Description
Copyright infringement not intended
Context - Rajiv Kumar appointed as the Chief Election Commissioner.
Details
- The President of India has appointed Rajiv Kumar as the Chief Election Commissioner in the Election Commission of India.
- Rajiv Kumar will assume the charge of the Chief Election Commissioner from 15th of May.
Election Commission of India
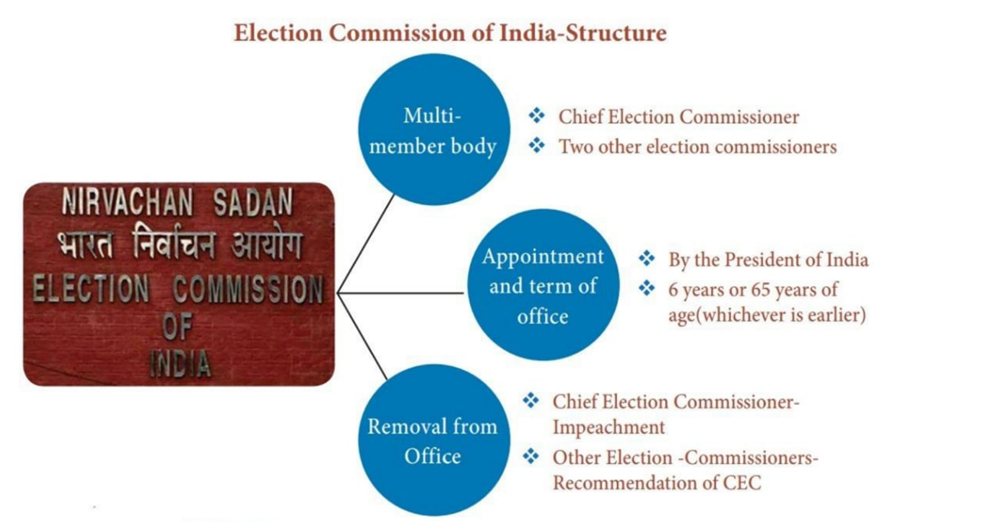
- It is a permanent constitutional body.
- Article 324 of the constitution establishes the Election Commission of India.
- It was established on 25th January 1950.
- It supervises the conduct of elections to Parliament and Legislature of every State and elections to the offices of President and Vice-President of India.
- It consists of the Chief Election Commissioner and two Election Commissioners.
- Originally, there was only Chief Election Commissioner, there were no Election Commissioners.
Appointment of Election Commissioners
- The President appoints Chief Election Commissioner and Election Commissioners.
- Tenure of 6 years, or up to the age of 65 years, whichever is earlier.
- The status, salary and perks of election commissioners are equivalent to Judges of the Supreme Court of India.
- The Chief Election Commissioner can be removed from office only through impeachment by
- Other members can be removed by the President in consultation with the Chief Election Commissioner.
- The President may appoint Regional Election Commissioners in consultation with the CEC before elections to the Parliament or Assemblies.
- The Chief Election Commissioner cannot hold any office of profit after retirement.
- The Chief Election Commissioner cannot be reappointed to the post.
Powers of the Election Commission
- The EC enjoys complete autonomy and is insulated from any interference from the Executive.
- It also functions as a quasi-judicial body regarding matters related to elections and electoral disputes.
- Its recommendations are binding on the President of India.
- However, its decisions are subject to judicial review by High Courts and the Supreme Court acting on electoral petitions.
- During the election process, the entire Central and state government machinery (including paramilitary and police forces) is deemed to be on deputation to the Commission.
- The Commission takes effective control of government personnel and movable and immovable property for the successful conduct of elections.
Functions of the Election Commission
- Demarcation of constituencies.
- Preparation of electoral rolls.
- Issue notification of election dates and schedules.
- Establish and enforce a code of conduct.
- Scrutiny of nomination papers of candidates.
- Scrutiny of election expenses.
- Allot symbols and accord recognition to political parties.
- Render advice to the President and Governors regarding the disqualification of MPs and MLAs.
- Allot schedules for broadcast and telecast of party campaigns.
- Grant exemptions to persons from disqualifications imposed by judicial decisions.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=President-appoints-Rajiv-Kumar-as-Chief-Election-Commissioner&id=440838













