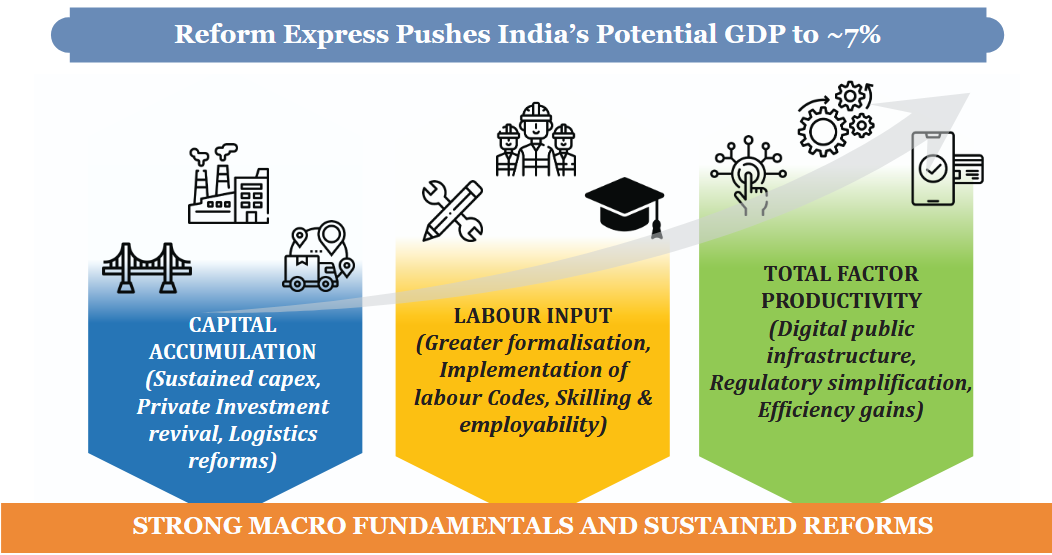
Real GDP is projected to grow by 7.4% in FY26, with a medium-term growth potential revised upwards to around 7%. The forecast for FY27 is pegged between 6.8% and 7.2%, driven by strong domestic demand.
Benign Inflation
The average headline CPI inflation dropped to a historic low of 1.7% between April and December 2025, one of the sharpest declines among major emerging economies.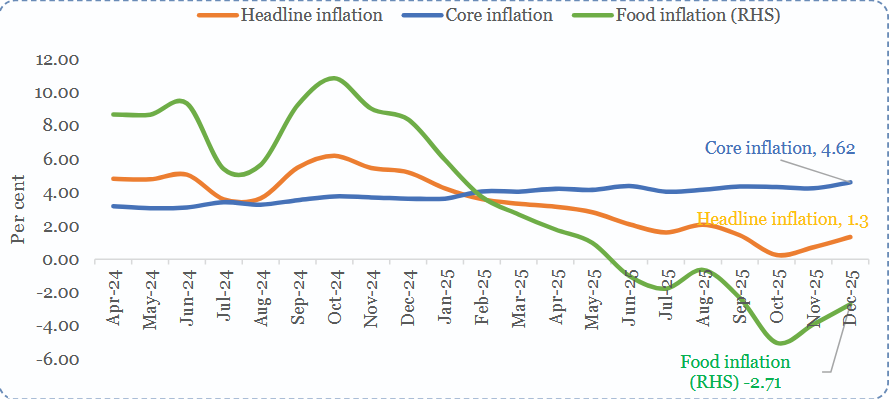
Broad-Based Recovery
The economic expansion is well-distributed across all sectors, with agriculture providing a stable base, manufacturing gaining momentum, and services continuing to be the primary engine of growth.
The survey highlights a multi-sectoral growth strategy, with strong performance across the primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors.
Agriculture: The Pillar of Stability
Steady Growth
Agriculture and allied activities sector is estimated to grow by 3.1% in FY26. Allied sectors like livestock and fisheries are showing stable growth of around 5-6%, enhancing resilience against climatic shocks.
Income Support & Rural Demand
Government schemes focused on income support and productivity enhancement have been crucial in bolstering rural demand and stabilizing the economy.
Case Study - PM-KISAN: The Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) scheme gives farmer families ₹6,000 yearly for direct income support, boosting their liquidity for agricultural investment and stabilizing rural consumption.
Manufacturing: Gaining Momentum
The industrial sector, led by manufacturing, is emerging as a powerful growth engine, indicating a structural economic recovery.
Accelerated Growth: Manufacturing Gross Value Added (GVA) growth accelerated to 9.13% in the second quarter of FY26.
Policy Catalyst - PLI Scheme: The Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes across 14 key sectors have been a game-changer.
|
Metric |
Achievement (as of Sep 2025) |
|
Actual Investment Attracted |
Over ₹2.0 lakh crore |
|
Employment Generated |
Over 12.6 lakh jobs |
 Case Study - Mobile Phone Manufacturing: The PLI scheme has transformed India from a net importer into a major exporter of mobile phones.
Case Study - Mobile Phone Manufacturing: The PLI scheme has transformed India from a net importer into a major exporter of mobile phones.
Services Sector: The Dominant Growth Engine
Dominant GVA Share: The sector's share in India's GVA reached a historic high of 56.4%.
Export Powerhouse: India is now the world’s 7th largest services exporter, with its share in global services trade reached 4.3% in 2024.
Case Study - Global Capability Centers (GCCs): India has become the world's largest hub for GCCs, with over 1,700 centers employing more than 19 lakh professionals.
High growth is being supported by strong and stable macroeconomic fundamentals, achieved through a coordinated policy framework.
Prudent Fiscal Policy
Fiscal Consolidation: Fiscal deficit projected to decline to 4.4% of GDP in FY26. This has strengthened India's fiscal credibility, leading to sovereign rating upgrades.
Quality of Expenditure: Shift towards growth-enhancing capital expenditure (Capex), which rose to 4% of GDP in FY25. This boosts private investment through a "crowding-in" effect.
N.K. Singh Committee: The fiscal strategy aligns with the FRBM Review Committee's recommendations, which advocated for a stable debt-to-GDP ratio as a primary fiscal anchor.
Supportive Monetary Policy
Accommodative Stance: The RBI's Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) has balanced inflation control with growth support, reducing the repo rate to 5.25% by December 2025.
Healthy Banking Sector: Supported by policy measures, bank credit growth stood at a healthy 14.5% in December 2025, and the banking sector is robust, with Gross NPAs at multi-decadal lows and a high Capital Adequacy Ratio of 17.2% as of September 2025.
Resilient External Sector
Strong Forex Reserves: Foreign exchange reserves stood at a comfortable USD 701.4 billion as of January 2026, providing an import cover of around 11 months.
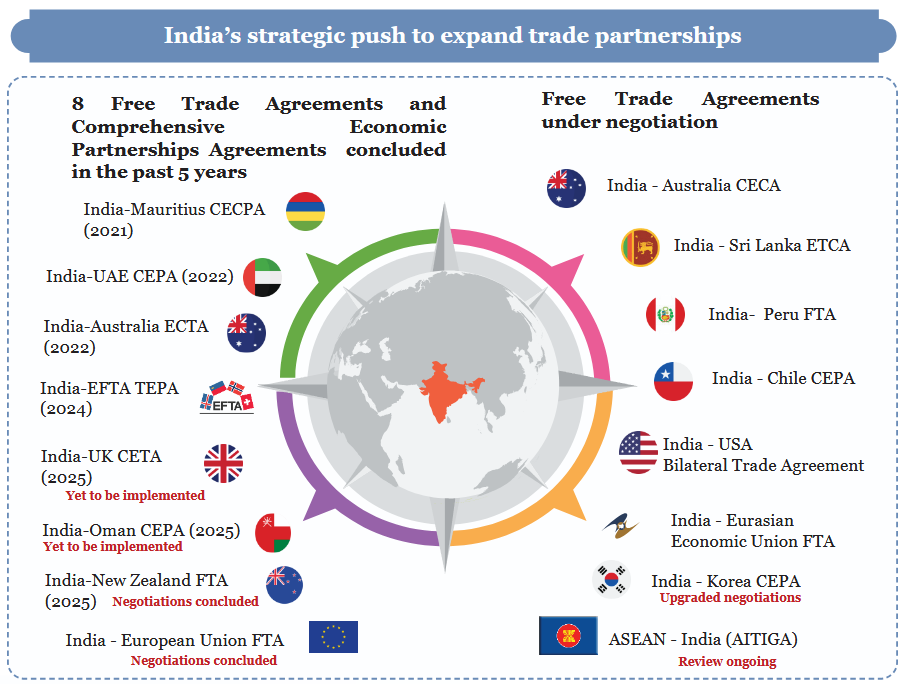
Trade Diversification: India has diversified its trade partnerships, ranking third among Global South countries in trade diversity, which reduces dependency on any single market (Source: UNCTAD, 2025).
Highest Remittance Recipient: India remains the world's largest recipient of remittances, with inflows reaching USD 135.4 billion in FY25, providing a stable source of foreign exchange and supporting the current account.
 Key Structural Transformations
Key Structural Transformations
The Survey highlights deep-seated changes enhancing the economy's long-term potential.
|
Parameter |
Indicator |
Latest Data (as per Survey) |
|
Labour Market |
Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) |
56.1% (Dec 2025) |
|
Female LFPR |
35.3% (Dec 2025) |
|
|
Unemployment Rate |
4.8% (Dec 2025) |
|
|
Financial Inclusion |
RBI’s Financial Inclusion Index |
Rose from 64.2 to 67.0 (Mar 2025) |
Case Study - Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY): A World Bank study highlighted its role in increasing bank account ownership among women by 26% and enabling effective Direct Benefit Transfers (DBT), thus strengthening both inclusion and state capacity.
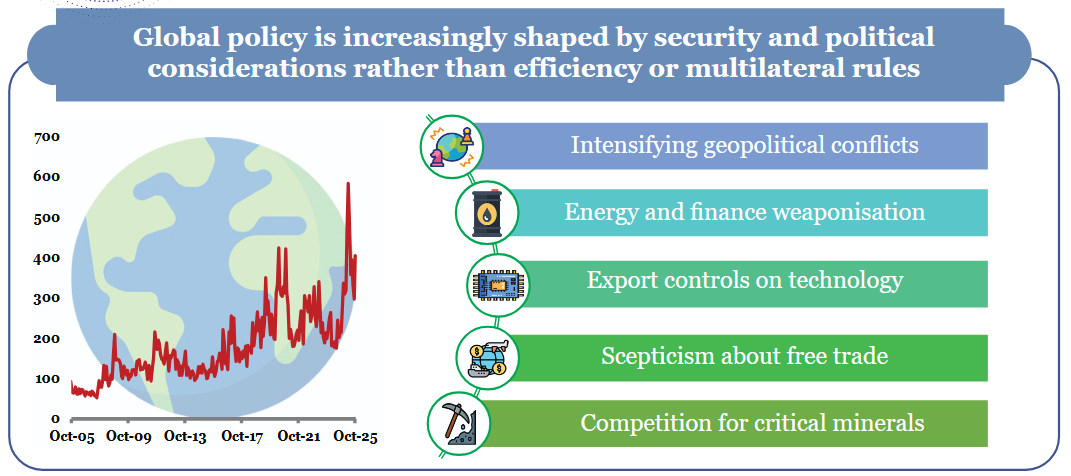
Global Uncertainties: Risks from geopolitical conflicts, global trade fragmentation, and financial market volatility remain key concerns.
Domestic Risks: Key domestic challenges include ensuring the quality of employment, addressing financial pressures on state governments, and mitigating the impacts of climate change on agriculture.
Manufacturing Competitiveness: To sustain manufacturing growth, India needs to address issues like upstream protectionism that can impact the competitiveness of MSMEs in global value chains.
The Economic Survey 2025-26 concludes that the Indian economy is on a firm footing, marked by resilience and momentum.
The path forward involves leveraging the stability to accelerate structural reforms and realize the goal of becoming a developed economy by 2047.
Source: PIB
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Discuss the 'stabilizing role' of the agriculture and allied sectors in India's growth cycle amidst global volatility. (150 words) |
The Economic Survey 2025-26 finds that the Indian economy is characterized by "stability alongside momentum." It projects a robust real GDP growth of 7.4% for FY26, benign inflation, and a broad-based economic recovery across agriculture, manufacturing, and services. It highlights strong macroeconomic fundamentals and significant structural reforms.
The Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme has been a game-changer by attracting over ₹2.0 lakh crore in investment and creating over 12.6 lakh jobs. As seen in the mobile phone industry, it has transformed India from a net importer to a major exporter by incentivizing large-scale electronics manufacturing and attracting global giants like Apple and Samsung.
As per the survey, macroeconomic stability refers to a combination of prudent fiscal management, supportive monetary policy, and a resilient external sector. This includes a declining fiscal deficit (4.4% of GDP in FY26), a focus on capital expenditure, controlled inflation, a healthy banking sector with low NPAs, and strong foreign exchange reserves.
© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved