Description
Copyright infringement not intended
In News
- Prime Minister of India addressed the meeting of the North Eastern Council (NEC) in Shillong,
- The meeting marks the golden jubilee celebration of the Council, which was formally inaugurated in 1972.
- The Prime Minister refers to the 8 states of the North Eastern region as Asht Lakshmi.
- He stated that the government working on 8 foundation pillars; Peace, Power, Tourism, 5G connectivity, Culture, Natural farming, Sports, and Potential for the development of the region.
- He highlighted that the Northeast is India’s gateway to the South -East Asia and can become a centre for the development of the entire region.
- He highlighted that many peace agreements had been signed, inter-state boundary agreements have been done and there has been a marked reduction in instances of extremism.
- He said that the Northeast can become a powerhouse of hydropower. This will help in the expansion of industries and generate a large number of jobs.
- He mentioned that both culture and nature of the region are attracting tourists from across the world.
.jpg)
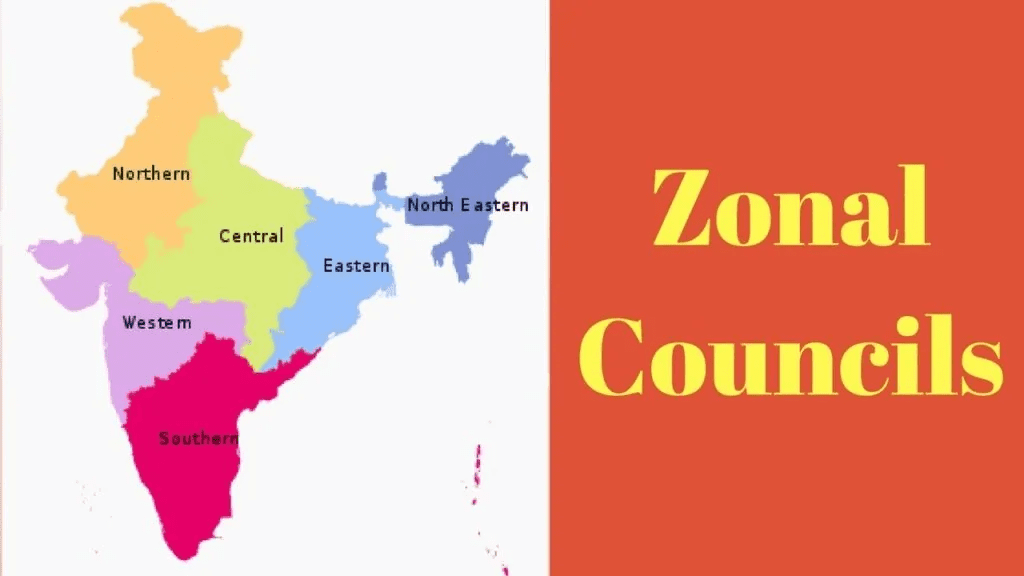
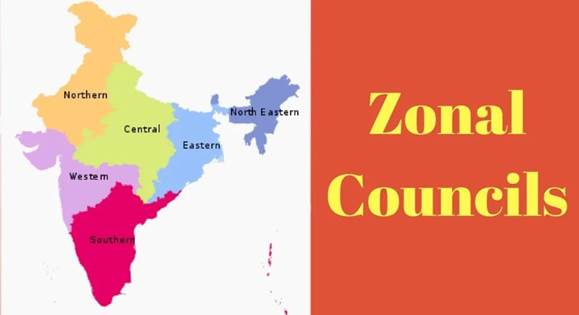
Zonal Councils
- Zonal Councils aim to promote collaboration and coordination among states, UTs, and the Union.
- They discuss and give recommendations on several topics.
- They are only consultative and deliberative bodies.
- The States Reorganization Act of 1956 established these statutory entities.
- The country is divided into 5 zones by the Act:
- Northern Zone
- Central Zone
- Eastern Zone
- Western Zone
- Southern Zone
- Each zonal council is made up of
- The Union Home Minister (who acts as a chairman).
- CM of all States in Zone + 2 other ministers from the states (Each CM acts as a Vice-Chairman by rotation, holding office for 1 year at a time).
- Administrators of all UTs in the zone.
North-Eastern Council
- A further Act of Parliament, the North-Eastern Council Act of 1971, established a North-Eastern Council in addition to the previous Zonal Councils.
- Assam, Manipur, Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Sikkim are among its members. Its responsibilities are similar to those of zonal councils, with a few exceptions.
- It is required to examine the actions taken by member states to maintain security and public order in the region regularly.
|
Name Members Headquarters
|
|
1. Northern Himachal Pradesh, Haryana, New Delhi Zonal Council Punjab, Rajasthan, Delhi,
Chandigarh, Jammu and Kashmir and
Ladakh
|
|
2. Central Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Allahabad Zonal Council Chhattisgarh, and Madhya Pradesh
|
|
3. Eastern Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal and Kolkata Zonal Council Odisha
|
|
4. Western Gujarat, Maharashtra, Goa, Dadra Mumbai Zonal Council and Nagar Haveli and Daman and
Diu
|
|
5. Southern Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Chennai Zonal Council Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Kerala and
Puducherry
|
Significance of Zonal council
- Zonal councils help in designing a collaborative strategy through discussions and exchange of views between the Union and States on important issues.
- It takes up issues involving the Union and states or between many states.
- The zonal councils provide a platform for resolving disputes between the Union and the States and among many States.
- Zonal Meetings are used by the Union, States and Union Territories to share their best practices.
- Zonal councils also discuss a wide range of issues, including;
- Boundary-related disputes.
- security
- Infrastructure-related matters like road, transport, industries, water, and power.
- Forests and environment.
- Housing
- Education
- Food security
- Tourism
- Transport
.jpg)
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1884555
https://t.me/+hJqMV1O0se03Njk9