Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Context: According to the latest data from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the country witnessed a 13.24% increase in digital payments in the fiscal year 2022-23.
Details
- The RBI attributed the rise in Digital Payments driven by significant growth in payment infrastructure and payment performance across the country over the period.

Digital Payments Index (DPI)
About
- The Digital Payments Index (DPI) was introduced by the RBI in January 2021 with March 2018 as a benchmark to measure the extent of digitisation of payments across the country.
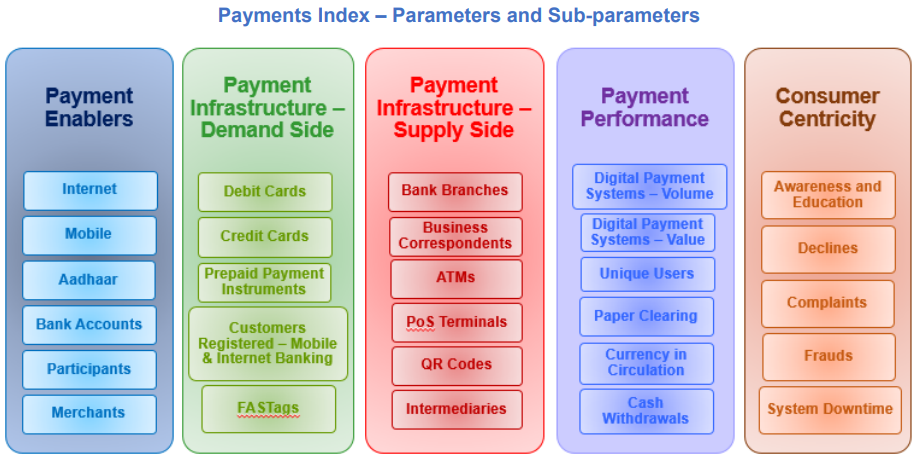
- The DPI is based on multiple indicators that reflect various aspects of digital payments in India. The indicators are grouped into five broad parameters with different weights assigned to them.
Parameters and their weights
- Payment Enablers (25%): This parameter captures the factors that enable customers and merchants to access and use digital payment services. The indicators under this parameter include internet and mobile penetration, bank accounts, Aadhaar enrolment, etc.
- Payment Infrastructure – Demand-side Factors (10%): This parameter captures the availability and usage of digital payment instruments by customers. The indicators under this parameter include debit cards, credit cards; prepaid payment instruments (PPIs), etc.
- Payment Infrastructure – Supply-side Factors (15%): This parameter captures the availability and usage of digital payment acceptance infrastructure by merchants. The indicators under this parameter include point-of-sale (POS) terminals, QR codes, etc.
- Payment Performance (45%): This parameter captures the volume and value of digital payment transactions across various modes and channels. The indicators under this parameter include real-time gross settlement (RTGS), national electronic funds transfer (NEFT), unified payments interface (UPI), immediate payment service (IMPS), Bharat bill payment system (BBPS), etc.
- Consumer Centricity (5%): This parameter captures the customer experience and satisfaction with digital payment services. The indicators under this parameter include grievances redressal, customer awareness, etc.
The DPI is computed by normalising the values of each indicator across periods using a min-max method. The normalised values are then aggregated using the assigned weights to obtain the DPI score for each period.
Significance of the Digital Payments Index (DPI)
- The Digital Payments Index plays a crucial role in assessing the progress of India's digital payments ecosystem.
- It provides policymakers, regulators, and other stakeholders with valuable insights into the growth and penetration of digital payment methods, such as mobile wallets, UPI (Unified Payments Interface), internet banking, credit/debit cards, and other electronic payment systems.
- By monitoring the DPI, the RBI can identify trends, understand consumer behaviour, and gauge the effectiveness of various initiatives aimed at promoting digital transactions. Additionally, it helps the RBI make informed decisions to foster a cashless economy and drive financial inclusion.
Steps taken to promote digital payments
- Enhancing interoperability: The RBI has enabled interoperability among PPIs, card networks, UPI platforms, BBPS platforms, etc., to facilitate the seamless movement of funds across different modes and channels of digital payments.
- Expanding acceptance infrastructure: The RBI has incentivised the deployment of POS terminals, QR codes, etc., by banks and non-banks to increase the availability and accessibility of digital payment acceptance infrastructure across urban and rural areas.
- Promoting innovation: The RBI has encouraged innovation in digital payments by introducing a regulatory sandbox framework, innovation hub; open banking framework, etc., to foster new products, services and business models that can cater to diverse customer needs and preferences.
- Strengthening security: The RBI has issued guidelines on security aspects of digital payments such as tokenisation, data localisation, cyber security framework, etc., to ensure the safety and security of customer data and transactions.
- Enhancing customer awareness: The RBI has launched various initiatives to create awareness and educate customers about the benefits and risks of digital payments such as digital literacy campaigns, customer protection frameworks, grievance redressal mechanisms, etc.
Some of the key challenges
- Digital divide: There is still a large gap between urban and rural areas in terms of access to and usage of digital payment services. The lacks of adequate internet connectivity, digital literacy, financial literacy, etc., are some of the factors that hinder the adoption of digital payments among the rural population.
- Behavioural barriers: There is still a strong preference for cash among some segments of customers and merchants due to various behavioural factors such as habit, convenience, trust, privacy, etc. The lack of awareness and familiarity with digital payment modes and channels also affects the customer's confidence and preference for digital payments.
- Regulatory gaps: There are still some regulatory gaps and uncertainties that affect the growth and innovation of digital payments in India. The lack of clarity on the legal status, taxation, consumer protection, etc., of some emerging digital payment modes such as cryptocurrencies, central bank digital currency (CBDC), etc., are some of the issues that need to be resolved.
- Cyber risks: There are increasing cyber threats and attacks that pose risks to the security and integrity of digital payment systems and transactions. The lacks of adequate cyber security infrastructure, skills, awareness, etc., are some of the challenges that need to be addressed to prevent and mitigate cyber risks.
The DPI provides a comprehensive picture of the current state and future potential of digital payments in India. The DPI also highlights the areas that need further improvement and intervention to achieve the vision of a less-cash society in India.
Steps to enhance the digital payments ecosystem in India
- Leveraging technology: Technology can play a key role in bridging the digital divide, enhancing interoperability, promoting innovation and strengthening security in digital payments. The use of technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), blockchain, biometrics, etc., can enable more efficient, inclusive, convenient and secure digital payment solutions.
- Fostering collaboration: Collaboration among various stakeholders such as regulators, operators, service providers, customers, merchants, etc., can facilitate the development and adoption of digital payments in India. The creation of platforms such as UPI or BBPS can enable collaboration among different players and offer a seamless and integrated customer experience.
- Building trust: Trust is a crucial factor that influences customer preference and behaviour towards digital payments. Building trust among customers and merchants can be achieved by ensuring transparency, accountability, reliability and responsiveness in digital payment services. The provision of adequate customer protection, grievance redressal, dispute resolution, etc., can also enhance customer trust and confidence.
- Creating awareness: Awareness is another important factor that affects the adoption and usage of digital payments in India. Creating awareness among customers and merchants about the benefits, features, risks and safeguards of various digital payment modes and channels can increase their familiarity and comfort with digital payments. The use of various channels such as media, social media, campaigns, events, etc., can help create awareness and educate customers and merchants about digital payments.
.jpg)
Conclusion
- The DPI by RBI is a valuable tool to monitor and evaluate the progress of digital payments in India. It can help in identifying the strengths and weaknesses of the existing system, as well as the opportunities and challenges for future development. It can also serve as a benchmark for comparing India's performance with other countries and regions, and for fostering cross-border cooperation and learning. It is expected to evolve, incorporating new data sources and indicators, to capture the dynamic nature of the digital payments landscape.
Must-Read Articles:
DIGITAL PAYMENTS: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/digital-payments
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Discuss the significance of digital payments in modern economies, highlighting their impact on financial inclusion, convenience, and transparency. Identify the main challenges hindering the widespread adoption of digital payments and propose potential solutions or the way forward to overcome these challenges and promote a cashless economy.
|
https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/markets/stocks/news/digital-payments-grow-13-24-in-fy23-rbi/articleshow/102185145.cms?from=mdr












