Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: www.indiatoday.in
Context: The Western Equine Encephalitis Virus (WEEV) is making headlines after a recent outbreak in Argentina raised concerns about the mosquito-borne illness.
Details
- Argentina reported a human case of Western Equine Encephalitis Virus (WEEV) infection on December 20, 2023. The outbreak has grown to 21 confirmed human cases, marking the first cases in over two decades in Argentina.
- WEEV outbreaks in South America emphasize the importance of monitoring and responding to emerging infectious diseases with the potential for regional and global impact.
|
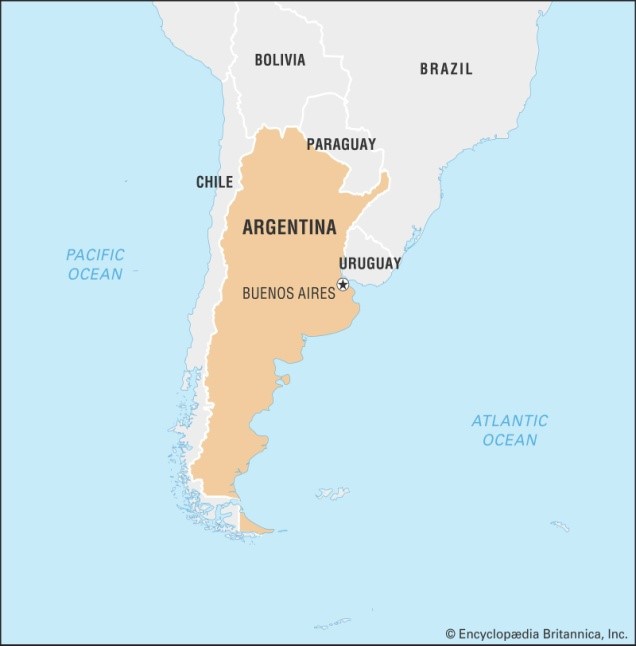
Argentina
- It is the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourth-largest country in the Americas, and the eighth-largest country in the world.
- Bordered by Chile to the west, Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, Brazil to the northeast, Uruguay and the South Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south.
- Variety of landscapes, including the Andes Mountains, the Pampas grasslands, and the Patagonian desert.
- Iguazu Falls are located on the border between Argentina and Brazil.
|
 |
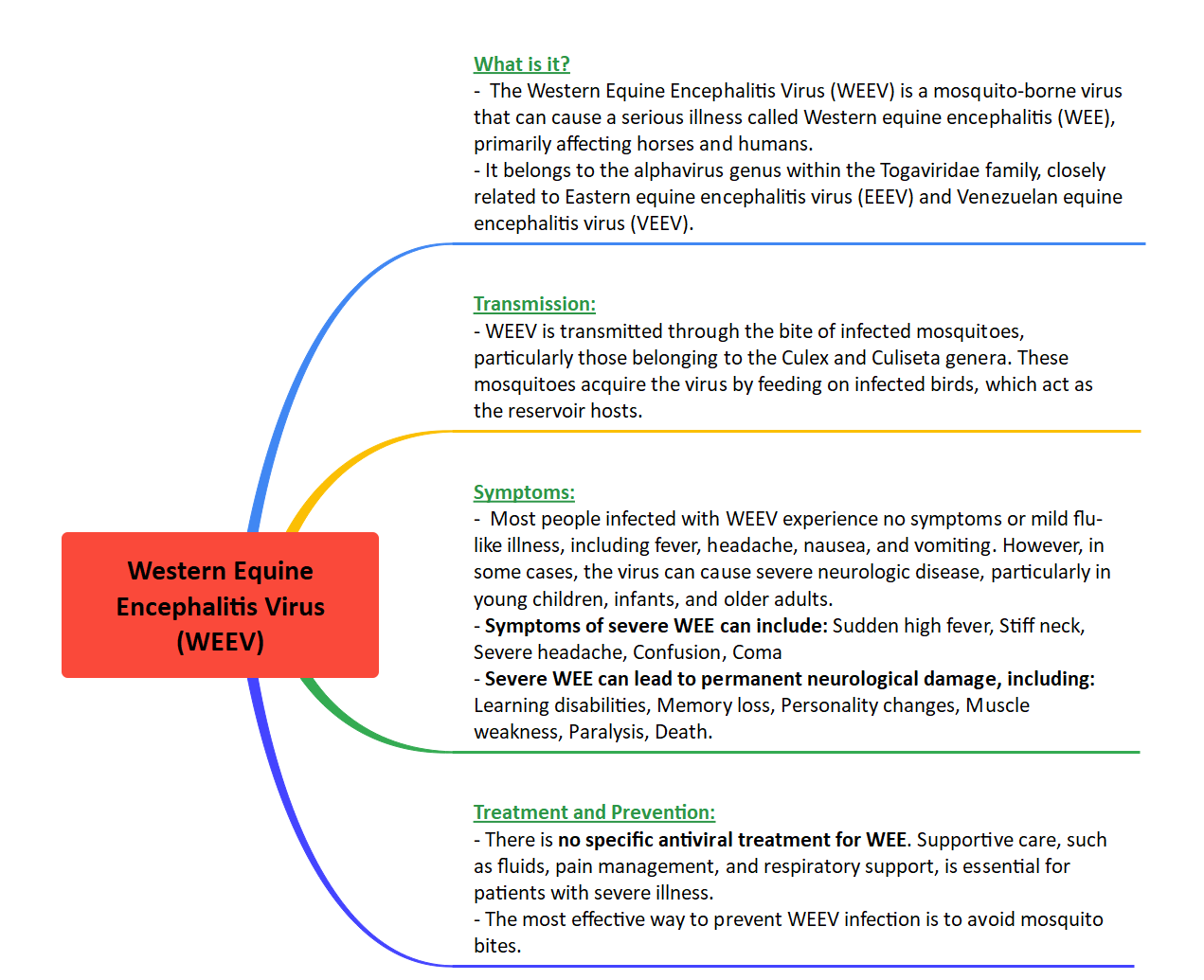
Virus and Transmission
- WEEV is a mosquito-borne infection belonging to the Togaviridae family.
- Transmission to humans occurs primarily through mosquitoes, acting as vectors for the virus.
- Passerine birds are considered reservoirs, and equine species serve as intermediate hosts.
Symptoms and Severity
- While most infections are asymptomatic, about 4-5% may lead to severe consequences, including inflammation of the brain.
- Neurological symptoms and sequelae can occur in rare cases.
- No specific antiviral treatment is available, and symptomatic care is crucial, especially for neurological symptoms.

Preventive Measures
- Pan American Health Organization/World Health Organization (PAHO/WHO) issued an alert on the risk of WEEV spread in the Americas.
- Enhanced surveillance, detection, and a One Health approach are crucial for preventing further spread.
- Control measures include environmental modifications, vector control, and equine vaccination in affected and high-risk regions.
Must Read Articles:
Rasmussen’s Encephalitis: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/rasmussens-encephalitis
Eastern equine encephalitis: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/eastern-equine-encephalitis
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. To track disease spread, authorities consider mandatory contact tracing and data collection from infected individuals. How can they balance disease control with individual privacy concerns?
A) Collect and store all individual data indefinitely for future public health analyses, prioritizing comprehensive disease surveillance.
B) Anonymize data before collection and ensure its secure storage and limited access to authorized personnel for control purposes.
C) Inform individuals about data collection purposes, obtain informed consent, and guarantee data deletion after a specific period.
D) Avoid data collection altogether to respect individual privacy, even if it hinders effective disease control efforts.
Answer: C
Explanation: Minimizing harm to individuals (non-maleficence) while maximizing public health benefits (beneficence) requires finding a middle ground. Option (c) balances the need for data for disease control with respecting individuals.
|