Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
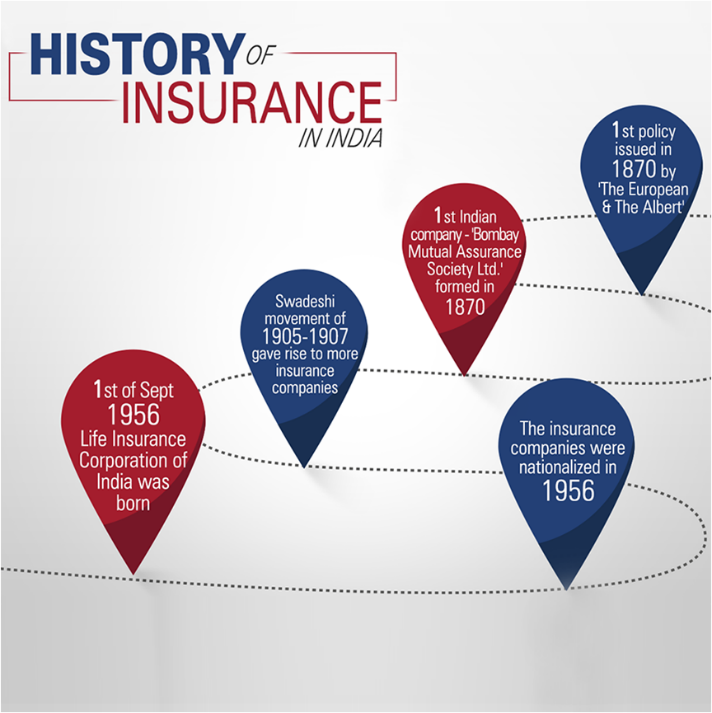
Context
- The Central Government appointed Siddhartha Mohanty as the chairman of Life Insurance Corporation of India for two years.
Life Insurance Corporation of India
About
- Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC) is an Indian public sector life insurance company headquartered in Mumbai.
Establishment
- The Life Insurance Corporation of India was established on 1 September 1956, when the Parliament of India passed the Life Insurance of India Act, nationalizing the insurance industry in India.
- Over 245 insurance companies and provident societies were merged together.
Size
- India's largest insurance company as well as the largest institutional investor with total assets under management worth ₹41 trillion (US$510 billion) as of May 2022.
Ownership and Administrative Control
- It is under the ownership of the Government of India and under the administrative control of the Ministry of Finance.
Offices
- The Central Office of LIC is based out of Mumbai. There are a total of 8 zonal offices, located in Delhi, Chennai, Mumbai, Hyderabad, Kanpur, Kolkata, Bhopal, and Patna.
Insurance Sector in India: Overview
- India’s Insurance industry is one of the premium sectors experiencing upward growth.
- India is the fifth largest life insurance market in the world's emerging insurance markets, growing at a rate of 32-34% each year.
- The insurance industry of India has 57 insurance companies - 24 are in the life insurance business, while 34 are non-life insurers. Among the life insurers, Life Insurance Corporation (LIC) is the sole public sector company.
- There are six public sector insurers in the non-life insurance segment.
- In addition to these, there is a sole national re-insurer, namely General Insurance Corporation of India (GIC Re).
- Other stakeholders in the Indian Insurance market include agents (individual and corporate), brokers, surveyors and third-party administrators servicing health insurance claims.
Market Size
Share in Market
- According to the latest data released by the insurance regulator – the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India - at the end of 2021-22, private players had 36.75% share of the life insurance market, while LIC had 63.25%.
Insurance Penetration
- The Economic Survey notes that insurance penetration in India has been steadily increasing.
- While this was 2.7% around 2000, this stood at 4.2% in 2020 and 2021.
- India’s insurance penetration was pegged at 4.2% in FY21, with life insurance penetration at 3.2% and non-life insurance penetration at 1.0%.
- The insurance penetration in the life insurance sector was 3.2% in 2021, which was nearly twice more than emerging markets and slightly above the global average.
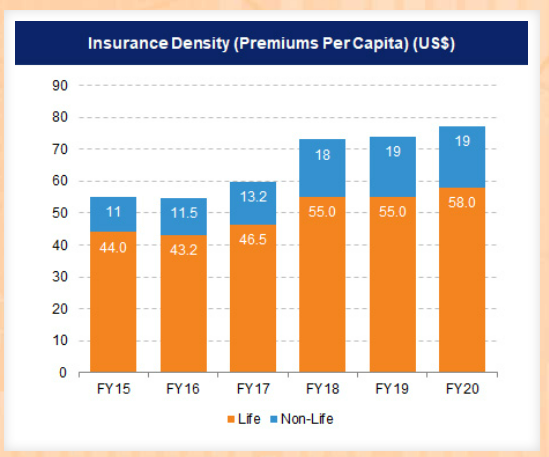
Insurance Density
- In terms of insurance density, India’s overall density stood at US$ 78 in FY21.
Market Share of Private Sector Companies
- The market share of private sector companies in the general and health insurance market increased from 48.03% in FY20 to 49.31% in FY21.
Gross direct premium of non-life insurers and life insurers
- The gross direct premium of non-life insurers and life insurers witnessed a YoY growth of 10.8% and 10.2%, respectively, in FY22.
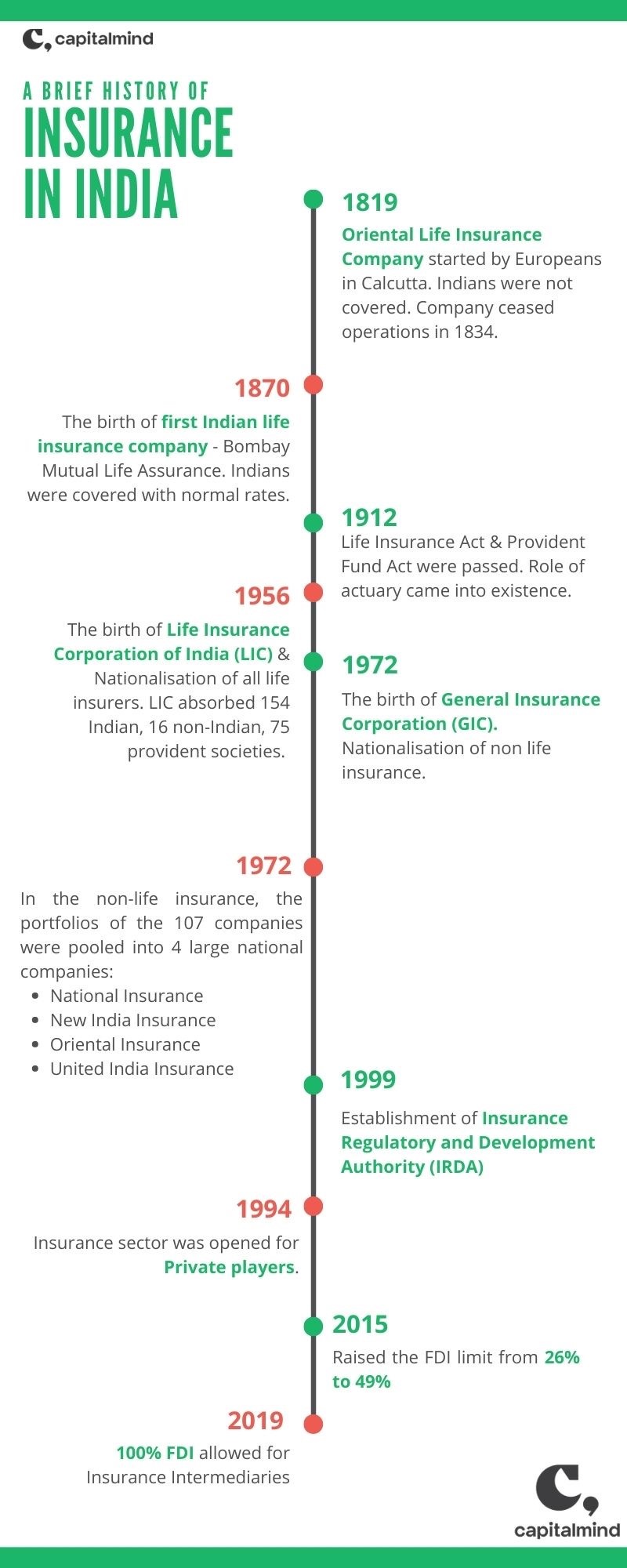
The appointment of IRDAI as a regulatory authority
- IRDAI (Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India) is a regulatory body under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Finance, that is responsible for the regulation and licensing of the insurance and reinsurance industries in India.
- Following the recommendations of the Malhotra Committee report, in 1999, the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority (IRDA) was
- It was constituted by the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority Act, 1999.
- It was established as an autonomous body to regulate and develop the insurance industry.
- The IRDA was incorporated as a statutory body in April, 2000.
- The key objectives of the IRDA include promotion of competition so as to enhance customer satisfaction through increased consumer choice and lower premiums, while ensuring the financial security of the insurance market.
- Ever since its inception, IRDAI has safeguarded the policyholder’s interest while ensuring fair procedural treatment, has ensured the impartial regulation of the insurance industry.
- The IRDAI monitors the management of the solvency margin and the investment of funds by insurance firms.
- Additionally, it renders decisions in disputes between insurers and brokers or other insurance avenues.
The Offices of Insurance Ombudsman
- As per the rules and regulations of the government, the Insurance Ombudsman is appointed by the Government Council following the policies of Insurance Ombudsman Rules ‘2017.
- Insurance policyholders across India can reach the office of the Insurance Ombudsman regarding insurance grievances related to -
- Delays in the resolution of claims,
- Any partial or complete denial of claims by the life, general, or health insurers,
- Disagreements regarding the premiums paid or due under the terms of the insurance policy,
- Any misrepresentation of the terms and circumstances of the policy in the contract or policy document, etc.

Key Pointers
- India allowed private companies in the insurance sector in 2000, setting a limit on FDI to 26%, which was increased to 49% in 2014 and further increased to 74% in the Union Budget (Feb’21).
- The market share of private sector companies in the non-life insurance market rose from 15% in FY2004 to 49.3% in FY2021.
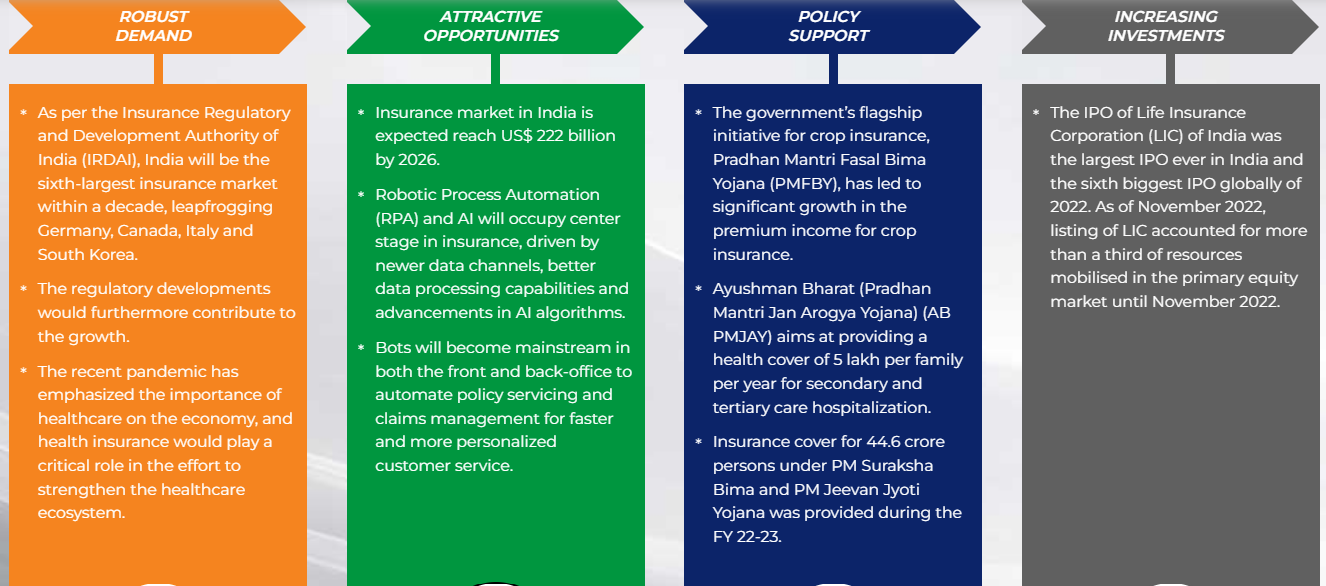
- The IPO of Life Insurance Corporation (LIC) of India was the largest IPO ever in India and the sixth biggest IPO globally of 2022.
- Insurers can now launch new health insurance products without IRDAI’s nod. Earlier the flexibility was given for group insurance products but now retail products have also come under the new norms.
Government Initiatives
Financial Inclusion Initiatives
- Various financial inclusion initiatives and schemes launched by the Government have driven insurance adoption and penetration across all segments.
Some of the key Programmes / Schemes are
- The Ayushman Bharat Yojana (to provide health coverage to poor and vulnerable families),
- The Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (to provide risk coverage in case of death),
- The Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (to provide risk coverage for accidental death and disability), and
- The Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (to provide risk coverage against crop damage due to non-preventable natural risks), which is the largest crop insurance scheme in the world.
Regulatory landscape & Initiatives.
- Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (“IRDAI”), has taken up a mission to achieve ‘Insurance for All’ by 2047 (i.e., the 100th (one hundredth) year of India’s independence). This is expected to lead to a significant increase in insurance penetration.
- To this end, IRDAI has taken several initiatives to promote healthy growth of the insurance industry, rationalize the regulatory framework and reduce compliance burden.
- Additionally, the Government has also undertaken measures to facilitate additional Foreign Direct Investment (“FDI”) in insurance. Certain key initiatives are as summarised below:
FDI
- FDI ceiling in the insurance sector was raised from 49% to 74% under the automatic route.
- Additionally, 100% FDI has been permitted in insurance intermediaries, including insurance brokers, reinsurance brokers, insurance consultants, etc.
- Further, 20% foreign investment has been allowed in Life Insurance Corporation (“LIC”) under the automatic route.
Digitization of the India’s insurance market accompanied by an increase in FDI limits are expected to increased flow of long-term capital, global technology and international best practices, which would in turn support the growth of the sector.
Other
- IRDAI has also taken measures to facilitate
- Video-based Know-Your-Customer processes,
- Launch a Single Window No Objection Certificate (NOC) Portal to facilitate incorporation of an insurer,
- Rationalise various returns / filings and do away with approval requirements for launch of certain insurance products.
- Also, with the sector reaching a level of maturity, IRDAI is considering offering more flexibility to regulated entities in business / operational decisions.

M&A activity, public listings in Insurance
- The Economic Survey recognizes that India is already witnessing mergers and acquisition (M&A) activity in the insurance space. This would only be further accelerated by additional FDI inflow, initial public offerings (IPO) and a simplified regulatory regime.
- The enactment of the General Insurance Business (Nationalisation) Amendment Act, 2021 would allow the Central Government to pare its stake to less than 51% equity capital in a specified insurer.
- In May 2022, the Central Government diluted its stake in LIC and the IPO of LIC raising two billion seven hundred million rupees - India’s largest IPO to date. Various private insurers have also been publicly listed, which in turn would improve public disclosure, corporate governance, and valuation.
Budget Snapshot
- The Budget noted the Government’s vision for ‘Amrit Kaal’ which includes a technology-driven and knowledge-based economy with a robust financial sector.
- Further, the Budget also identified the financial sector as a priority and made a few key announcements which are bound to impact the insurance sector as well:
- Public consultation would be brought to the process of regulation-making and issuing of subsidiary directions;
- Regulators would be requested to carry out a comprehensive review of existing regulations factoring in suggestions from the public and regulated entities;
- Time limits would be laid down to decide upon applications under various regulations.
Closing Remarks
- The Indian insurance sector is at an inflection point and is expected to be one of the main drivers of global insurance industry growth over the next decade.
- Further regulatory changes to facilitate ease of doing business coupled with greater operational flexibility sought to be provided by IRDAI would provide a further impetus to the fast-growing Indian insurance market.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q) The Indian insurance sector is at an inflection point and is expected to be one of the main drivers of global insurance industry growth over the next decade. Shed light on the various financial inclusion initiatives and schemes launched by the Government that have driven insurance adoption and penetration across all segments.
|

https://www.thehindu.com/business/siddhartha-mohanty-appointed-lic-chairman-sources/article66788889.ece















