



Tamil Nadu unveils a bold Electric Vehicles policy; to run 500 EV buses by 2019-20 end
Rolling out a slew of measures to push the idea of Electric Vehicles (EV) in the state, Tamil Nadu Chief Minister Edappadi K Palaniswami has released the EV policy intending to attract Rs 50,000 crores worth of investments and create 1.5 lakh new jobs.
- 32 state transport bus depots will get charging infrastructure within the next six months as the state is expecting over 500 electric buses for public transportation.
- For a better distribution of industrial units across the state, the policy offers 50 per cent subsidy on land if it is obtained from the public sector in southern districts, which are a key focus area for the government.
- In other districts, including Chennai, the subsidy on land will be just 15 per cent.
- 100 per cent road tax exemption for all types of EVs.
- Reimbursement of state GST.
- Subsidy on the land cost to set up facilities.
- Special incentives for EV projects that create jobs.
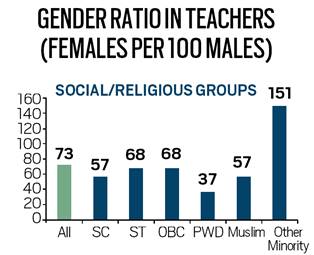
The number of teachers in the country’s higher education institutes was 14, 16,299 in 2018-19, according to the All India Survey on Higher Education 2018-19.
- Of the 14.16-lakh teachers, 57.85 per cent are male and 42.15 per cent are female.
- The skew is highest is recorded in Bihar, where the female-to-male ratio among teachers is 1:4.
- At an all-India level, teachers belonging to the general category represent more than half (56.7 per cent) of all teachers in India.
- Among major states, those with the highest SC/ST proportions among teachers are Andhra Pradesh (13.83 per cent SCs and 1.6 per cent STs), Maharashtra (11.39 per cent SCs and 1.52 per cent STs) and Telangana (11.17 per cent SCs and 3.5 per cent STs).
The Comprehensive National Nutrition Survey conducted by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and UNICEF between February 2016 and October 2018 is the first study undertaken to measure malnutrition, including micronutrient deficiencies through biochemical measures such as blood and urine samples, anthropometric data as well as details of non-communicable diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, cholesterol and kidney function in children and adolescents.
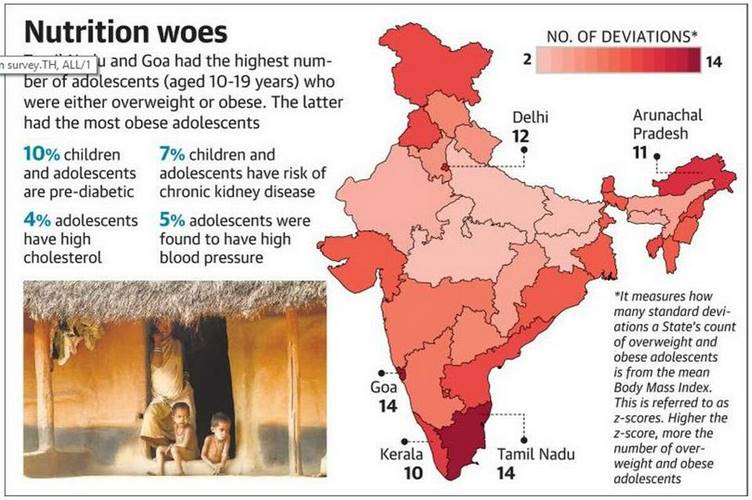
- A quarter of 5-9 years and 10-19 year-olds were thin for their age, one in five children 5-9 years’ old were stunted.
- A total of 1.12 lakh children and adolescents (0-19 years) were surveyed for height and weight measurements and 51,029 children (1-19 years) for biological samples.
- Nearly 10% of children in the age group of 5-9 years and adolescents in the age group of 10-19 years are pre-diabetic, 5% are overweight and another 5% suffer from blood pressure.
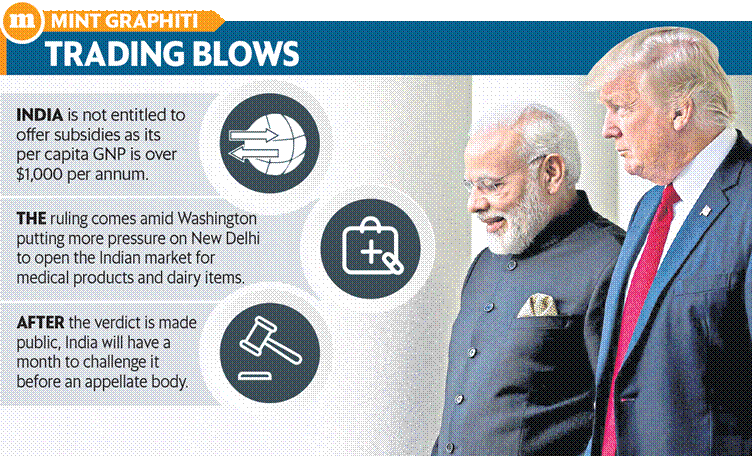
A WTO dispute settlement panel has upheld a US complaint that export subsidy programmes provided by the Indian government violated provisions of the trade body’s subsidies and countervailing measures (SCM) pact.
- In 2018, the US complained that India’s export-related programmes violated Article 3.1(a) of WTO’s SCM agreement.
- Under Article 3.1, developing countries with gross per capita of $1,000 per annum are not entitled to provide export subsidies that are contingent upon export performance.
- WTO has struck down Indian export promotion schemes because India is not entitled to provide such subsidies because its per capita gross national product (GNP) has crossed $1,000 per annum.
- Once the panel’s final report is made public, India will have a month to challenge the ruling before an appellate body, the highest court for global trade disputes.
- If the appellate body upholds the panel’s ruling, India will be required to discontinue the existing export promotion schemes.
- The programmes that could be affected are export-oriented units scheme, electronics hardware technology parks scheme, bio-technology parks scheme, merchandise exports from India scheme, export promotion capital goods scheme, special economic zones and duty-free imports for exporters.
WTO SCM (Subsidy and Counter-veiling) Agreement: It covers subsidation by WTO members and counter-vailing measures.
It follows traffic light approach for subsidies.
- Red Subsidy (Prohibited)
- Yellow or Amber (Actionable): These subside are allowed if does not have adverse impact on other members. Otherwise, other members can apply counter vailing measures.
- Green (Non-Actionable): These subside are allowed which cover mostly research subsidy, environmental subsidy and assistance to other nations.
Prohibited subsidies are those, which are contingent on export performance (Export Subsidies) except agreement on agriculture. It also prohibits Import substitution subsidies, which allow use of domestic products over imported goods.

© 2026 iasgyan. All right reserved